|
204 Kallisto
204 Kallisto is a fairly typical, although sizeable Main belt asteroid. It is classified as an S-type asteroid. Like other asteroids of its type, it is light in colour. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 8 October 1879, in Pola, and was named after the same nymph Callisto in Greek mythology as Jupiter's moon Callisto. Photometric measurements during 2009 produced a lightcurve that indicated a sidereal rotation period of with a variation amplitude The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ... of magnitudes. This result conflicted with previous determinations of the period, so the latter were ruled out. References External links The Asteroid Orbital Elements Database* * 000204 Discoveries by Johann Palisa Named minor planets 000204 18791008 Callisto (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Johann Palisa
Johann Palisa (6 December 1848 – 2 May 1925) was an Austrian astronomer, born in Troppau, Austrian Silesia, now Czech Republic. He was a prolific discoverer of asteroids, discovering 122 in all, from 136 Austria in 1874 to 1073 Gellivara in 1923. Some of his notable discoveries include 153 Hilda, 216 Kleopatra, 243 Ida, 253 Mathilde, 324 Bamberga, and the near-Earth asteroid 719 Albert. Palisa made his discoveries without the aid of photography, and he remains the most successful visual (non-photographic) asteroid discoverer of all time. He was awarded the Valz Prize from the French Academy of Sciences in 1906. The asteroid 914 Palisana, discovered by Max Wolf in 1919, and the lunar crater '' Palisa'' were named in his honour. Biography Palisa was born on 6 December 1848, in Troppau in Austrian Silesia (now called ''Opava'' and located in the Czech Republic). From 1866 to 1870, Palisa studied mathematics and astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined and slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Its diameter is 11 times that of Earth and a tenth that of the Sun. Jupiter orbits the Sun at a distance of , with an orbital period of . It is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third-brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky, after the Moon and Venus, and has been observed since prehistoric times. Its name derives from that of Jupiter (god), Jupiter, the chief deity of ancient Roman religion. Jupiter was the first of the Sun's planets to form, and its inward migration during the primordial phase of the Solar System affected much of the formation history of the other planets. Jupiter's atmosphere consists of 76% hydrogen and 24% helium by mass, with a denser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
S-type Asteroids (Tholen)
S-type (stony-type or silicaceous-type) asteroids are asteroids with a spectral type that is indicative of a siliceous (i.e. stony) mineralogical composition, hence the name. They have relatively high density. Approximately 17% of asteroids are of this type, making it the second-most common after the carbonaceous C-type. Characteristics S-type asteroids, with an astronomical albedo of typically 0.20, are moderately bright and consist mainly of iron- and magnesium-silicates. They are dominant in the inner part of the asteroid belt within 2.2 AU, common in the central belt within about 3 AU, but become rare farther out. The largest are 3 Juno (about 240–250 km across) and 15 Eunomia (230 km), with other large S-types being 29 Amphitrite, 532 Herculina and 7 Iris. These largest S-types are visible in 10x50 binoculars at most oppositions; the brightest, 7 Iris, can occasionally become brighter than +7.0, which is a higher magnitude than any asteroid ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Named Minor Planets
Named may refer to something that has been given a name. Named may also refer to: * named (computing), a widely used DNS server * Naming (parliamentary procedure) * The Named (band), an American industrial metal group In literature: * ''The Named'', a fantasy novel by Marianne Curley * The Named, a fictional race of prehistoric big cats, depicted in ''The Books of the Named'' series by Clare Bell See also * Name (other) * Names (other) Names are words or terms used for identification. Names may also refer to: * ''Names'' (EP), by Johnny Foreigner * ''Names'' (journal), an academic journal of onomastics * The Names (band), a Belgian post-punk band * ''The Names'' (novel), b ... * Naming (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Discoveries By Johann Palisa
Discoveries may refer to: Media Film and television * ''Discoveries'' (film), a 1939 British film * ''Discoveries'' (TV series), a Canadian youth science television series * "Discoveries", a Series D episode of the television series ''QI'' (2006) * "Discoveries" (''Hotel Portofino''), a 2022 TV episode Literature * ''Discoveries'' (Robertson Davies), a 2002 book by Robertson Davies * ''Abrams Discoveries'', a series of illustrated non-fiction books published by Harry N. Abrams * ''Discoveries'', a work by William Butler Yeats, written in 1907 * ''Discoveries'', a magazine published by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Music * ''Discoveries'' (Cannonball Adderley album), 1955 * ''Discoveries'' (Josh Nelson album), 2011 * ''Discoveries'' (Northlane album), 2011 Other uses * Discoveries (horse), a racehorse See also * Age of Discoveries * Discovery (other) * Explorations (other) Exploration is the process of discovery. Exploration or explorations may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Background Asteroids
Background may refer to: Performing arts and stagecraft * Background actor * Background artist * Background light * Background music * Background story * Background vocals * ''Background'' (play), a 1950 play by Warren Chetham-Strode Recorded works * ''Background'' (1953 film), a British drama * ''Background'' (1973 film), a documentary * ''Background'' (TV series), a Canadian journalistic television series * ''Background'' (Lifetime album), 1992 * ''Background'' (Bassi Maestro album), 2002 Science and engineering * Background extinction rate * Background independence, a condition in theoretical physics * Background noise * Background radiation, the natural radiation that is always present in a location ** Background (astronomy), small amounts of light coming from otherwise dark parts of the sky ** Cosmic background (other) ** Gravitational wave background ** X-ray background * Background process, software that is running but not being displaye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude (see below), which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude. Definitions Peak amplitude and semi-amplitude For symmetric periodic waves, like sine waves or triangle waves, ''peak amplitude'' and ''semi amplitude'' are the same. Peak amplitude In audio system measurements, telecommunications and others where the measurand is a signal that swings above and below a reference value but is not sinusoidal, peak amplitude is often used. If the reference is zero, this is the maximum absolute value of the signal; if the reference is a mean value ( DC component), the peak amplitude is the maximum ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rotation Period
In astronomy, the rotation period or spin period of a celestial object (e.g., star, planet, moon, asteroid) has two definitions. The first one corresponds to the '' sidereal rotation period'' (or ''sidereal day''), i.e., the time that the object takes to complete a full rotation around its axis relative to the background stars ( inertial space). The other type of commonly used "rotation period" is the object's '' synodic rotation period'' (or ''solar day''), which may differ, by a fraction of a rotation or more than one rotation, to accommodate the portion of the object's orbital period around a star or another body during one day. Measuring rotation For solid objects, such as rocky planets and asteroids, the rotation period is a single value. For gaseous or fluid bodies, such as stars and giant planets, the period of rotation varies from the object's equator to its pole due to a phenomenon called differential rotation. Typically, the stated rotation period for a giant pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lightcurve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph (discrete mathematics), graph of the Radiance, light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude (astronomy), magnitude of light received on the ''y''-axis and with time on the ''x''-axis. The light is usually in a particular frequency interval or frequency band, band. Light curves can be periodic, as in the case of eclipsing binary, eclipsing binaries, Cepheid variables, other periodic variables, and Methods of detecting extrasolar planets#Transit photometry, transiting extrasolar planets; or aperiodic, like the light curve of a nova, cataclysmic variable star, supernova, gravitational microlensing, microlensing event, or binary as observed during occultation events. The study of a light curve and other observations can yield considerable information about the physical process that produces such a light curve, or constrain the physical theories about it. Variable stars Graphs of the ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Photometry (astronomy)
In astronomy, photometry, from Greek '' photo-'' ("light") and '' -metry'' ("measure"), is a technique used in astronomy that is concerned with measuring the flux or intensity of light radiated by astronomical objects. This light is measured through a telescope using a photometer, often made using electronic devices such as a CCD photometer or a photoelectric photometer that converts light into an electric current by the photoelectric effect. When calibrated against standard stars (or other light sources) of known intensity and colour, photometers can measure the brightness or apparent magnitude of celestial objects. The methods used to perform photometry depend on the wavelength region under study. At its most basic, photometry is conducted by gathering light and passing it through specialized photometric optical bandpass filters, and then capturing and recording the light energy with a photosensitive instrument. Standard sets of passbands (called a photometric system) are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
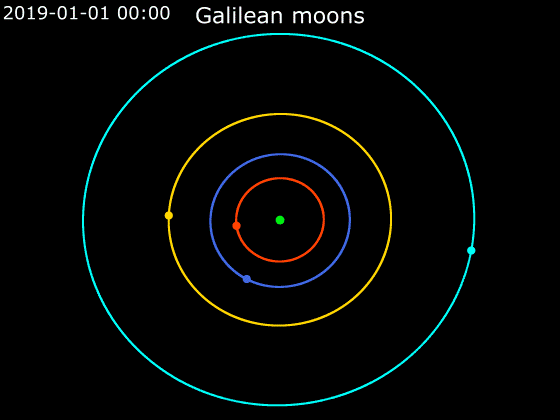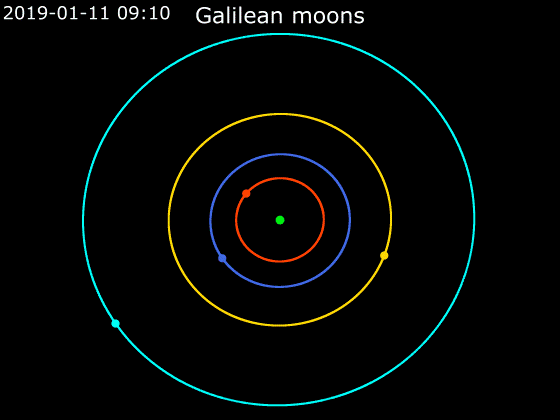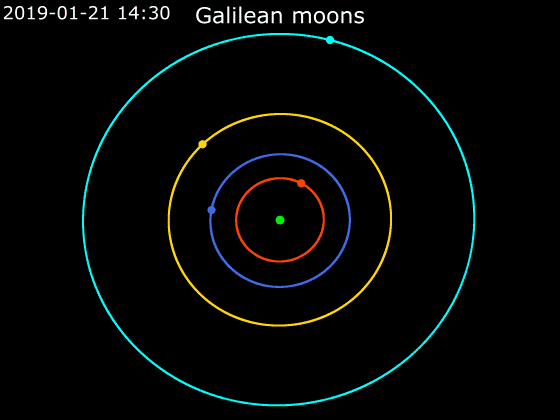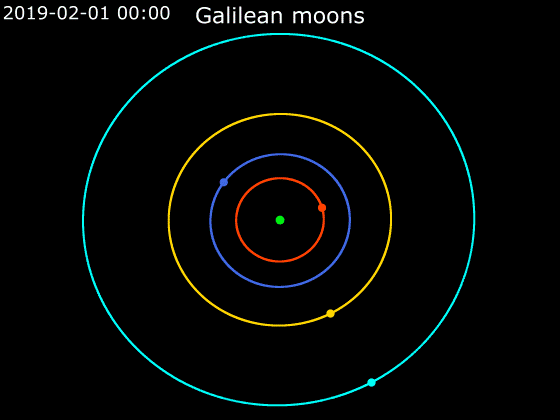
Callisto (moon)
Callisto ( ) is the second-largest moon of Jupiter, after Ganymede. In the Solar System it is the third-largest moon after Ganymede and Saturn's largest moon Titan, and nearly as large as the smallest planet Mercury. Callisto is, with a diameter of , roughly a third larger than Earth's Moon and orbits Jupiter on average at a distance of , which is about five times further out than the Moon orbiting Earth. It is the outermost of the four large Galilean moons of Jupiter, which were discovered in 1610 with one of the first telescopes, and is today visible from Earth with common binoculars. The surface of Callisto is the oldest and most heavily cratered in the Solar System. Its surface is completely covered with impact craters. It does not show any signatures of subsurface processes such as plate tectonics or volcanism, with no signs that geological activity in general has ever occurred, and is thought to have evolved predominantly under the influence of impacts. Promine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Natural Satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are colloquially referred to as moons, a derivation from the Moon of Earth. In the Solar System, there are six planetary satellite systems containing 418 known natural satellites altogether. Seven objects commonly considered dwarf planets by astronomers are also known to have natural satellites: , Pluto, Haumea, , Makemake, , and Eris. As of January 2022, there are 447 other minor planets known to have natural satellites. A planet usually has at least around 10,000 times the mass of any natural satellites that orbit it, with a correspondingly much larger diameter. The Earth–Moon system is a unique exception in the Solar System; at 3,474 kilometres (2,158 miles) across, the Moon is 0.273 times the diameter of Earth and about of its mass. The next largest ratios are the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |