|
2020 In Spaceflight
This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2020. Overview Astronomy and astrophysics The GECAM A and B satellites were launched on 9 December. They were built for research in electromagnetic counterparts of gravitational waves. Exploration of the Solar System Three missions to Mars were launched in 2020, including two rovers, two orbiters, and a lander. NASA has launched the Mars 2020 mission, which includes the ''Perseverance'' rover and ''Ingenuity'' helicopter, and will cache samples for eventual return to Earth. The China National Space Administration (CNSA) has launched its Tianwen-1 mission, which includes an orbiter, a lander, a small rover and a group of deployable and remote cameras; it is China's first mission to another planet using its own delivery vehicle. Finally, the United Arab Emirates, in partnership with American universities, has launched the Hope Mars Mission orbiter on a Japanese rocket. In November, China launched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LauncherOne
LauncherOne was a two-stage orbital launch vehicle developed and flown by Virgin Orbit that had operational flights from 2021 to 2023, after being in development from 2007 to 2020. It was an air-launched rocket, designed to carry smallsat payloads of up to into Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), following air launch from a carrier aircraft at high altitude. The rocket was carried to the upper atmosphere on a modified Boeing 747-400, named '' Cosmic Girl'', and released over ocean. Initial work on the program was done by Virgin Galactic, another Virgin Group subsidiary, before a separate entity — Virgin Orbit — was formed in 2017 to complete development and operate the launch service provider business separately from the passenger-carrying Virgin Galactic business. The first successful flight was on 17 January 2021, which delivered a payload of 10 CubeSats to low Earth orbit (LEO). Three further launches successfully reached orbit. An initial test flight was unsucces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Missions To Mars
This is a list of spacecraft missions (including unsuccessful ones) to the planet Mars, such as orbiters, landers, and rovers. Missions ;Mission Type Legend: Landing locations In 1999, Mars Climate Orbiter accidentally entered Mars' atmosphere and either burnt up or left Mars' orbit on an unknown trajectory. There are a number of derelict spacecraft orbiting Mars whose location is not known precisely. There is a proposal to use the Optical Navigation Camera on the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' to search for small moons, dust rings and old orbiters. As of 2016, there were believed to be eight derelict spacecraft in orbit around Mars (barring unforeseen event). The Viking 1 orbiter was not expected to decay until at least 2019. Mariner 9, which entered Mars orbit in 1971, was expected to remain in orbit until approximately 2022, when it was projected to enter the Martian atmosphere and either burn up, or crash into the planet's surface. Timeline Missions to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Waves
Gravitational waves are oscillations of the gravitational field that travel through space at the speed of light; they are generated by the relative motion of gravitating masses. They were proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as the gravitational equivalent of electromagnetic waves. In 1916, Albert Einstein demonstrated that gravitational waves result from his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime. Gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does not provide for their existence, instead asserting that gravity has instantaneous effect everywhere. Gravitational waves therefore stand as an important relativistic phenomenon that is absent from Newtonian physics. Gravitational-wave astronomy has the advantage that, unlike electromagnetic radiation, gravitational waves are not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Wave High-energy Electromagnetic Counterpart All-sky Monitor
Gravitational Wave High-energy Electromagnetic Counterpart All-sky Monitor (GECAM) () is a space observatory composed of a constellation of two X-ray and gamma-ray all-sky observing small satellites, called GECAM A (aka KX 08A or Xiaoji, COSPAR 2020-094A) and GECAM B (aka KX 08B or Xiaomu, COSPAR 2020-094B), for research in electromagnetic counterparts of gravitational waves (GWs). It was launched on 9 December 2020 from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center at 20:14 UTC by a Long March 11 The Long March 11 (), or Chang Zheng 11 as in pinyin, abbreviated LM-11 for export or CZ-11 within China (and designated 11H when launched from sea), is a Chinese four stage solid-propellant carrier rocket of the Long March family, which is d ... rocket. GECAM will focus on detecting electromagnetic counterparts of gravitational waves. In addition to signals from GWs, the observatory studies Ultra-long GRBs, X-ray Flashes, X-ray-rich GRBs, Magnetars and Terrestrial Gamma-ray Flashes. Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 In Spaceflight
The year 2021 broke the record for the most orbital launch attempts till then (146) and most humans in space concurrently (19) despite the effects of COVID-19 pandemic. Overview Astronomy and astrophysics The IXPE telescope was launched on a Falcon 9 on 9 December 2021. The long-delayed James Webb Space Telescope, the largest optical space telescope ever built, was launched to the Sun–Earth point by a European Ariane 5 rocket on 25 December 2021. Planetary science Spacecraft from three Mars exploration programs from the United Arab Emirates, China, and the United States (Hope, Tianwen-1, and Mars 2020) arrived at Mars in February. The '' Perseverance'' rover landed on 18 February. As part of the Mars 2020 mission, the '' Ingenuity'' solar-powered drone performed the first powered aircraft flight on another planet in human history. It has a communications link with the ''Perseverance'' rover and used autonomous control during its short scripted flights. The ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 In Spaceflight
This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2019. Overview Astronomy and astrophysics The Russian-German X-ray observing satellite Spektr-RG was launched on 13 July. Lunar exploration The Chinese probe Chang'e 4 made humanity's first soft landing on the far side of the Moon on 3 January and released its ''Yutu 2'' rover to explore the lunar surface on the far side for the first time in human history. Israel's SpaceIL, one of the participants in the expired Google Lunar X Prize, launched the first private mission to the Moon in February. The '' Beresheet'' lander from SpaceIL made the landing attempt in April, but crashed onto the Moon. India launched the delayed Chandrayaan-2 lunar orbiter/lander/rover in July; the orbiter reached lunar orbit in September, but the ''Vikram'' lander crashed onto the lunar surface. Exploration of the Solar System The probe ''New Horizons'' encountered the Kuiper belt object 486958 Arrokoth on 1 January. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Spaceflight
This is a timeline of known spaceflights, both crewed and uncrewed, sorted chronologically by launch date. Due to its large size, the timeline has been split into smaller articles, one for each year since 1951. There is a separate list for all flights that occurred before 1951. The list for the year and for its subsequent years may contain planned launches, but the statistics will only include past launches. For the purpose of these lists, a spaceflight is defined as any flight that crosses the Kármán line, the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, FAI-recognized edge of space, which is Above mean sea level, above mean sea level (AMSL). The timeline contains all the flights which have either crossed the edge of space, were intended to do so but failed, or are planned in the near future. Notable test flights of spaceflight systems may be listed even if they were not planned to reach space. Some lists are further divided into orbital launches (sending a payload into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was developed by Lockheed Martin and has been operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA) since 2006. Primarily used to launch payloads for the United States Department of Defense, NASA, and commercial customers, Atlas V is the longest-serving active rocket in the United States. Each Atlas V vehicle consists of two main stages. The First stage (rocketry), first stage is powered by a single Russian-made RD-180 engine that burns kerosene and liquid oxygen. The Centaur (rocket stage), Centaur upper stage uses one or two American-made Aerojet Rocketdyne RL10 engines that burn liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. Strap-on booster, Strap-on Solid rocket booster, solid rocket boosters (SRBs) are used in several configurations. Originally equipped with AJ-60A SRBs, the vehicle switched to Graphite-Epoxy Motor (GEM 63) boosters beginning in November 2020, except for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
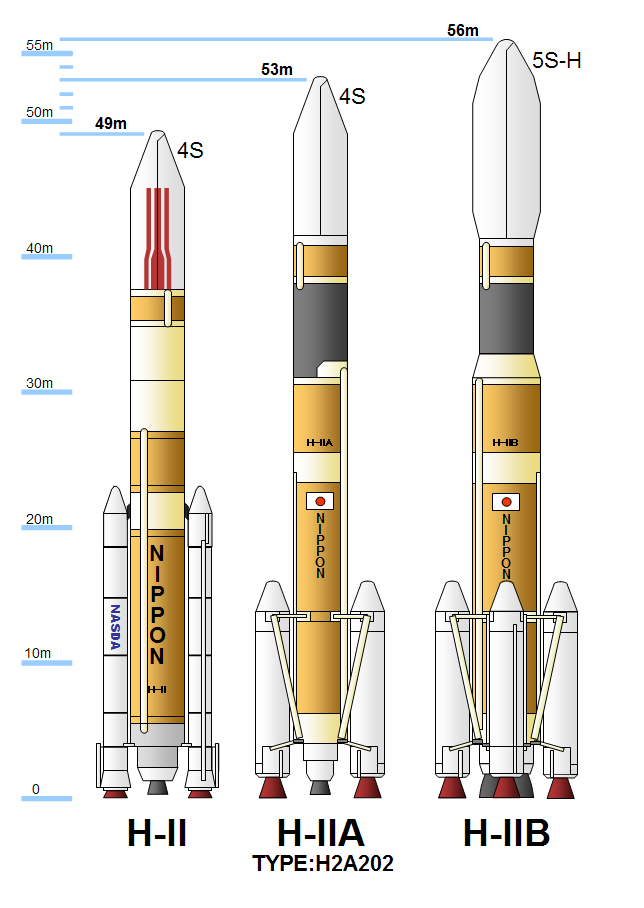
H-IIB
H-IIB (H2B) was an expendable space launch system jointly developed by the Japanese government's space agency JAXA and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. It was used to launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV, or ''Kōnotori'') cargo spacecraft for the International Space Station. The H-IIB was a liquid-fueled rocket, with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan. H-IIB made its first flight in 2009, and had made a total of nine flights through 2020 with no failures. H-IIB was able to carry a payload of up to to Geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), compared with the payload of 4000–6000 kg for the H-IIA, a predecessor design. Its performance to low Earth orbit (LEO) was sufficient for the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV). The first H-IIB was launched in September 2009 and the last H-IIB was launched in May 2020. Development The H-IIB was a space launch vehicle jointly designed, manufactured and operated by JAXA and Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Lunar Exploration Program
The Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (CLEP; ), also known as the Chang'e Project () after the Chinese Moon goddess Chang'e, is an ongoing series of robotic Moon missions by the China National Space Administration (CNSA). Engineering Program The program encompasses lunar orbiters, landers, rovers and sample return spacecraft, launched using the Long March series of rockets. A human lunar landing component may have been added to the program, after China publicly announced crewed lunar landing plans by the year 2030 during a conference in July 2023. The program's launches and flights are monitored by a telemetry, tracking, and command (TT&C) system, which uses radio antennas in Beijing and antennas in Kunming, Shanghai, and Ürümqi to form a VLBI antenna. A proprietary ground application system is responsible for downlink data reception. In 2019, China National Space Administration head Zhang Kejian announced that China is planning to build a scientific research s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockets By Astra
The Astra Rocket was a small-lift space launch vehicle series designed, manufactured, and operated by American company Astra (formerly known as Ventions). The rockets were designed to be manufactured at minimal cost, employing very simple materials and techniques. They were also designed to be launched by a very small team, and be transported from the factory to the launch pad in standard shipping containers. The Rocket name was shared by several launch vehicles. Rocket 1 was test vehicle made up of a booster equipped with five Delphin electric-pump-fed rocket engines, and a mass simulator meant to occupy the place of a second stage. Rocket 2 was a prototype similar to Rocket 1. Rocket 3 was a launch vehicle which added a pressure-fed second stage to the Delphin-powered booster. Its definitive variant, Rocket 3.3, featured a lengthened booster, and delivered satellites to orbit. Rocket 4 was to have been an all-new design for a larger, more powerful rocket. The rocket fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |