|
1975–78 French Nuclear Tests
The 1975–1978 nuclear test series was a group of 29 nuclear test Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine the performance of nuclear weapons and the effects of their explosion. Nuclear testing is a sensitive political issue. Governments have often performed tests to signal strength. Bec ...s conducted by France in 1975–1978. These tests followed the '' 1971–1974 French nuclear tests'' series and preceded the '' 1979–1980 French nuclear tests'' series. References {{DEFAULTSORT:1975-78 French nuclear tests French nuclear weapons testing 1975 in France 1976 in France 1977 in France 1978 in France 1979 in France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
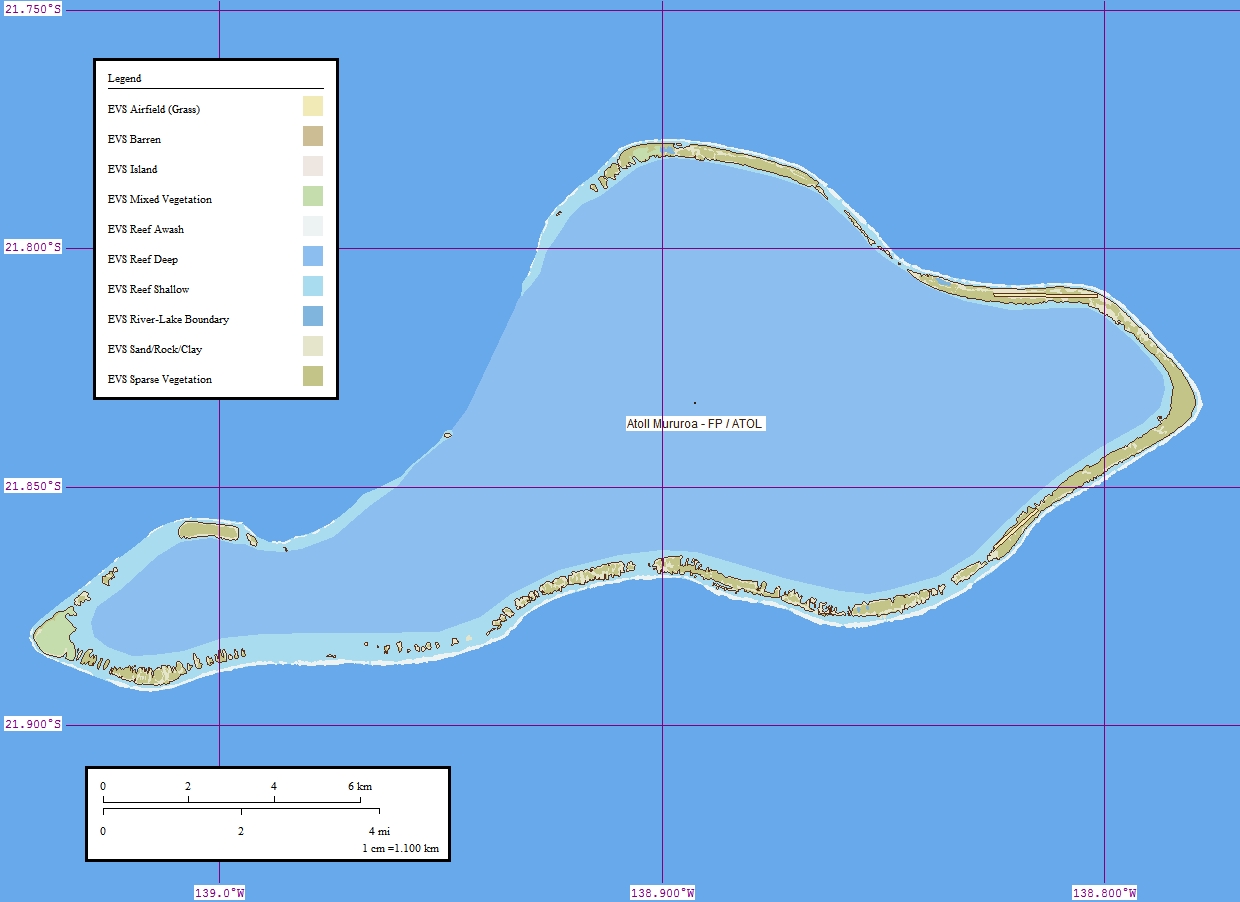
Moruroa
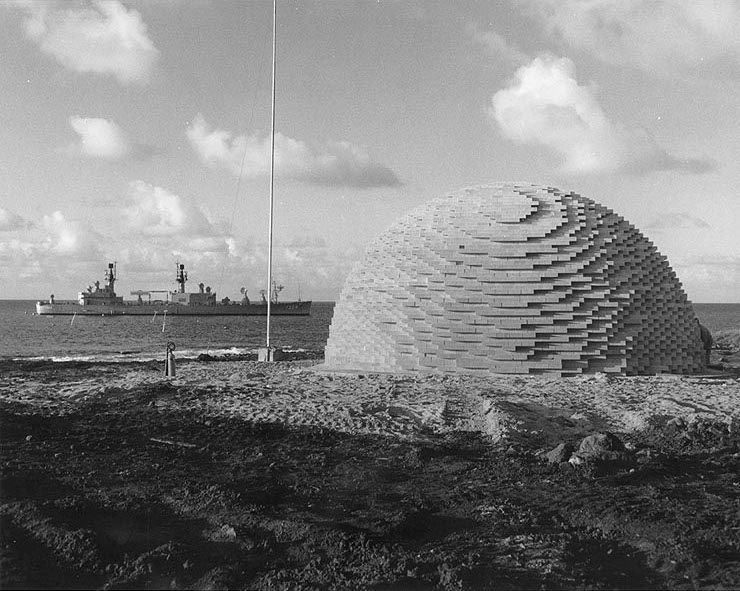
Moruroa (Mururoa, Mururura), also historically known as Aopuni, is an atoll which forms part of the Tuamotu Archipelago in French Polynesia in the southern Pacific Ocean. It is located about southeast of Tahiti. Administratively Moruroa Atoll is part of the Commune of France, commune of Tureia, which includes the atolls of Tureia, Fangataufa, Tematangi and Vanavana. France undertook nuclear weapon tests between 1966 and 1996 at Moruroa and Fangataufa, causing international protests, notably in 1974 and 1995. The number of tests performed on Moruroa has been variously reported as 175 and 181. History The first recorded visit this atoll was Commander Philip Carteret on HMS ''Swallow'' in 1767, just a few days after he had discovered Pitcairn Island. Carteret named Mururoa "Bishop of Osnaburgh Island". In 1792, the British whaler was wrecked here, and it became known as Matilda's Rocks. Frederick William Beechey visited it in 1826. Early European explorers found that the atoll w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nuclear Weapons
This is a list of nuclear weapons listed according to country of origin, and then by type within the states. The United States, Russia, China and India are known to possess a nuclear triad, being capable to deliver nuclear weapons by land, sea and air. United States American nuclear weapons of all types – bombs, warheads, shells, and others – are numbered in the same sequence starting with the Mark 1 and () ending with the W91 (which was cancelled prior to introduction into service). All designs which were formally intended to be weapons at some point received a number designation. Pure test units which were experiments (and not intended to be weapons) are not numbered in this sequence. Early weapons were very large and could only be used as free fall bombs. These were known by "Mark" designators, like the Mark 4 which was a development of the Fat Man weapon. As weapons became more sophisticated they also became much smaller and lighter, allowing them to be used in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1977 In France
Events January * January 8 – 1977 Moscow bombings, Three bombs explode in Moscow within 37 minutes, killing seven. The bombings are attributed to an Armenian separatist group. * January 10 – Mount Nyiragongo erupts in eastern Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo). * January 17 – 49 marines from the and are killed as a result of a collision in Barcelona harbour, Spain. * January 18 ** Scientists identify a previously unknown Bacteria, bacterium as the cause of the mysterious Legionnaires' disease. ** Australia's worst Granville rail disaster, railway disaster at Granville, a suburb of Sydney, leaves 83 people dead. ** SFR Yugoslavia Prime minister Džemal Bijedić, his wife and 6 others are killed in a plane crash in Bosnia and Herzegovina. * January 19 – An Ejército del Aire CASA C-207 Azor, CASA C-207C Azor (registration T.7-15) plane crashes into the side of a mountain near Chiva, Valencia, Chiva, on approach to Valencia Airport in Spain, killing all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1976 In France
Events from the year 1976 in France. Incumbents * President: Valéry Giscard d'Estaing * Prime Minister: Jacques Chirac (until 29 August), Raymond Barre (starting 29 August) Events *21 January – The first commercial ''Concorde'' flight takes off. *7 March – Cantonales Elections held. *14 March – Cantonales Elections held. *9 April – Peugeot takes over Citroen to form PSA Peugeot Citroen. *27 June – Palestinian extremists hijack an Air France plane in Greece with 246 passengers and 12 crew. They take it to Entebbe, Uganda. *June – Launch of the Renault 14, a five-door small family hatchback with front-wheel drive which is similar in concept to the hugely successful Volkswagen Golf from West Germany. *4 July – Entebbe Raid: Israeli airborne commandos free 103 hostages being held by Palestinian hijackers of an Air France plane at Uganda's Entebbe Airport; 1 Israeli and several Ugandan soldiers are killed in the raid. *25 August – Resignation of Jacques Chira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1975 In France
Events from the year 1975 in France. Incumbents * President: Valéry Giscard d'Estaing * Prime Minister: Jacques Chirac Events *1 January – Work is abandoned on the British end of the Channel Tunnel. *March – Launch of the Renault 30, Renault's first postwar six-cylinder car and Renault's flagship car to compete with the likes of the Citroen CX and BMW 5 Series, and the first production car of its size to feature a hatchback. *6 March – A bomb explodes in the Paris offices of Springer Press. The 6 March Group (connected to the Red Army Faction) demands amnesty for the Baader-Meinhof Group. *6 July – The Comoros declare their independence from France. *September – Chrysler Europe launches the Simca 1307, a large five-door hatchback which will go on sale in Britain in the new year as the Chrysler Alpine. It is similar in size and design to the Renault 16, and is one of the first cars of its size to feature a hatchback. *15 September – The department of ''Corse'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Nuclear Weapons Testing
France is one of the five "Nuclear Weapons States" under the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, but is not known to possess or develop any chemical or biological weapons. France is the only member of the European Union to possess independent (non-NATO) nuclear weapons. France was the fourth country to test an independently developed nuclear weapon, doing so in 1960 under the government of Charles de Gaulle. The French military is currently thought to retain a weapons stockpile of around 290 operational (deployed) nuclear warheads, making it the fourth-largest in the world, speaking in terms of warheads, not megatons. The weapons are part of the country's ''Force de dissuasion'', developed in the late 1950s and 1960s to give France the ability to distance itself from NATO while having a means of nuclear deterrence under sovereign control. France did not sign the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, which gave it the option to conduct further nuclear tests until it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fallout
Nuclear fallout is residual radioactive material that is created by the reactions producing a nuclear explosion. It is initially present in the mushroom cloud, radioactive cloud created by the explosion, and "falls out" of the cloud as it is moved by the atmosphere in the minutes, hours, and days after the explosion. The bulk of the radioactivity from nuclear fallout comes from fission products, which are created by the nuclear fission reactions of the nuclear device. Un-fissioned bomb fuel (such as plutonium and uranium), and radioactive isotopes created by neutron activation, make up a smaller amount of the radioactive content of fallout. The amount of fallout and its distribution is dependent on several factors, including the overall yield of the weapon, the fission yield of the weapon, the height of burst of the weapon, and meteorological conditions. Fallout can have serious human health consequences on both short- and long-term time scales, and can cause radioactive conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNT Equivalent
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. A ton of TNT equivalent is a unit of energy defined by convention to be (). It is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a metric ton (1,000 kilograms) of trinitrotoluene (TNT). In other words, for each gram of TNT exploded, (or 4184 joules) of energy are released. This convention intends to compare the destructiveness of an event with that of conventional explosive materials, of which TNT is a typical example, although other conventional explosives such as dynamite contain more energy. A related concept is the physical quantity TNT-equivalent mass (or mass of TNT equivalent), expressed in the ordinary units of mass Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon Yield
The explosive yield of a nuclear weapon is the amount of energy released such as blast, thermal, and nuclear radiation, when that particular nuclear weapon is detonated. It is usually expressed as a ''TNT equivalent'', the standardized equivalent mass of trinitrotoluene (TNT) which would produce the same energy discharge if detonated, either in kilotonnes (symbol kt, thousands of tonnes of TNT), in megatonnes (Mt, millions of tonnes of TNT). It is also sometimes expressed in terajoules (TJ); an explosive yield of one terajoule is equal to . Because the accuracy of any measurement of the energy released by TNT has always been problematic, the conventional definition is that one kilotonne of TNT is held simply to be equivalent to 1012 calories. The yield-to-weight ratio is the amount of weapon yield compared to the mass of the weapon. The practical maximum yield-to-weight ratio for fusion weapons (thermonuclear weapons) has been estimated to six megatonnes of TNT per tonne of bomb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
The Partial Test Ban Treaty (PTBT), formally known as the 1963 Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests in the Atmosphere, in Outer Space and Under Water, prohibited all nuclear weapons testing, test detonations of nuclear weapons except for those conducted underground nuclear weapons testing, underground. It is also abbreviated as the Limited Test Ban Treaty (LTBT) and Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (NTBT), though the latter may also refer to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), which succeeded the PTBT for ratifying parties. Negotiations initially focused on a comprehensive ban, but that was abandoned because of technical questions surrounding the detection of underground tests and Soviet concerns over the intrusiveness of proposed verification methods. The impetus for the test ban was provided by rising public anxiety over the magnitude of nuclear tests, particularly tests of new thermonuclear weapons (hydrogen bombs), and the resulting nuclear fallout. A test ban was also se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1971–74 French Nuclear Tests
France carried out a series of 24 nuclear tests from 1971 to 1974 These tests followed the 1966–70 French nuclear tests, 1966–1970 French nuclear tests series and preceded the 1975–78 French nuclear tests, 1975–1978 French nuclear tests. Notes References Further reading * {{DEFAULTSORT:1971-74 French nuclear tests French nuclear weapons testing 1971 in France 1972 in France 1973 in France 1974 in France 1971 in the French colonial empire 1972 in the French colonial empire 1973 in the French colonial empire 1974 in the French colonial empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location (geography), ''location'' is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational equipotential surface, surface (see Geodetic datum#Vertical datum, Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while ''altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and ''three-dimensional space, depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo (volcano), Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest ECEF, geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation, the term ''elevation'' or ''aerodrome elevation'' is defined by the IC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |