|
1962 In Spaceflight (July–September)
This is a list of spaceflights launched between July and September 1962. For launches in the rest of the year, see 1962 in spaceflight (January–March), 1962 in spaceflight (April–June) and 1962 in spaceflight (October–December). For an overview of the whole year, see 1962 in spaceflight. Orbital launches , colspan=8 style="background:white;", July , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", August , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", September , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", Suborbital launches , colspan=8 style="background:white;", July , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", August , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", September , - Reference External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceflight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly objects, usually spacecraft, into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in orbit around Earth, but also includes space probes for flights beyond Earth orbit. Such spaceflights operate either by telerobotic or autonomous control. The first spaceflights began in the 1950s with the launches of the Soviet Sputnik satellites and American Explorer and Vanguard missions. Human spaceflight programs include the Soyuz, Shenzhou, the past Apollo Moon landing and the Space Shuttle programs. Other current spaceflight are conducted to the International Space Station and to China's Tiangong Space Station. Spaceflights include the launches of Earth observation and telecommunications satellites, interplanetary missions, the rendezvouses and dockings with space stations, and crewed spaceflights on sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thor-Agena
Thor-Agena was a series of orbital launch vehicles. The launch vehicles used the Douglas Aircraft Company, Douglas-built Thor (rocket family), Thor first Multistage rocket, stage and the Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed-built RM-81 Agena, Agena second stages. They are thus cousins of the more-famous Thor-Deltas, which founded the Delta (rocket family), Delta rocket family. The first attempted launch of a Thor-Agena was in January 1959. The first successful launch was on 28 February 1959, launching ''Discoverer 1''. It was the first two-stage launch vehicle to place a satellite into orbit. Missions Among other uses, the clandestine CORONA (satellite), CORONA program used Thor-Agena from June 1959 until January 1968 to launch United States military reconnaissance satellites operated by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). During this program, Thor-Agena launch vehicles were used in 145 launch attempts, now known to have been part of satellite surveillance programs. Also, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 7
Kosmos 7 ( meaning ''Cosmos 7''), also known as Zenit-2 No.4 and occasionally in the West as Sputnik 17 was a Soviet reconnaissance satellite launched in 1962. It was the seventh satellite to be designated under the Kosmos system, and the second successful launch of a Soviet reconnaissance satellite. Spacecraft Kosmos 7 was a Zenit-2 satellite, a first generation, low resolution reconnaissance satellite derived from the Vostok spacecraft used for crewed flights. It also marked the first successful launch of a Vostok-2, on the second attempt. It had a mass of . The first Vostok-2 launch, also carrying a Zenit-2 satellite, suffered an engine failure seconds after launch on 1 June 1962, fell back to earth and exploded within of the launch pad. Kosmos 7 was one of a series of Soviet Earth satellites whose purpose was to study outer space, the upper layers of the atmosphere, and the Earth. Scientific data and measurements were relayed to Earth by multichannel telemetry systems e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gagarin's Start
Gagarin's Start (, ''Gagarinskiy start''), also known as Baikonur Site 1 or Site 1/5 was a launch site at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan that was used by the Soviet space program and Roscosmos. History 20th century The launchpad for the world's first human spaceflight made by Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1 in 1961, the site was referred to as Site No.1 (, ''Ploshchadka No. 1'') as the first one of its kind. It is also sometimes referred to as NIIP-5 LC1, Baikonur LC1, LC-1/5, LC-1, Pad 1/5 or GIK-5 LC1. At Baikonur, site numbers refer to facilities. Site 0 was the construction headquarters and residential area and, as the first major project, this launch pad was named Site 1. Its processing facilities were called Site 2 and its oxygen/nitrogen plant was Site 3. The facility was later designated as Pad No. 5 for the R-7 programme. The numbering of the sites reflected Baikonur's role as a secondary ICBM base, with the primary being the Plesetsk Cosmodrome, which featured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vostok-2 (rocket)
The Vostok-2 ( meaning ''"East"''), GRAU index 8A92 was an expendable carrier rocket used by the Soviet Union between 1962 and 1967. Forty five were launched, of which five failed. It was derived from the earlier Vostok-K, with uprated engines. It was a member of the Vostok family of rockets. The Vostok-2 switched to the newer 8K74 core and featured the 8D74K first stage engines from the Molniya 8K78 booster which gave it improved performance over the older Vostok 8K72K. The Vostok-2 made its maiden flight on 1 June 1962, from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. One of the booster engines shut down 1.8 seconds after launch, and the rocket came down away from the pad. The resulting explosion damaged the launch complex, and necessitated delays to several other launches that had been scheduled from that complex, including Vostok 3 and Vostok 4. Thirteen months later, on 10 July 1963, an almost identical failure occurred. The other three failures were caused by a second stage malf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
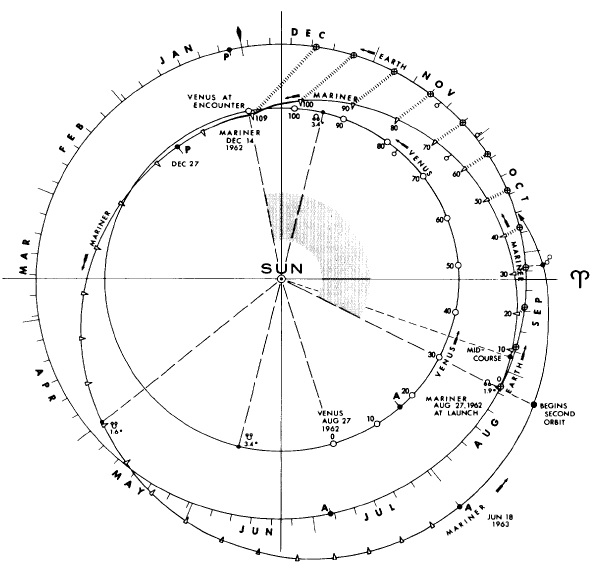
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker and denser than Earth and any other rocky body in the Solar System. Its atmosphere is composed of mostly carbon dioxide (), with a global sulfuric acid cloud cover and no liquid water. At the mean surface level the atmosphere reaches a temperature of and a pressure 92 times greater than Earth's at sea level, turning the lowest layer of the atmosphere into a supercritical fluid. Venus is the third brightest object in Earth's sky, after the Moon and the Sun, and, like Mercury, appears always relatively close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star", resulting from orbiting closer ( inferior) to the Sun than Earth. The orbits of Venus and Earth make the two planets approach each other in synodic periods of 1.6 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliocentric Orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun itself are in such orbits, as are many artificial probes and pieces of debris. The moons of planets in the Solar System, by contrast, are not in heliocentric orbits, as they orbit their respective planet (although the Moon has a convex orbit around the Sun). The barycenter of the Solar System, while always very near the Sun, moves through space as time passes, depending on where other large bodies in the Solar System, such as Jupiter and other large gas planets, are located at that time. A similar phenomenon allows the detection of exoplanets by way of the radial-velocity method. The ''helio-'' prefix is derived from the Greek word "ἥλιος", meaning "Sun", and also Helios, the personification of the Sun in Greek mythology. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariner 1
Mariner 1, built to conduct the first American planetary flyby of Venus, was the first spacecraft of NASA's interplanetary Mariner program. Developed by Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and originally planned to be a purpose-built probe launched summer 1962, Mariner 1's design was changed when the Centaur (rocket stage), Centaur proved unavailable at that early date. Mariner 1 (and its sibling spacecraft, Mariner 2), were then adapted from the lighter Ranger program, Ranger lunar spacecraft. Mariner 1 carried a suite of experiments to determine the temperature of Venus as well to measure magnetic fields and charged particles near the planet and in interplanetary space. Mariner 1 was launched by an Atlas-Agena rocket from Cape Canaveral Launch Complex 12, Cape Canaveral's Pad 12 on July 22, 1962. Shortly after Takeoff, liftoff, errors in communication between the rocket and its ground-based guidance systems caused the rocket to veer off course, and it had to be destroyed by range safet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 12
Launch Complex 12 (LC-12) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida was a launch pad used by Atlas rockets and missiles between 1958 and 1967. It was the second-most southern of the pads known as Missile Row, between LC-11 to the south and LC-13 to the north. Along with Complexes 11, 13 and 14, LC-12 featured a more robust design than many contemporary pads, due to the greater power of the Atlas compared to other rockets of the time. It was larger, and featured a concrete launch pedestal that was tall and a reinforced blockhouse. The rockets were delivered to the launch pad by means of a ramp on the southwest side of the launch pedestal. Currently, LC-12 is leased by Blue Origin, and has been used by them as a storage site. History Atlas operations Atlas A, C and D missiles were tested from the site. It was also used for orbital launches of Atlas-Able and later Atlas-Agena rockets, and two Project FIRE suborbital tests for Project Apollo, using Atlas D rockets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Intellegence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and conducting covert operations. The agency is headquartered in the George Bush Center for Intelligence in Langley, Virginia, and is sometimes metonymously called "Langley". A major member of the United States Intelligence Community (IC), the CIA has reported to the director of national intelligence since 2004, and is focused on providing intelligence for the president and the Cabinet. The CIA is headed by a director and is divided into various directorates, including a Directorate of Analysis and Directorate of Operations. Unlike the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the CIA has no law enforcement function and focuses on intelligence gathering overseas, with only limited domestic intelligence collection. The CIA is responsible for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Reconnaissance Office
The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) is a member of the United States Intelligence Community and an agency of the United States Department of Defense which designs, builds, launches, and operates the reconnaissance satellites of the U.S. federal government. It provides satellite intelligence to several government agencies, particularly signals intelligence (SIGINT) to the National Security Agency (NSA), imagery intelligence (IMINT) to the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA), and measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) to the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA). The NRO announced in 2023 that it plans within the following decade to quadruple the number of satellites it operates and increase the number of signals and images it delivers by a factor of ten. NRO is considered, along with the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), NSA, DIA, and NGA, to be one of the "big five" U.S. intelligence agencies. The NRO is headquartered in Chantilly, Virginia, south of Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |