|
1962 In Spaceflight (January–March)
This is a list of spaceflights launched between January and March 1962. For launches in the rest of the year, see 1962 in spaceflight (April–June), 1962 in spaceflight (July–September) and 1962 in spaceflight (October–December). For an overview of the whole year, see 1962 in spaceflight. Orbital launches , colspan=8 style="background:white;", January , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", February , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", March , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", Suborbital launches , colspan=8 style="background:white;", January , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", February , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", March , - Reference External links {{DEFAULTSORT:1962 in spaceflight (January-March) 1962 in spaceflight Spaceflight by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceflight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly objects, usually spacecraft, into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in orbit around Earth, but also includes space probes for flights beyond Earth orbit. Such spaceflights operate either by telerobotic or autonomous control. The first spaceflights began in the 1950s with the launches of the Soviet Sputnik satellites and American Explorer and Vanguard missions. Human spaceflight programs include the Soyuz, Shenzhou, the past Apollo Moon landing and the Space Shuttle programs. Other current spaceflight are conducted to the International Space Station and to China's Tiangong Space Station. Spaceflights include the launches of Earth observation and telecommunications satellites, interplanetary missions, the rendezvouses and dockings with space stations, and crewed spaceflights on sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SECOR
SECOR (Sequential Collation of Ranges) was a series of small United States Armed Forces satellites launched in the 1960s for geodesy measurements that precisely determined the locations of points on the Earth's surface, particularly of isolated islands in the Pacific Ocean. This data allowed for improved global mapping and precise positioning of ground stations for other satellites. Any SECOR satellite could be linked to four mobile ground stations: three were placed in accurately determined known locations, and a fourth one was placed in an unknown location. By measuring a satellite's distance from the three known stations, its position in space was determined. Then, the distance between the unknown ground station and the previously determined satellite's position was used to compute the unknown ground station's coordinates. This process was repeated many times, to enhance the accuracy of the measurement. Once the unknown station's position was accurately determined, it became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a List of human spaceflight programs, human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member of a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the term is sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists, and space tourists. "Astronaut" technically applies to all human space travelers regardless of nationality. However, astronauts fielded by Russia or the Soviet Union are typically known instead as cosmonauts (from the Russian "kosmos" (космос), meaning "space", also borrowed from Greek ). Comparatively recent developments in crewed spaceflight made by China have led to the rise of the term taikonaut (from the Standard Chinese, Mandarin "tàikōng" (), meaning "space"), although its use is somewhat informal and its origin is unclear. In China, the People' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
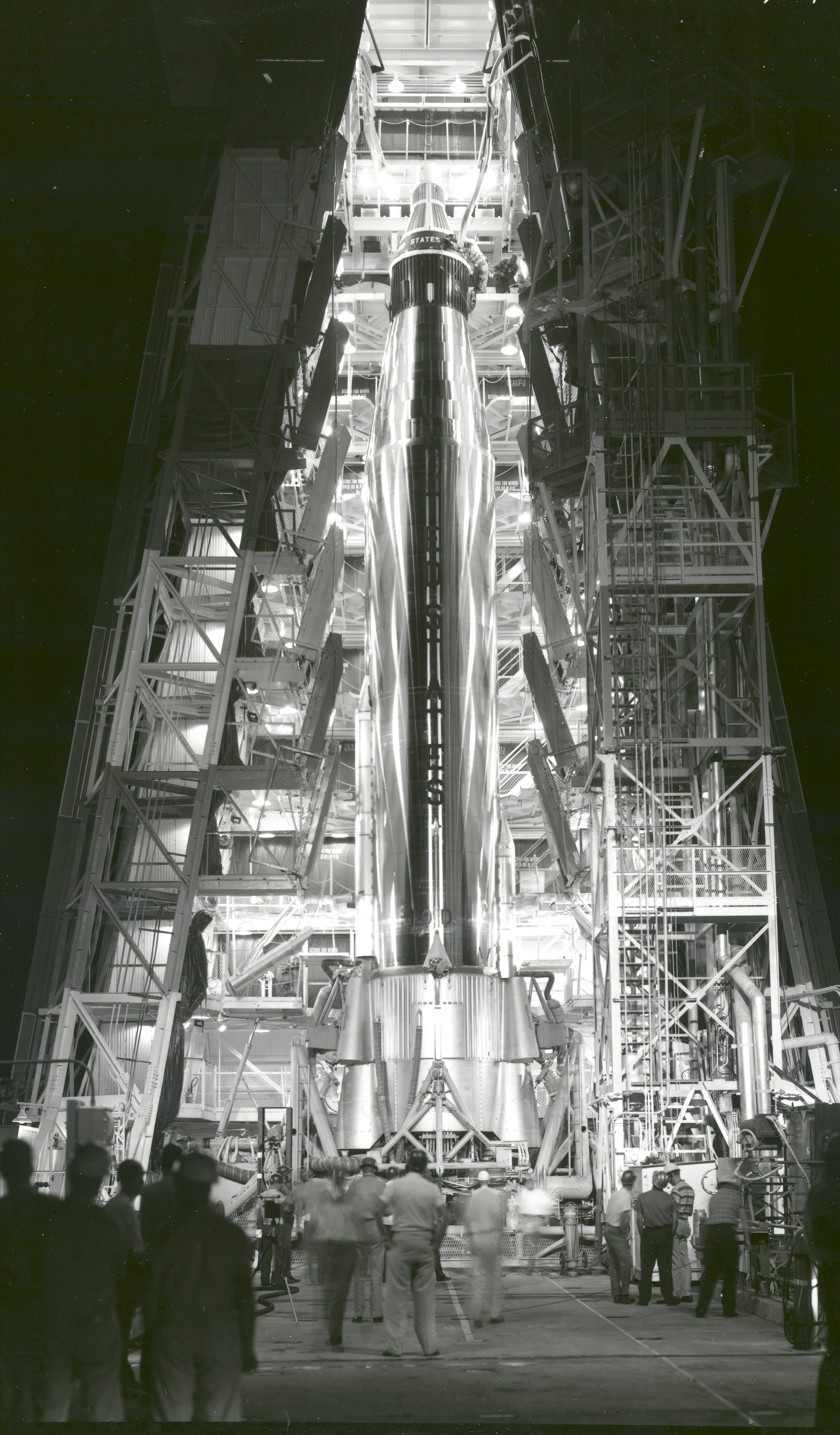
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 14
Launch Complex 14 (LC-14) is a launch site at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Part of the Missile Row lineup of launch sites in the region, LC-14 was used for various crewed and uncrewed Atlas launches, including the February 1962 ''Friendship 7'' flight aboard which John Glenn became the first American to orbit the Earth. LC-14 is currently leased to Stoke Space for their Nova launch vehicle. History Atlas and Mercury LC-14 was the first Atlas pad in operation and hosted the initial Atlas A and B test flights in 1957-58 It was also the only one of the original four pads to never have a booster explode on it. By 1959, it was decided to convert the pad for Atlas D missile and space launches, and a large service tower was added early in the year. The first Atlas flown from the renovated LC-14 was Missile 7D on May 18; however, a problem with the launcher hold-down arms damaged the missile and caused its explosion shortly after launcThis was traced to improper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas LV-3B
The Atlas LV-3B, Atlas D Mercury Launch Vehicle or Mercury-Atlas Launch Vehicle, was a Human-rating certification, human-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. Manufactured by Convair, it was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, and was a member of the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas family of rockets. With the Atlas having been originally designed as a weapon system, testing and design changes were made to the missile to make it a safe and reliable launch vehicle. After the changes were made and approved, the US launched the LV-3B nine times, four of which had human spaceflight, crewed Mercury spacecraft. Design The Atlas LV-3B was a Human-rating certification, human-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. Manufactured by American aircraft manufacturing company Convair, it was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TIROS-4
TIROS-4 (also called TIROS-D and A9) was a spin-stabilized meteorological satellite. It was the fourth in a series of Television Infrared Observation Satellites. Launch TIROS-4 was launched on February 8, 1962, by a Thor-Delta rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The spacecraft functioned nominally until June 30, 1962. The satellite orbited the Earth once every 1 hour and 30 minutes, at an inclination of 48.3°. Its perigee was and apogee was . Mission The satellite was in the form of an 18-sided right prism, 107 cm in diameter and 56 cm high. The top and sides of the spacecraft were covered with approximately 9000 1- by 2-cm silicon solar cells. It was equipped with two independent television camera subsystems for taking cloud cover pictures and three radiometers (two-channel low-resolution, omnidirectional, and five-channel scanning) for measuring radiation from the Earth and its atmosphere. The satellite spin rate was maintained between 8 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliocentric Orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun itself are in such orbits, as are many artificial probes and pieces of debris. The moons of planets in the Solar System, by contrast, are not in heliocentric orbits, as they orbit their respective planet (although the Moon has a convex orbit around the Sun). The barycenter of the Solar System, while always very near the Sun, moves through space as time passes, depending on where other large bodies in the Solar System, such as Jupiter and other large gas planets, are located at that time. A similar phenomenon allows the detection of exoplanets by way of the radial-velocity method. The ''helio-'' prefix is derived from the Greek word "ἥλιος", meaning "Sun", and also Helios, the personification of the Sun in Greek mythology. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
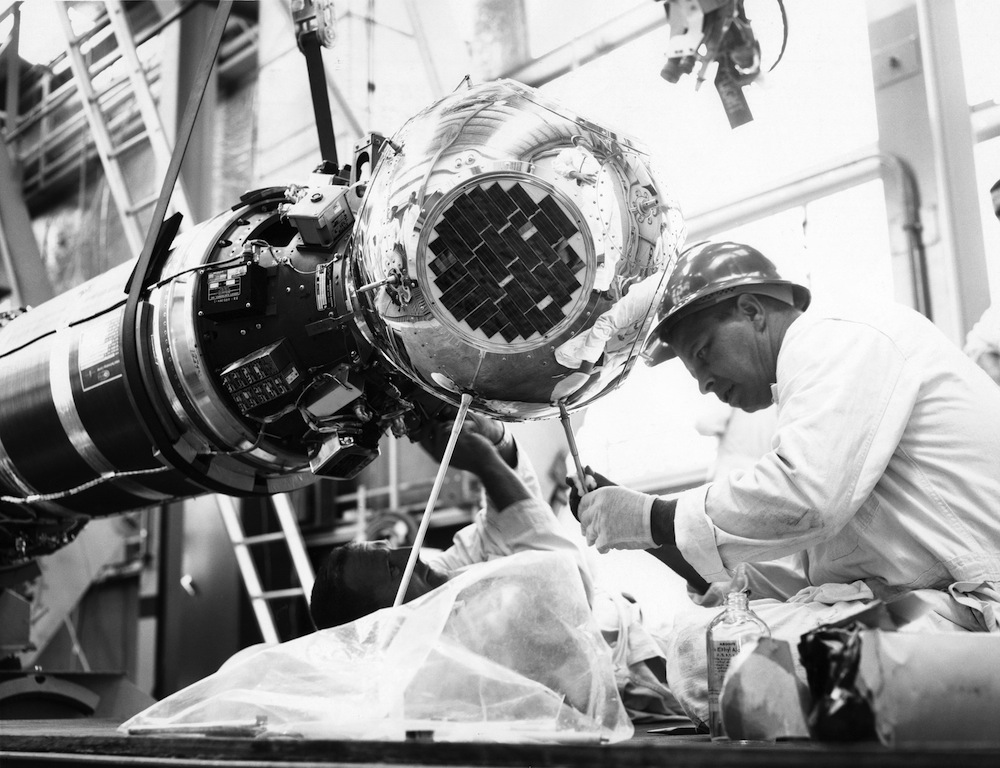
Ranger 3
Ranger 3 was a space exploration mission conducted by NASA to study the Moon. The Ranger 3 robotic spacecraft was launched January 26, 1962 as part of the Ranger program. Due to a series of malfunctions, the spacecraft missed the Moon by and entered a heliocentric orbit. The Ranger 3 space probe was designed to transmit pictures of the lunar surface during a period of 10 minutes of flight prior to impacting on the Moon, to rough-land a seismometer capsule on the Moon, to collect gamma-ray data in flight, to study radar reflectivity of the lunar surface, and to continue testing of the Ranger program for development of lunar and interplanetary spacecraft. Spacecraft design Ranger 3 was the first of the Block II Ranger designs. The basic vehicle was 3.1 m high and consisted of a lunar capsule covered with a balsa wood impact-limiter, 635 mm in diameter (25 inches), a mono-propellant mid-course motor, a retrorocket with a thrust of 5080 pounds force (22.6 kN), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 12
Launch Complex 12 (LC-12) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida was a launch pad used by Atlas rockets and missiles between 1958 and 1967. It was the second-most southern of the pads known as Missile Row, between LC-11 to the south and LC-13 to the north. Along with Complexes 11, 13 and 14, LC-12 featured a more robust design than many contemporary pads, due to the greater power of the Atlas compared to other rockets of the time. It was larger, and featured a concrete launch pedestal that was tall and a reinforced blockhouse. The rockets were delivered to the launch pad by means of a ramp on the southwest side of the launch pedestal. Currently, LC-12 is leased by Blue Origin, and has been used by them as a storage site. History Atlas operations Atlas A, C and D missiles were tested from the site. It was also used for orbital launches of Atlas-Able and later Atlas-Agena rockets, and two Project FIRE suborbital tests for Project Apollo, using Atlas D rockets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
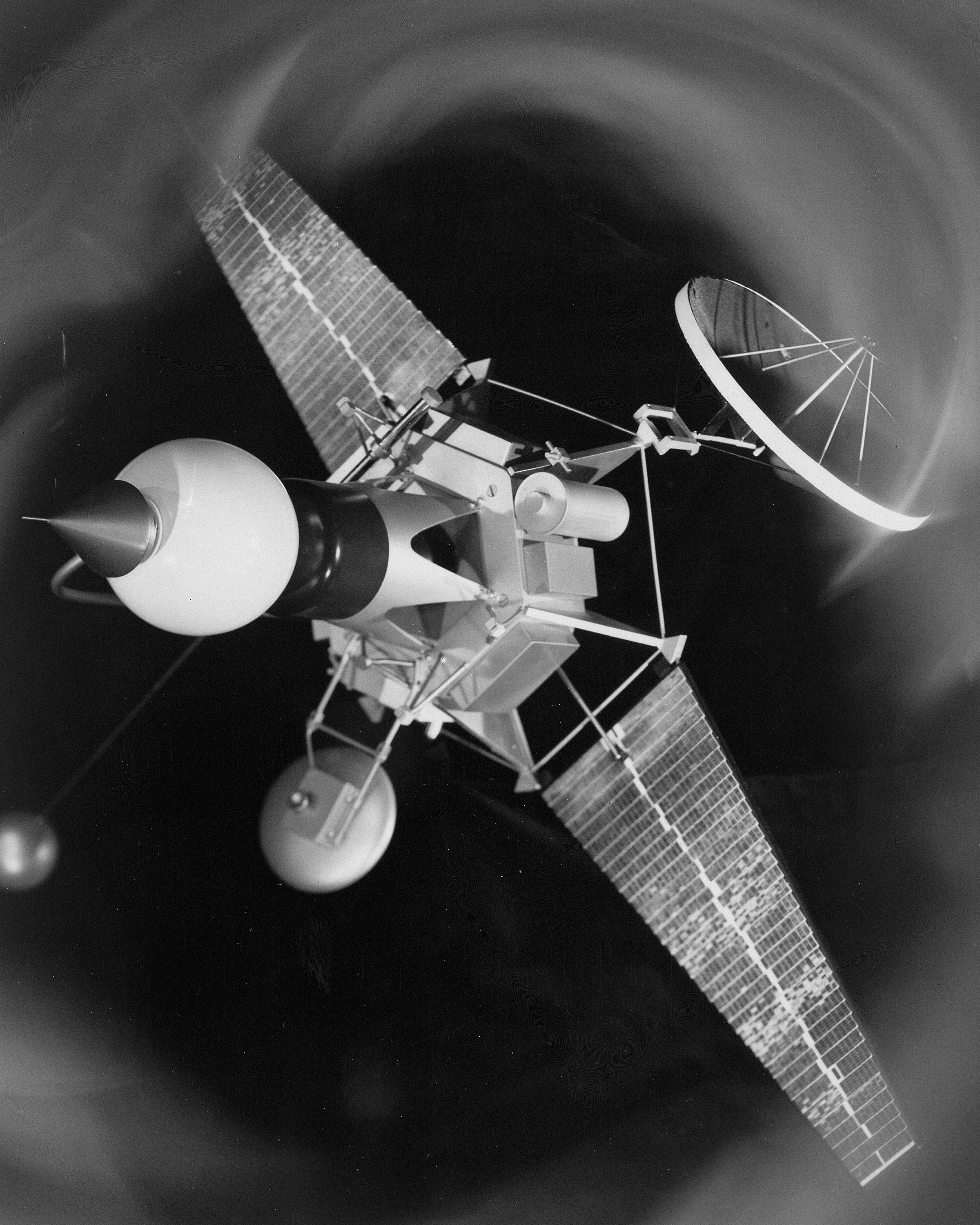
Atlas-Agena
The Atlas-Agena was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas family of rockets, and was launched 109 times between 1960 and 1978. It was used to launch the first five Mariner program, Mariner uncrewed probes to the planets Venus and Mars, and the Ranger program, Ranger and Lunar Orbiter program, Lunar Orbiter uncrewed probes to the Moon. The upper stage was also used as an uncrewed orbital Agena target vehicle, target vehicle for the Project Gemini, Gemini crewed spacecraft to practice space rendezvous, rendezvous and docking and berthing of spacecraft, docking. However, the launch vehicle family was originally developed for the Air Force and most of its launches were classified DoD payloads. The Atlas-Agena was a two-and-a-half-stage rocket, with a SM-65 Atlas#'Stage-and-a-half', stage-and-a-half Atlas missile as the first stage, and an RM-81 Agena second stage. Initially, SM-65D Atlas, Atlas D m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SURCAL 1
The Surveillance Calibration (or SURCAL) satellites were a series of radar calibration satellites for the Naval Space Surveillance radar system. They were launched in the 1960s. Background The SURCAL series of satellites were produced by the Naval Research Laboratory to act as test and calibration targets for the Naval Space Surveillance radar. The first SURCAL satellite was intended to remain attached to the launch vehicle and was a 5.5 inch long, 5.5 inch diameter cylinder. The other four SURCAL satellites were box-shaped with solar panels, a transponder, and antennas. They transmitted a 216 MHz signal on command. Launches Other vehicles Astronautix The ''Encyclopedia Astronautica'' is a reference web site on space travel. The encyclopedia includes 79,433 articles with 13,741 illustrations, a comprehensive catalog of missiles, spacecraft, space technology, astronauts, and spaceflight from ... includes passive satellites such as the SURCAL 150B and SURCAL 160 targe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Iowa
The University of Iowa (U of I, UIowa, or Iowa) is a public university, public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is organized into 12 colleges offering more than 200 areas of study and 7 professional degrees. On an urban 1,880-acre campus on the banks of the Iowa River, the University of Iowa is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". In fiscal year 2021, research expenditures at Iowa totaled $818 million. The university was the original developer of the Master of Fine Arts degree, and it operates the Iowa Writers' Workshop, whose alumni include 17 of the university's 46 Pulitzer Prize winners. Iowa is a member of the Association of American Universities and the Universities Research Association. Among public universities in the United States, UI was the first to beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |