|
1950 United States Elections
Elections were held on November 7, 1950, and elected the members of the 82nd United States Congress. The election took place during the Korean War, during Democratic President Harry S. Truman's second (only full) term. The Democrats lost twenty-eight seats to the Republican Party in the House of Representatives. The Democrats also lost five seats in the U.S. Senate to the Republicans. The defeat of the Labor Party congressman Vito Marcantonio left third parties without representation in Congress for the first time since 1908. Like his predecessor Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1938, Truman and the Democratic party managed to maintain control of both houses, defying the six-year itch phenomenon for the second time in a row. However, the election was still a defeat for Truman, as it strengthened the conservative coalition and ensured that none of Truman's Fair Deal policies would pass. Republicans also ran against Truman's prosecution of the Korean War, and the 82nd Congress subsequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
United States Midterm Election
Midterm elections in the United States are the Elections in the United States, general elections that are held near the midpoint of a President of the United States, president's four-year term of office, on Election Day (United States), Election Day on the Tuesday after the first Monday in November. Federal offices that are up for election during the midterms include all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives, and 33 or 34 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate. In addition, 34 of the 50 U.S. states elect their Governor (United States), governors for four-year terms during midterm elections, while Vermont and New Hampshire elect governors to two-year terms in both midterm and presidential elections. Thus, 36 governors are elected during midterm elections. Many states also elect officers to their State legislature (United States), state legislatures in midterm years. There are also elections held at the municipal level. On the ballot are many mayors, other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Franklin D
Franklin may refer to: People and characters * Franklin (given name), including list of people and characters with the name * Franklin (surname), including list of people and characters with the name * Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class Places * Franklin (crater), a lunar impact crater * Franklin County (other), in a number of countries * Mount Franklin (other), including Franklin Mountain Australia * Franklin, Tasmania, a township * Division of Franklin, federal electoral division in Tasmania * Division of Franklin (state), state electoral division in Tasmania * Franklin, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb in the Canberra district of Gungahlin * Franklin River, river of Tasmania * Franklin Sound, waterway of Tasmania Canada * District of Franklin, a former district of the Northwest Territories * Franklin, Quebec, a municipality in the Montérégie region * Rural Municipality of Franklin, Manitoba * Franklin, Manitoba, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
General Elections In The United States
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air and space forces, marines or naval infantry. In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. French Revolutionary system Arab system Other variations Other nomenclatures for general officers include the titles and ranks: * Adjutant general * Commandant-general * Inspector general * General-in-chief * General of the Air Force (USAF only) * General of the Armies of the United States (of America), a title created for General John J. Pershing, and subsequently granted posthumously to George Washington and Ulysses S. Grant * (" general admiral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
1950 Elections In The United States
Year 195 ( CXCV) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in Rome as the Year of the Consulship of Scrapula and Clemens (or, less frequently, year 948 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 195 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus has the Roman Senate deify the previous emperor Commodus, in an attempt to gain favor with the family of Marcus Aurelius. * King Vologases V and other eastern princes support the claims of Pescennius Niger. The Roman province of Mesopotamia rises in revolt with Parthian support. Severus marches to Mesopotamia to battle the Parthians. * The Roman province of Syria is divided and the role of Antioch is diminished. The Romans annex the Syrian cities of Edessa and Nisibis. Severus re-establishes his headquarters and the colonies th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
1950 United States Gubernatorial Elections
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1950, in 33 states, concurrent with the United States House elections, 1950, House and United States Senate elections, 1950, Senate elections, on November 7, 1950. Elections took place on September 11 in Maine. In Connecticut, the governor was elected to a 4-year term for the first time, instead of a 2-year term. Results References 1950 United States gubernatorial elections, September 1950 in the United States November 1950 in the United States Long stubs with short prose {{US-election-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
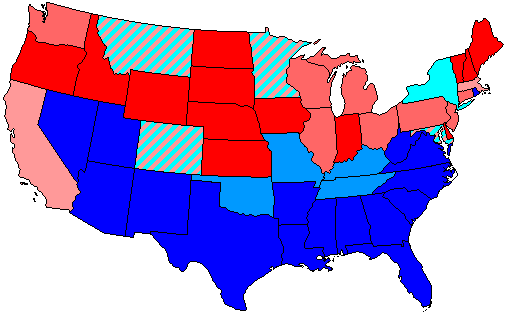
1950 United States Senate Elections
The 1950 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Harry S. Truman's second term as president. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and four special elections were held to fill vacancies. As with most 20th-century second-term midterms, the party not holding the presidency made significant gains. The Republican opposition made a net gain of five seats, taking advantage of the Democratic administration's declining popularity during the Cold War and the aftermath of the Recession of 1949. The Democrats held a narrow 49-to-47-seat majority after the election. This was the first time since 1932 that the Senate majority leader lost his seat, and the only instance of the majority leader losing his seat while his party retained the majority. Results summary ''Colored shading indicates party with largest share of that row.'' Source: Clerk of the U.S. House of Representatives Gains, losses, and holds Retirements One Republican and three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
1950 United States House Of Representatives Elections
The 1950 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 82nd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 7, 1950, while Maine held theirs on September 11. These elections occurred in the middle of President Harry Truman's second term. As the Korean War began and Truman's personal popularity plummeted for a second time during his presidency, his Democratic Party lost a net 28 seats to the Republican Party. This was the first election since 1908 where no third parties acquired any seats in the House. Special elections There were six special elections throughout the year, listed here by date and district. Overall results SourceElection Statistics - Office of the Clerk Alabama Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware Florida Georgia Idaho Illinois Indiana Iow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dwight D
Dwight may refer to: People and fictional characters * Dwight (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters * Dwight (surname), a list of people Places Canada * Dwight, Ontario, village in the township of Lake of Bays, Ontario United States * Dwight (neighborhood), part of an historic district in New Haven, Connecticut * Dwight, Illinois, a village * Dwight, Kansas, a city * Dwight, Massachusetts, a village * Dwight, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Dwight, Nebraska, a village * Dwight, North Dakota, a city * Dwight Township, Livingston County, Illinois * Dwight Township, Michigan Other uses * Dwight Airport, a public-use airport north of Dwight, Illinois * Dwight Correctional Center, a maximum security prison for adult females in Illinois * Dwight School, New York City {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fair Deal
The Fair Deal was a set of proposals put forward by U.S. President Harry S. Truman to Congress in 1945 and in his January 1949 State of the Union Address. More generally, the term characterizes the entire domestic agenda of the Truman administration, from 1945 to 1953. It offered new proposals to continue New Deal liberalism, but with a conservative coalition controlling Congress during most of Truman's presidency, only a few of its major initiatives became law and then only if they had considerable Republican Party support. As Richard Neustadt concludes, the most important proposals were aid to education, national health insurance, the Fair Employment Practices Commission, and repeal of the Taft–Hartley Act. They were all debated at length, then voted down. Nevertheless, enough smaller and less controversial items passed that liberals could claim some success. The Korean War made military spending the nation's priority and killed almost the entire Fair Deal, but did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Conservative Coalition
The conservative coalition, founded in 1937, was an unofficial alliance of members of the United States Congress which brought together the conservative wings of the Republican and Democratic parties to oppose President Franklin Delano Roosevelt's New Deal. In addition to Roosevelt, the conservative coalition dominated Congress for four presidencies, blocking legislation proposed by Roosevelt and his successors. By 1937, the conservatives were the largest faction in the Republican Party which had opposed the New Deal in some form since 1933. Despite Roosevelt being a Democrat himself, his party did not universally support the New Deal agenda in Congress. Democrats who opposed Roosevelt's policies tended to hold conservative views, and allied with conservative Republicans. These Democrats were mostly located in the South. According to James T. Patterson: "By and large the congressional conservatives agreed in opposing the spread of federal power and bureaucracy, in denouncing d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Six-year Itch
The six-year itch, according to political scientists, is the pattern which takes place during a U.S. president's sixth year in office. This year is characterized by the nation's disgruntled attitude towards the president and their political party. During this time, there is a midterm election and the incumbent president's party usually loses a significant number of seats in Congress. The term is derived from the phrase " seven-year itch", referring to a supposed pattern that relationships often sour after seven years of marriage, and the 1955 film of the same name. One of the earliest uses of the term in politics was by Republican strategist Kevin Phillips in a nationally-syndicated 1973 column which looked ahead to the 1974 midterms. History Pre-Reconstruction Prior to Reconstruction, the six-year itch saw the president's party gain seats in one house, while losing seats in the other house. Presidents before Reconstruction whose party had this occur: * 1814 – Democrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
United States Elections, 1938
Elections were held on November 8, 1938, in the middle of Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt's second term. The Democratic Party lost 72 seats, mostly to the Republican Party, in the House of Representatives. The Democrats also lost eight seats to the Republicans in the U.S. Senate. Despite these heavy losses, the Democrats maintained control of Congress. The election was a defeat for Roosevelt, as the conservative coalition (an alliance of Republicans and Southern Democrats) took control of Congress and stymied Roosevelt's domestic agenda. Roosevelt had campaigned openly against members of his own party who had not supported the New Deal, but Roosevelt's preferred candidates met with little success across the country. The election took place in the aftermath of the recession of 1937–38 and the defeat of the Judicial Procedures Reform Bill of 1937 ("the court-packing plan"), and President Roosevelt was at the nadir of his popularity. Republicans picked up congres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |