|
16th Canadian Battalion (The Canadian Scottish), CEF
The 16th Battalion (Canadian Scottish), CEF was a unit of the First World War Canadian Expeditionary Force. It was organized at Valcartier on 2 September 1914 and was composed of recruits from the 91st Regiment Canadian Highlanders, the 79th Cameron Highlanders of Canada, the 72nd Regiment "Seaforth Highlanders of Canada", and the 50th Regiment "Highlanders". History The 16th Battalion served in the 3rd Canadian Brigade of the 1st Canadian Division. Since its early beginnings, the battalion had a high standard of conduct on the battlefield and was commanded by outstanding leaders. One such was Lieutenant-General Sir Arthur Currie, KCMG, who rose to command the Canadian Corps during the Great War. Currie was a master tactician whose skills led the Canadians to victory at Vimy Ridge and Amiens. Lieutenant-Colonel Cyrus Wesley Peck commanded the battalion for many months in the trenches. Four members of the 16th Battalion were awarded the Victoria Cross: Piper James Clelan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Expeditionary Force
The Canadian Expeditionary Force (CEF; French: ''Corps expéditionnaire canadien'') was the expeditionary warfare, expeditionary field force of Canada during the First World War. It was formed on August 15, 1914, following United Kingdom declaration of war upon Germany (1914), Britain’s declaration of war on the German Empire, with an initial strength of one infantry Division (military), division. The division subsequently fought at Second Battle of Ypres, Ypres on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front, with a newly raised second division reinforcing the committed units to form the Canadian Corps. The CEF and corps was eventually expanded to four infantry divisions, which were all committed to the fighting in France and Belgium along the Western Front. A fifth division was partially raised in 1917, but was broken up in 1918 and used as reinforcements following heavy casualties. Personnel Recruitment The CEF was mostly volunteers; a bill allowing conscription was pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medals21
A medal or medallion is a small portable artistic object, a thin disc, normally of metal, carrying a design, usually on both sides. They typically have a commemorative purpose of some kind, and many are presented as awards. They may be intended to be worn, suspended from clothing or jewellery in some way, although this has not always been the case. They may be struck like a coin by dies or die-cast in a mould. A medal may be awarded to a person or organisation as a form of recognition for sporting, military, scientific, cultural, academic, or various other achievements. Military awards and decorations are more precise terms for certain types of state decoration. Medals may also be created for sale to commemorate particular individuals or events, or as works of artistic expression in their own right. In the past, medals commissioned for an individual, typically with their portrait, were often used as a form of diplomatic or personal gift, with no sense of being an award for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
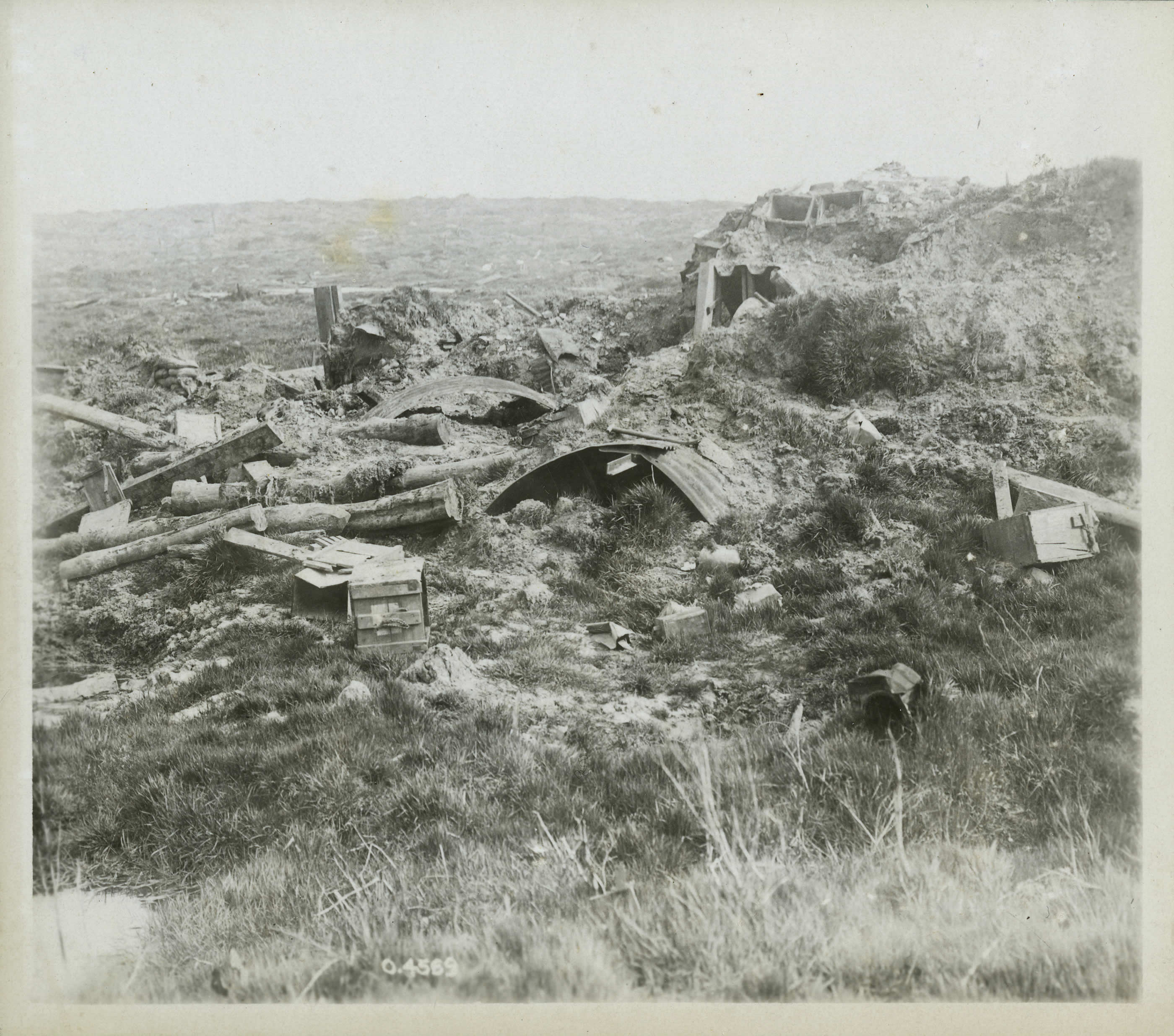
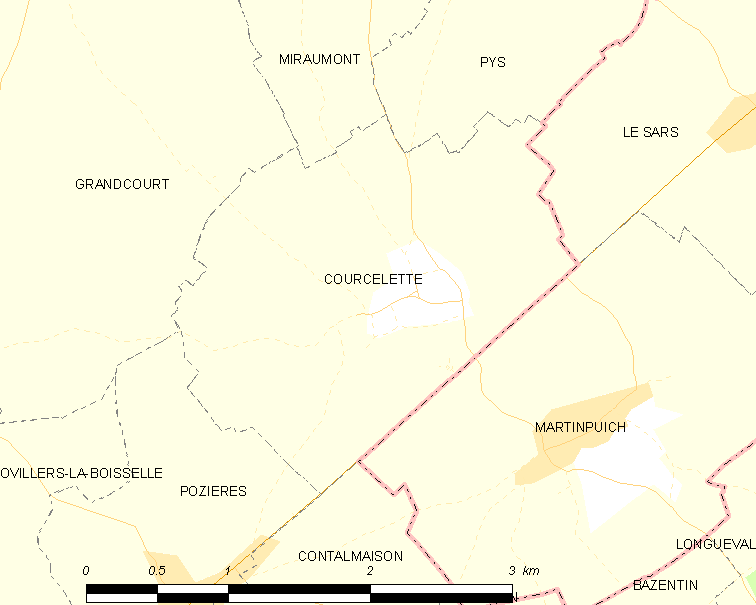
Battle Of The Ancre Heights
The Battle of the Ancre Heights (1 October – 11 November 1916), is the name given to the continuation of British attacks after the Battle of Thiepval Ridge from during the Battle of the Somme. The battle was conducted by the Reserve Army (renamed Fifth Army on 29 October) from Courcelette near the Albert–Bapaume road, west to Thiepval on Bazentin Ridge. British possession of the heights would deprive the German 1st Army of observation towards Albert to the south-west and give the British observation north over the Ancre valley to the German positions around Beaumont-Hamel, Serre and Beaucourt. The Reserve Army conducted large attacks on and from Many smaller attacks were made in the intervening periods, amid interruptions caused by frequent heavy rain, which turned the ground and roads into rivers of mud and grounded aircraft. German forces in footholds on the ridge, at the east end of ( Regina Trench) and in the remaining parts of ( Schwaben Redoubt) to the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Thiepval Ridge
The Battle of Thiepval Ridge was the first big offensive of the Reserve Army (Lieutenant General Hubert Gough), during the Battle of the Somme on the Western Front during the First World War. The attack was intended to benefit from the Fourth Army attack in the Battle of Morval by starting afterwards. The battle was fought on a front from Courcelette in the east, near the Albert–Bapaume road, to Thiepval and the Schwaben Redoubt () in the west, which overlooked the German defences further north in the Ancre valley, the rising ground towards Beaumont-Hamel and Serre beyond. Thiepval Ridge was elaborately fortified and the German defenders fought with great determination, while the British co-ordination of infantry and artillery declined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pozières
The Battle of Pozières (23 July – 3 September 1916) took place in northern France around the village of Pozières, during the Battle of the Somme. The costly fighting ended with the British in possession of the plateau north and east of the village, in a position to menace the German bastion of Thiepval from the rear. The Australian official historian Charles Bean wrote that Pozières ridge "is more densely sown with Australian sacrifice than any other place on earth". Prelude The village of Pozières, on the Albert–Bapaume road, lies atop a ridge approximately in the centre of what was the British sector of the Somme battlefield. Close by the village is the highest point on the battlefield. Pozières was an important German defensive position; the fortified village was an outpost to the second defensive trench system, which had become known to the British as the O.G. (Old German) lines. This German second line extended from beyond Mouquet Farm in the north, ran behi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mont Sorrel
The Battle of Mont Sorrel (Battle of Mount Sorrel) was a local operation in World War I by three divisions of the German 4th Army and three divisions of the British Second Army in the Ypres Salient, near Ypres in Belgium, from 2 to 13 June 1916. To divert British resources from the build-up being observed on the Somme, the XIII (Royal Württemberg) Corps and the 117th Infantry Division attacked an arc of high ground defended by the Canadian Corps in Flanders. The German forces captured the heights at Mount Sorrel and Tor Top, before entrenching on the far slope of the ridge. Following a number of attacks and counterattacks, two divisions of the Canadian Corps, supported by the 20th Light Division and Second Army siege and howitzer battery groups, recaptured the majority of their former positions. Background Mount Sorrel Located in the Ypres Salient, east of Ypres, Belgium and from Hill 60, the Battle of Mount Sorrel took place along a ridge between Hooge and Zwart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Festubert
The Battle of Festubert (15–25 May 1915) was an attack by the British army in the Artois region of France on the western front during World War I. The offensive formed part of a series of attacks by the French Tenth Army and the British First Army in the Second Battle of Artois . After the failure of the breakthrough attempt by the First Army in the attack at Aubers Ridge (9 May 1915) tactics of a short hurricane bombardment and an infantry advance with unlimited objectives, were replaced by the French practice of slow and deliberate artillery-fire intended to prepare the way for an infantry attack. A continuous three-day bombardment by the British heavy artillery was planned, to cut wire and demolish German machine-gun posts and infantry strong points. The German defences were to be captured by a continuous attack, by one division from Rue du Bois to Chocolat Menier Corner and by a second division north, which was to capture the German trenches to the left of Festuber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of St Julien
The Second Battle of Ypres was fought from 22 April – 25 May 1915, during the First World War, for control of the tactically-important high ground to the east and the south of the Flemish town of Ypres, in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the previous autumn. The Second Battle of Ypres was the first mass use by Germany of poison gas on the Western Front. Background The German chemist Walther Nernst, who in 1914 was a volunteer driver, proposed to Colonel Max Bauer, the German general staff officer responsible for liaison with scientists, that they could empty the opposing trenches by a surprise attack with tear gas. Observing a field test of this idea, the chemist Fritz Haber instead proposed using heavier-than-air chlorine gas. The German commander Erich von Falkenhayn agreed to try the new weapon but intended to use it in a diversionary attack by the 4th Army. Falkenhayn wanted to use the gas to cover the transfer of Imperial German Army un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravenstafel Ridge (Ypres)
The Second Battle of Ypres was fought from 22 April – 25 May 1915, during the First World War, for control of the tactically-important high ground to the east and the south of the Flemish town of Ypres, in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the previous autumn. The Second Battle of Ypres was the first mass use by Germany of poison gas on the Western Front. Background The German chemist Walther Nernst, who in 1914 was a volunteer driver, proposed to Colonel Max Bauer, the German general staff officer responsible for liaison with scientists, that they could empty the opposing trenches by a surprise attack with tear gas. Observing a field test of this idea, the chemist Fritz Haber instead proposed using heavier-than-air chlorine gas. The German commander Erich von Falkenhayn agreed to try the new weapon but intended to use it in a diversionary attack by the 4th Army. Falkenhayn wanted to use the gas to cover the transfer of Imperial German Army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypres, 1917
The Third Battle of Ypres (; ; ), also known as the Battle of Passchendaele ( ), was a campaign of the First World War, fought by the Allies against the German Empire. The battle took place on the Western Front, from July to November 1917, for control of the ridges south and east of the Belgian city of Ypres in West Flanders, as part of a strategy decided by the Entente at conferences in November 1916 and May 1917. Passchendaele lies on the last ridge east of Ypres, from Roulers (now Roeselare), a junction of the Bruges-(Brugge)-to-Kortrijk railway. The station at Roulers was on the main supply route of the German 4th Army. Once Passchendaele Ridge had been captured, the Allied advance was to continue to a line from Thourout (now Torhout) to Couckelaere (Koekelare). Further operations and a British supporting attack along the Belgian coast from Nieuport ( Nieuwpoort), combined with an amphibious landing ( Operation Hush), were to have reached Bruges and then the Dutch fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Ypres
The Second Battle of Ypres was fought from 22 April – 25 May 1915, during the First World War, for control of the tactically-important high ground to the east and the south of the Flanders, Flemish town of Ypres, in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the previous autumn. The Second Battle of Ypres was the first mass use by Germany of Chemical weapon, poison gas on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front. Background The Germans, German chemist Walther Nernst, who in 1914 was a volunteer driver, proposed to Colonel Max Bauer, the German general staff officer responsible for liaison with scientists, that they could empty the opposing trenches by a surprise attack with tear gas. Observing a field test of this idea, the chemist Fritz Haber instead proposed using heavier-than-air chlorine gas. The German commander Erich von Falkenhayn agreed to try the new weapon but intended to use it in a diversionary attack by the 4th Army (German Empire), 4t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Canadian Scottish Regiment (Princess Mary's)
The Canadian Scottish Regiment (Princess Mary's) is a Primary Reserve infantry regiment of the Canadian Army based on Vancouver Island in British Columbia. The regiment is in Victoria, Nanaimo, and Courtenay, British Columbia. It is part of the 3rd Canadian Division's 39 Canadian Brigade Group, which commands all army reserve units in British Columbia. One of four infantry regiments in British Columbia, the Canadian Scottish is the largest reserve unit in Western Canada. As a light infantry regiment the regiment trains in raids, reconnaissance patrolling, ambushes, amphibious operations and airmobile operations. The unit also trains to meet the realities of the "Three Block War" – warfighting, peacekeeping, and humanitarian support. General The Canadian Scottish Regiment (Princess Mary's) is actively involved in sending troops to various Canadian missions around the world. As of 2012, all members of the regiment who were serving on combat operations with the Canadian Expediti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |