|
1-Butyne
1-Butyne is an organic compound with the formula . It is a terminal alkyne. The compound is a common terminal alkyne substrate in diverse studies of catalysis. It is a colorless combustible gas. In 2017, was produced in the USA. 1-Butyne participates in reactions typical for terminal alkynes, such as alkyne metathesis, hydrogenation, condensation with formaldehyde. Based on its heat of combustion, it is slightly more stable than its isomer 2-butyne. The combustion of 1-Butyne produces propargyl radicals, a pre-cursor to soot and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, as the propargyl radicals can form basic aromatic rings, making butyne's fuel usage a concern for emissions. 1-Butyne is in unsaturated C4 petroleum cuts, and has to be separated out in industrial hydrorefining to make 1-butene, which is used to make low density polyethylene and polybutene. Distillation is impractical due to similar boiling points, so 1-butyne is removed by catalytic hydrogenation. Usually the cata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 118 picometers (for C2H2) is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (132 pm, for C2H4) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Of Combustion
The heating value (or energy value or calorific value) of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it. The ''calorific value'' is the total energy released as heat when a substance undergoes complete combustion with oxygen under standard conditions. The chemical reaction is typically a hydrocarbon or other organic molecule reacting with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water and release heat. It may be expressed with the quantities: * energy/ mole of fuel * energy/mass of fuel * energy/volume of the fuel There are two kinds of enthalpy of combustion, called high(er) and low(er) heat(ing) value, depending on how much the products are allowed to cool and whether compounds like are allowed to condense. The high heat values are conventionally measured with a bomb calorimeter. Low heat values are calculated from high heat value test data. They may also be calculated as the difference be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene. Although butadiene breaks down quickly in the atmosphere, it is nevertheless found in ambient air in urban and suburban areas as a consequence of its constant emission from motor vehicles. The name butadiene can also refer to the isomer, 1,2-butadiene, which is a cumulated diene with structure H2C=C=CH−CH3. This allene has no industrial significance. History In 1863, French chemist E. Caventou isolated butadiene from the pyrolysis of amyl alcohol. This hydrocarbon was identified as butadiene in 1886, after Henry Edward Armstrong isolated it from among the pyrolysis products of petroleum. In 1910, the Russian chemist Sergei Lebedev polymerized butadiene and obtained a material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Gas
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovered its property of producing water when burned; hence its name means 'wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas (formally 2 Pallas), which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired by her when she slew Pallas. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form together a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs). They have similar chemical properties, but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them. More than half the supply of palladium and its congener platinum is used in catalytic converters, which convert as much as 90% of the harmful gases in automobile exhaust (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide) into nontoxic substances (nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor). Palladium is also used in electronics, dentistry, medicine, hydrogen purification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distillation
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective boiling of the mixture and the condensation of the vapors in a still. Distillation can operate over a wide range of pressures from 0.14 bar (e.g., ethylbenzene/ styrene) to nearly 21 bar (e.g., propylene/propane) and is capable of separating feeds with high volumetric flowrates and various components that cover a range of relative volatilities from only 1.17 ( o-xylene/ m-xylene) to 81.2 (water/ ethylene glycol). Distillation provides a convenient and time-tested solution to separate a diversity of chemicals in a continuous manner with high purity. However, distillation has an enormous environmental footprint, resulting in the consumption of approximately 25% of all industrial energy use. The key issue is that distillation operates based on phase changes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybutene
Polybutene is an organic polymer made from a mixture of 1-butene, 2-butene, and isobutylene. Ethylene steam cracker C4s are also used as supplemental feed for polybutene. It is similar to polyisobutylene (PIB), which is produced from essentially pure isobutylene made in a C4 complex of a major refinery. The presence of isomers other than isobutylene can have several effects including: 1) lower reactivity due to steric hindrance at the terminal carbon in, e.g., manufacture of polyisobutenyl succinic anhydride (PIBSA) dispersant manufacture; 2) the molecular weight—viscosity relationships of the two materials may also be somewhat different. Applications Industrial product applications include sealants, adhesives, extenders for putties used for sealing roofs and windows, coatings, polymer modification, tackified polyethylene films, personal care, polybutene emulsions. Hydrogenated polybutenes are used in a wide variety of cosmetic preparations, such as lipstick and lip gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Density Polyethylene
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic made from the monomer ethylene. It was the first grade of polyethylene, produced in 1933 by John C. Swallow and M.W Perrin who were working for Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) using a high pressure process via free radical polymerization. Its manufacture employs the same method today. The EPA estimates 5.7% of LDPE ( resin identification code 4) is recycled in the United States. Despite competition from more modern polymers, LDPE continues to be an important plastic grade. In 2013 the worldwide LDPE market reached a volume of about US$33 billion. Despite its designation with the recycling symbol, it cannot be as commonly recycled as No. 1 (polyethylene terephthalate) or 2 plastics (high-density polyethylene). Properties LDPE is defined by a density range of 917–930 kg/m3. At room temperature it is not reactive, except to strong oxidizers; some solvents cause it to swell. It can withstand temperatures of continuous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
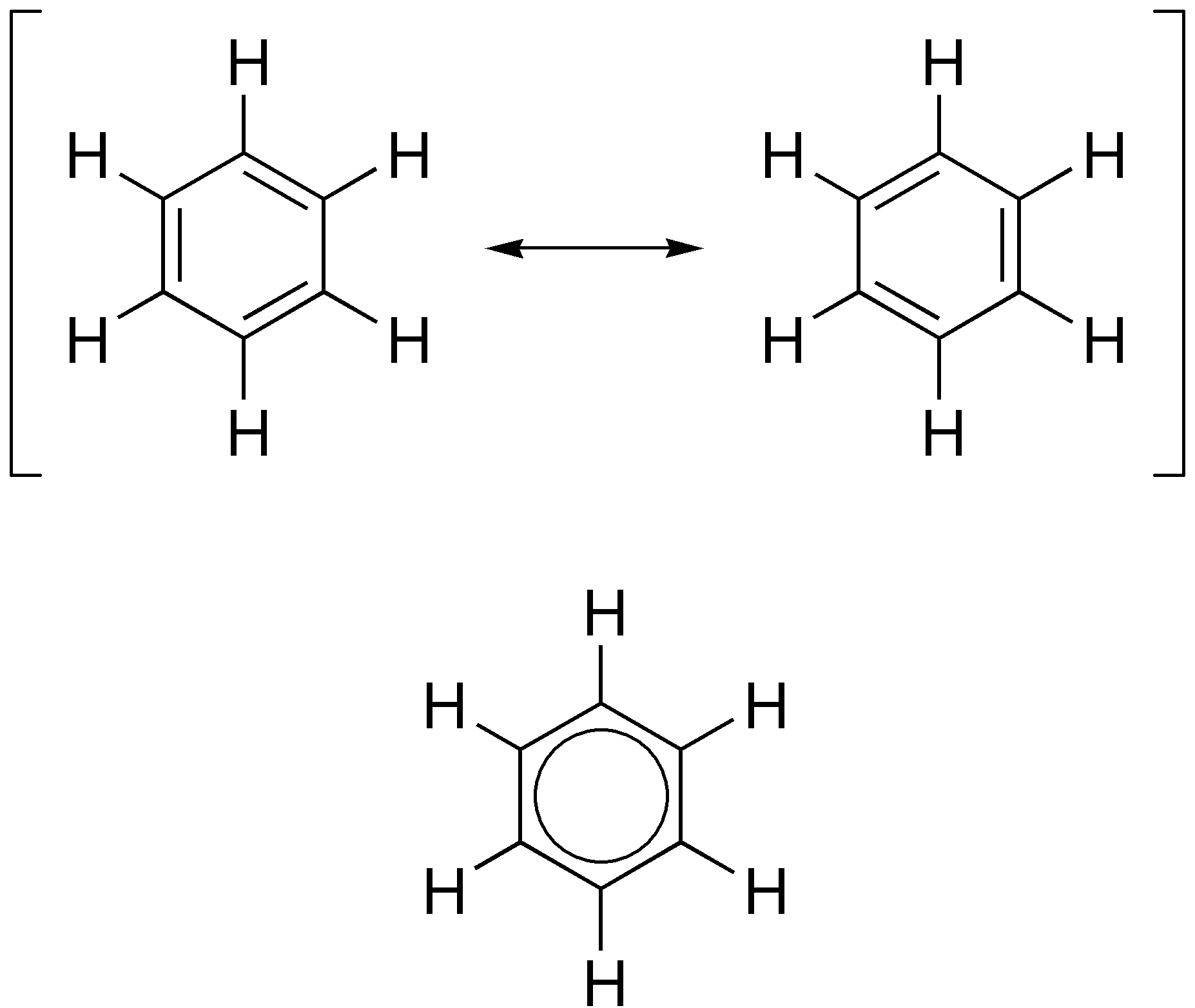
Aromatic Ring
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double- bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). Each bond may be seen as a hybrid of a single bond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-butene
1-Butene (IUPAC name: But-1-ene, also known as 1-butylene) is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas, but easily condensed to give a colorless liquid. It is classified as a linear alpha-olefin (terminal alkene). It is one of the isomers of butene (butylene). It is a precursor to diverse products. Reactions Polymerization of 1-butene gives polybutylene, which is used to make piping for domestic plumbing. Another application is as a comonomer in the production of certain kinds of polyethylene, such as linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE). It has also been used as a precursor to polypropylene resins, 1,2-Epoxybutane, butylene oxide, and butanone. Manufacturing 1-Butene is produced by separation from crude C4 refinery streams and by ethylene dimerization. The former affords a mixture of 1-and 2-butenes, while the latter affords only the terminal alkene. It is distilled to give a very high purity product. An estimated 12 billion kilograms were pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |