|
1,4-Butynediol
1,4-Butynediol is an organic compound that is an alkyne and a diol. It is a colourless, hygroscopic solid that is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a commercially significant compound in its own right and as a precursor to other products. Synthesis 1,4-Butynediol can be produced in the Reppe synthesis, where formaldehyde and acetylene are the reactants: :2 CH2O + HC≡CH → HOCH2CCCH2OH Several patented production methods use copper bismuth catalysts coated on an inert material. The normal temperature range for the reaction is 90 °C up to 150 °C, depending on the pressure used for the reaction which can range from 1 to 20 bar. Applications 1,4-Butynediol is a precursor to 1,4-butanediol and 2-butene-1,4-diol by hydrogenation. It is also used in the manufacture of certain herbicides, textile additives, corrosion inhibitors, plasticizers, synthetic resins, and polyurethanes. It is the major raw material used in the synthesis of vitamin B6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne Derivatives
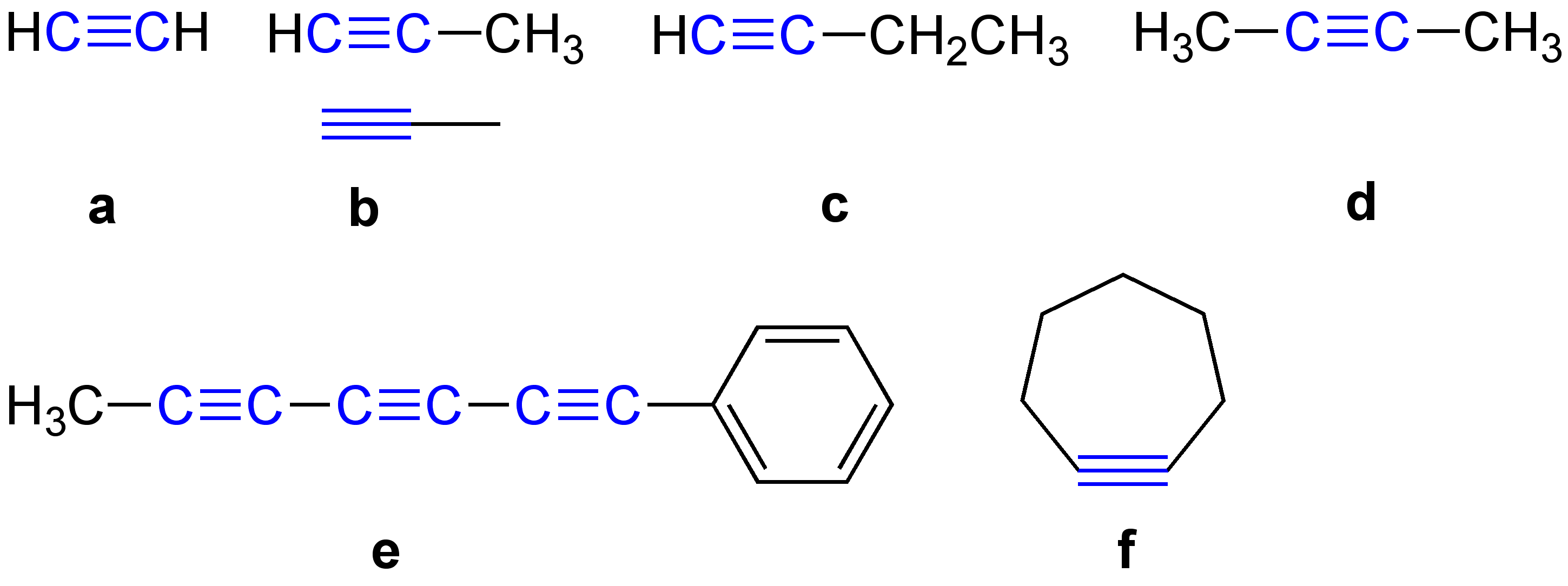
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 118 picometers (for C2H2) is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (132 pm, for C2H4) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 118 picometers (for C2H2) is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (132 pm, for C2H4) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylene
Acetylene (Chemical nomenclature, systematic name: ethyne) is a chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities such as divinyl sulfide and phosphine.Compressed Gas Association (1995Material Safety and Data Sheet – Acetylene As an alkyne, acetylene is Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are Chemical bond, bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. The triple bond in acetylene results in a high energy content that is released when acetylene is burned. Discovery Acetylene was discovered in 1836 by Edmund Davy, who identified it as a "new carburet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucobromic Acid
Mucobromic acid is an organic compound that consists of a dibrominated alkene with aldehyde and carboxylic acid functional groups. It easily tautomerizes to a furanone hemiacetal form. This compound, and the analogous mucochloric acid (CAS #87-56-9), form the group of known mucohalic acids. The bromide appears to behave similarly to the more heavily studied chloride. Synthesis and structure Mucobromic acid can be synthesized by bromination of furfural via an oxidation/decarboxylation process: :C4H4OCHO + 3 Br2 + 3 H2O → C2Br2CHO(CO2H) + CO2 + 8 HBr Mucobromic acid exists as a mixture acyclic and cyclic isomers. The compound can be reduced using sodium borohydride to give the lactone. Hydrolysis under basic conditions of either the chloro or bromo compound involves substitution of the halide adjacent to the acid. The resulting mucoxyhalic acids exist as a mixture of keto–enol tautomerism, keto and enol forms. The reaction occurs via a conjugate addition/elimination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is one of the B vitamins, and is an essential nutrient for humans. The term essential nutrient refers to a group of six chemically similar compounds, i.e., "vitamers", which can be interconverted in biological systems. Its active form, pyridoxal phosphate, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, serves as a coenzyme in more than 140 enzyme reactions in amino acid, glucose, and lipid metabolism. Plants synthesize pyridoxine as a means of protection from the UV-B, UV-B radiation found in sunlight and for the role it plays in the synthesis of chlorophyll. Animals cannot synthesize any of the various forms of the vitamin, and hence must obtain it via diet, either of plants, or of other animals. There is some absorption of the vitamin produced by intestinal bacteria, but this is not sufficient to meet dietary needs. For adult humans, recommendations from various countries' food regulatory agencies are in the range of 1.0 to 2.0 milligrams (mg) per day. These same agencies also recogni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term does not refer to the single type of polymer but a group of polymers. Unlike polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethanes can be produced from a wide range of starting materials resulting in various polymers within the same group. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many List of polyurethane applications, different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, Potting (electronics), electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016. A polyurethane is typically produced by reacting a polymeric isocyanate with a polyol. Since a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces Double bond, double and Triple bond, triple bonds in hydrocarbons. Process Hydrogenation has three components, the Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The redox, reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst. Related or competing reactions The same cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |