|
🮻
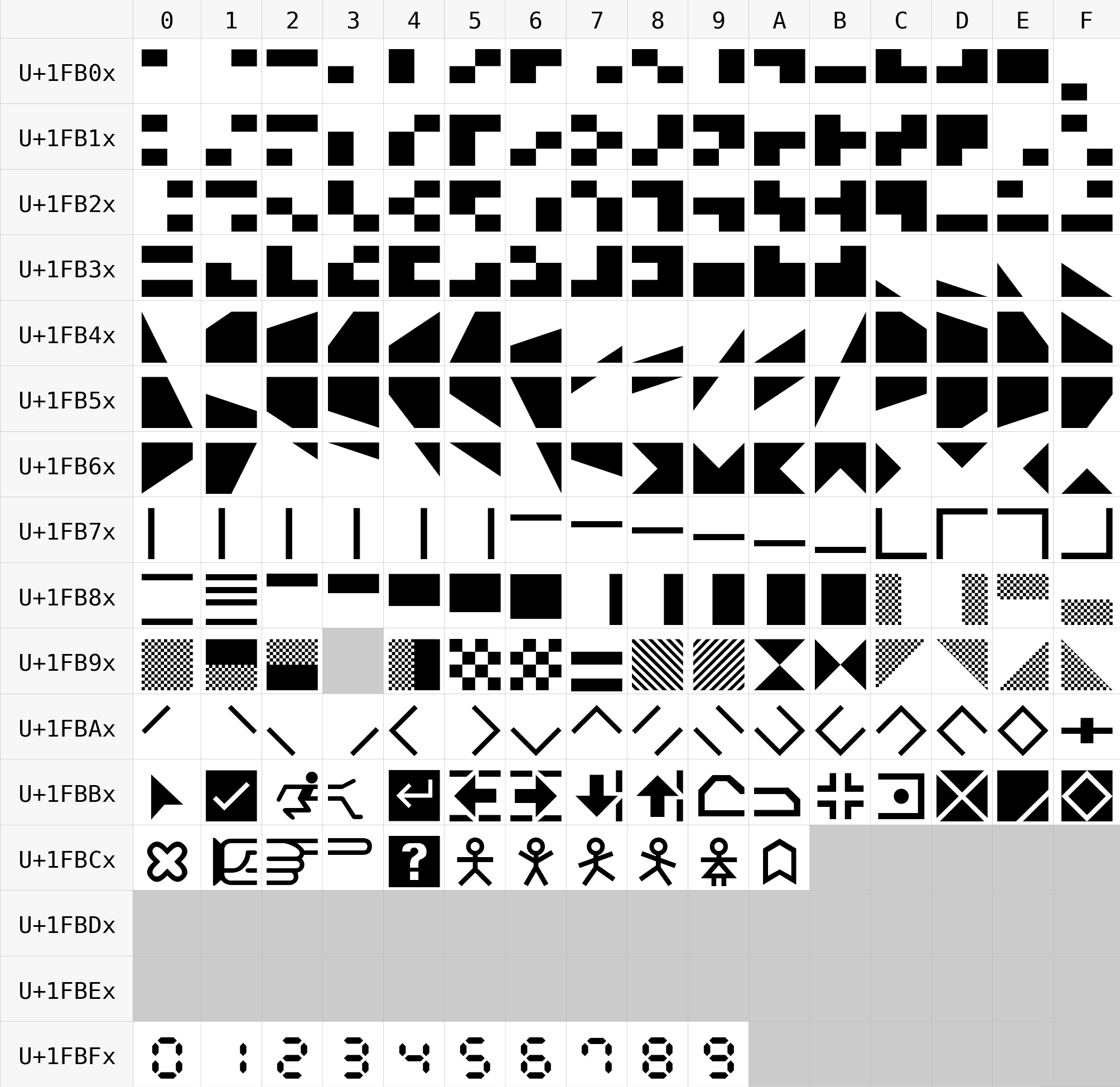
Symbols for Legacy Computing is a Unicode block containing graphic characters that were used for various home computers from the 1970s and 1980s and in teletext broadcasting standards. It includes characters from the Amstrad CPC character set, Amstrad CPC, MSX character set, MSX, Mattel Aquarius, RISC OS character set, RISC OS, MouseText, Atari ST character set, Atari ST, TRS-80 Color Computer, Oric computers, Oric, TI-99/4A, Texas Instruments TI-99/4A, TRS-80 character set, TRS-80, Minitel, Teletext character set, Teletext, ATASCII, PETSCII, ZX80 character set, ZX80, and ZX81 character set, ZX81 character sets. Semigraphics characters are also included in the form of new block-shaped characters, line-drawing characters, and 60 "sextant" characters (semigraphic character made up of six smaller blocks). Additional characters were added to this block in Unicode 16.0 as well. A supplemental block (Symbols for Legacy Computing Supplement) was added with Unicode 16.0. Block The imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MouseText
MouseText is a set of 32 graphical characters designed by Bruce Tognazzini and first implemented in the Apple IIc. They were then retrofitted to the Apple IIe forming part of the Enhanced IIe upgrade. A slightly revised version was then released with the Apple IIGS. By including box-drawing characters, MouseText made it possible to display simple text user interfaces resembling the Macintosh graphical user interface. Since the Apples lacked the ability to display user-defined characters in text mode, all GUI-like displays beyond crude ASCII art approximations had to use the slower and more memory-hungry graphical mode before MouseText was available. MouseText resulted in an eightfold increase in display speed for mouse applications, bringing such text-based applications as word processors up to the same speed as the original Macintosh. Word processors running on the two computers would not be confused with one another, however, as the mouse under MouseText would move in discrete j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Script (Unicode)
In Unicode, a script is a collection of Letter (alphabet), letters and other written signs used to represent textual information in one or more writing systems. Some scripts support only one writing system and Written language, language, for example, Armenian language, Armenian. Other scripts support many different writing systems; for example, the Latin script in Unicode, Latin script supports English alphabet, English, French alphabet, French, German alphabet, German, Italian alphabet, Italian, Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, Latin alphabet, Latin itself, and several other languages. Some languages make use of multiple alternate writing systems and thus also use several scripts; for example, in Turkish language, Turkish, the Ottoman Turkish alphabet, Arabic script was used before the 20th century but transitioned to Latin in the early part of the 20th century. More or less complementary to scripts are Unicode symbols, symbols and Unicode control characters. The unified Combi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PETSCII
PETSCII (PET Standard Code of Information Interchange), also known as CBM ASCII, is the character set used in Commodore Business Machines' 8-bit home computers. This character set was first used by the PET from 1977, and was subsequently used by the CBM-II, VIC-20, Commodore 64, Commodore 16, Commodore 116, Plus/4, and Commodore 128. However, the Amiga personal computer family instead uses standard ISO/IEC 8859-1. History The character set was largely designed by Leonard Tramiel (the son of Commodore CEO Jack Tramiel) and PET designer Chuck Peddle. The graphic characters of PETSCII were one of the extensions Commodore specified for Commodore BASIC when laying out desired changes to Microsoft's existing 6502 BASIC to Microsoft's Ric Weiland in 1977.mirror The VIC-20 used the same pixel-for-pixel font as the PET, although the characters appeared wider due to the VIC's 22-column screen. The Commodore 64, however, used a slightly re-designed, heavy upper-case font, es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Shapes (Unicode Block)
Geometric Shapes is a Unicode block of 96 symbols at code point range U+25A0–25FF. Font coverage Font sets like Code2000 and the DejaVu fonts, DejaVu family include coverage for each of the glyphs in the Geometric Shapes range. GNU Unifont, Unifont also contains all the glyphs. Among the fonts in widespread use, full implementation is provided by Segoe UI Symbol and significant partial implementation of this range is provided by Arial Unicode MS and Lucida Sans Unicode, which include coverage for 83% (80 out of 96) and 82% (79 out of 96) of the symbols, respectively. Block Emoji The Geometric Shapes block contains eight emoji: U+25AA–U+25AB, U+25B6, U+25C0 and U+25FB–U+25FE. The block has sixteen Variant form (Unicode), standardized variants defined to specify emoji-style (U+FE0F VS16) or text presentation (U+FE0E VS15) for the eight emoji. History The following Unicode-related documents record the purpose and process of defining specific characters in the Geometri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block Elements
Block Elements is a Unicode block containing square block symbols of various fill and shading. Used along with block elements are box-drawing characters, shade characters, and terminal graphic characters. These can be used for filling regions of the screen and portraying drop shadows. Its block name in Unicode 1.0 was Blocks. Character table Font coverage Font sets like Code2000 and the DejaVu family include coverage for each of the glyphs in the Block Elements range. Unifont also contains all the glyphs. Among the fonts in widespread use, full implementation is provided by Segoe UI Symbol. The glyphs in Block Elements each share the same character width in most supported fonts, allowing them to be used graphically in row and column arrangements. However, the block does not contain a space character of its own and ASCII space may or may not render at the same width as Block Elements glyphs, as those characters are intended to be used exclusively for monospaced fonts. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Drawing
Box Drawing is a Unicode block containing characters for compatibility with legacy graphics standards that contained characters for making bordered charts and tables, i.e. box-drawing characters. Its block name in Unicode 1.0 was Form and Chart Components. Block See also * Box-drawing characters * Code page 437 * Dingbat * Semigraphics (or pseudographics) * other Unicode blocks ** Block Elements ** Geometric Shapes ** Halfwidth and Fullwidth Forms ** Symbols for Legacy Computing Symbols for Legacy Computing is a Unicode block containing graphic characters that were used for various home computers from the 1970s and 1980s and in teletext broadcasting standards. It includes characters from the Amstrad CPC, MSX, Mattel Aqua ... References {{Unicode navigation Unicode blocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingbat
In typography, a dingbat (sometimes more formally known as a printer's ornament or printer's character) is an ornament, specifically, a glyph used in typesetting, often employed to create box frames (similar to box-drawing characters), or as a dinkus (section divider). Some of the dingbat symbols have been used as signature marks or used in bookbinding to order sections. In the computer industry, a dingbat font or pi font is a computer font that has symbols and shapes located at the code points normally designated for alphabetical or numeric characters. This practice was necessitated by the limited number of code points available in 20th century operating systems. Modern computer fonts containing dingbats are based on Unicode encoding, which has unique code points for dingbat glyphs. Examples Examples of characters included in Unicode ( ITC Zapf Dingbats series 100 and others): Dingbats Unicode block Unicode provides code points for many commonly used dingbats, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box-drawing Characters
Box-drawing characters, also known as line-drawing characters, are a form of semigraphics widely used in text user interfaces to draw various geometric frames and boxes. These characters are characterized by being designed to be connected horizontally and/or vertically with adjacent characters, which requires proper alignment. Box-drawing characters therefore typically only work well with monospaced fonts. In graphical user interfaces, these characters are much less useful as it is simpler to draw lines and rectangles directly with graphical APIs. However, they are still useful for command-line interfaces and plaintext Comment (computer programming), comments within source code. Some recent embedded systems also use proprietary character sets, usually extensions to ISO 8859 character sets, which include box-drawing characters or other special symbols. Other types of box-drawing characters are block elements, shade characters, and terminal graphic characters; these can be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 Coded character sets is a standardization subcommittee of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), that develops and facilitates standards within the field of coded character sets. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 is the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC), located in Japan. SC 2 is responsible for the development of the Universal Coded Character Set standard (ISO/IEC 10646), which is the international standard corresponding to the Unicode Standard. History The subcommittee was established in 1987 under ISO/TC 97 as ISO/TC 97/SC 2, originally with the title "Character Sets and Information Coding", with the area of work being, "the standardization of bit and byte coded representation of information for interchange including among others, sets of graphic characters, of control functions, of picture elements and audi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee For Information Technology Standards
The InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS), (pronounced "insights"), is an ANSI-accredited standards development organization composed of Information technology developers. It was formerly known as the X3 and NCITS. INCITS is the central U.S. forum dedicated to creating technology standards. INCITS is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and is affiliated with the Information Technology Industry Council, a global policy advocacy organization that represents U.S. and global innovation companies. INCITS coordinates technical standards activity between ANSI in the US and joint ISO The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Me .../ IEC committees worldwide. This provides a mechanism to create standards that will be implemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Character (computing), characters and 168 script (Unicode), scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts. Unicode has largely supplanted the previous environment of a myriad of incompatible character sets used within different locales and on different computer architectures. The entire repertoire of these sets, plus many additional characters, were merged into the single Unicode set. Unicode is used to encode the vast majority of text on the Internet, including most web pages, and relevant Unicode support has become a common consideration in contemporary software development. Unicode is ultimately capable of encoding more than 1.1 million characters. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbols For Legacy Computing Unicode Block
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise different concepts and experiences. All communication is achieved through the use of symbols: for example, a red octagon is a common symbol for " STOP"; on maps, blue lines often represent rivers; and a red rose often symbolizes love and compassion. Numerals are symbols for numbers; letters of an alphabet may be symbols for certain phonemes; and personal names are symbols representing individuals. The academic study of symbols is called semiotics. In the arts, symbolism is the use of a concrete element to represent a more abstract idea. In cartography, an organized collection of symbols forms a legend for a map. Etymology The word ''symbol'' derives from the late Middle French masculine noun , which appeared around 1380 in a theological sense signifying a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |