|
įø¤
įø¤ (Lower case, minuscule: įø„) is a letter of the Latin alphabet, formed from H with the addition of a dot (diacritic), dot diacritic. Usage įø¤ is used to represent the voiceless pharyngeal fricative () in Heth#Arabic_.E1.B8.A5.C4.81.CA.BE, Arabic, some Syriac language, Syriac languages (such as Turoyo and Sureth), Egyptian language, Ancient Egyptian, and traditional Hebrew (whereas Modern Israeli Hebrew, Hebrew-speaking Israelis and Ashkenazi Hebrew, Ashkenazi Jews (though not strictly) have usually replaced the pronunciation of įø¤ in the respective eighth letter of the Semitic abjads, įø¤et with a voiceless uvular fricative ()). This sound also exists in the Tigrinya language, Tigrinya and Somali languages, in Modern South Arabian languages and in smaller North East African languages. Asturian įø¤ is used in Asturian language, Asturian to represent a voiceless glottal fricative (/h/) sound in Asturian words such as įø„ou and įø„ue, as well as some place names in the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
įø¤et
Heth, sometimes written Chet or įø¤et, is the eighth Letter (alphabet), letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician ''įø„Ät'' š¤, Hebrew alphabet, Hebrew ''įø„Ät'' , Aramaic alphabet, Aramaic ''įø„Äį¹Æ'' š”, Syriac alphabet, Syriac ''įø„Äį¹Æ'' Ü, and Arabic alphabet, Arabic ''įø„ÄŹ¾'' . It is also related to the Ancient North Arabian šŖāāā, Ancient South Arabian script, South Arabian , and GeŹ½ez script, Ge'ez . Heth originally represented a voiceless fricative, either voiceless pharyngeal fricative, pharyngeal , or voiceless velar fricative, velar . In Arabic, two corresponding letters were created for both phonemic sounds: unmodified ' represents , while ' represents . The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek alphabet, Greek eta , Etruscan alphabet, Etruscan , Latin alphabet, Latin H, and Cyrillic script, Cyrillic I (Cyrillic), Š. While H is a consonant in the Latin alphabet, the Greek and Cyrillic equivalents represent v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heth
Heth, sometimes written Chet or įø¤et, is the eighth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician ''įø„Ät'' š¤, Hebrew ''įø„Ät'' , Aramaic ''įø„Äį¹Æ'' š”, Syriac ''įø„Äį¹Æ'' Ü, and Arabic ''įø„ÄŹ¾'' . It is also related to the Ancient North Arabian šŖāāā, South Arabian , and Ge'ez . Heth originally represented a voiceless fricative, either pharyngeal , or velar . In Arabic, two corresponding letters were created for both phonemic sounds: unmodified ' represents , while ' represents . The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek eta , Etruscan , Latin H, and Cyrillic Š. While H is a consonant in the Latin alphabet, the Greek and Cyrillic equivalents represent vowel sounds, though the letter was originally a consonant in Greek and this usage later evolved into the rough breathing character. The Phoenician letter also gave rise to the archaic Greek letter '' heta'', as well as a variant of Cyrillic letter I, short I. The Arabic letter ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern South Arabian Languages
The Modern South Arabian languages, also known as Eastern South Semitic languages, are a group of endangered languages spoken by small populations inhabiting the Arabian Peninsula, in Yemen and Oman, and Socotra Island. Together with the Ethiosemitic and Sayhadic languages, the Western branch, they form the South Semitic sub-branch of the Afroasiatic language family's Semitic branch. Mehri and Hobyot are spoken in both Yemen and Oman. Soqotri is only spoken in the Yemeni archipelago of Socotra, and the Harsusi, Bathari, and Shehri languages are only spoken in Oman. Classification In his glottochronology-based classification, Alexander Militarev presents the Modern South Arabian languages as a South Semitic branch opposed to a North Semitic branch that includes all the other Semitic languages. They are no longer considered to be descendants of the Old South Arabian language, as was once thought, but instead "nephews". Languages * Mehri: It is the largest Moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
įø¤ontoria
įø¤ontoria () is one of 28 parishes (administrative divisions) in Llanes, a municipality within the province and autonomous community of Asturias, in northern Spain Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur .... Villages * Cardosu * įø¤ontoria * Villaįø„ormes References Parishes in Llanes {{asturias-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic Abjads
An abjad ( or abgad) is a writing system in which only consonants are represented, leaving the vowel sounds to be inferred by the reader. This contrasts with alphabets, which provide graphemes for both consonants and vowels. The term was introduced in 1990 by Peter T. Daniels. Other terms for the same concept include partial phonemic script, segmentally linear defective phonographic script, consonantary, consonant writing, and consonantal alphabet. Impure abjads represent vowels with either optional diacritics, a limited number of distinct vowel glyphs, or both. Etymology The name ''abjad'' is based on the Arabic alphabet's first (in its original order) four corresponding to ''a'', ''b'', ''j'', and to replace the more common terms "consonantary" and "consonantal alphabet" in describing the family of scripts classified as " West Semitic". It is similar to other Semitic languages such as Phoenician, Hebrew and Semitic proto-alphabets: specifically, aleph, bet, gimel, dalet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Pharyngeal Fricative
The voiceless pharyngeal fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some Speech communication, spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is an h with stroke, h-bar, , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is X\. In the transcription of Arabic, Berber (and other Afro-Asiatic languages) as well as a few other scripts, it is often written , . Typically characterized as fricative in the upper pharynx, it is often characterized as a whispering, whispered . Features Features of the voiceless pharyngeal fricative: Occurrence This sound is the most commonly cited realization of the Semitic letter hÄth, which occurs in all dialects of Arabic language, Arabic, Syriac language, Classical Syriac, Western Neo-Aramaic, Central Neo-Aramaic, Ge'ez language, Ge'ez, Tigre language, Tigre, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya as well as Biblical Hebrew, Biblical, Mishnaic Hebrew, Mishnaic and Mizrahi Hebrew, Mizrahi Hebrew language, Hebrew. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villaįø„ormes
Villaįø„ormes () (formerly, Villahormes, in Spanish language, until 2005 when it changed its name to the Asturian one) is a village in the parish of įø¤ontoria in Llanes municipality, in eastern Asturias, Spain. Its railway station has linked the city of Llanes with Ribadesella Ribadesella () is a small municipality in the Autonomous Community of the Principality of Asturias, Spain. Known for its location on the Cantabrian Sea, at the outlet of the River Sella, Ribadesella is a town that forms part of the Picos de Eur ... since 1905. Neighboring villages include Cardosu, Naves and the capital of the parish, įø¤ontoria. Geography of Asturias {{Asturias-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asturian Language
Asturian (; )Art. 1 de lLey 1/1998, de 23 de marzo, de uso y promociĆ³n del bable/asturiano [Law 1/93, of March 23, on the Use and Promotion of the Asturian Language/nowiki>] is a West Iberian languages, West Iberian Romance languages, Romance language spoken in the Principality of Asturias, Spain. Asturian is part of a wider linguistic group, the Asturleonese languages. The number of speakers is estimated at 100,000 (native) and 450,000 (second language). The dialects of the Astur-Leonese language family are traditionally classified in three groups: Western, Central, and Eastern. For historical and demographic reasons, the Standard language, standard is based on #Dialects, Central Asturian. Asturian has a distinct grammar, dictionary, and orthography. It is regulated by the Academy of the Asturian Language. Although it is not an official language of Spain, it is protected under the Statute of Autonomy of Asturias and is an elective language in schools. For much of its history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Israeli Hebrew
Modern Hebrew (, or ), also known as Israeli Hebrew or simply Hebrew, is the standard form of the Hebrew language spoken today. It is the only surviving Canaanite language, as well as one of the oldest languages still spoken as a native language, on account of Hebrew being attested since the 2nd millennium BC. It uses the Hebrew Alphabet, an abjad script written from right-to-left. The current standard was codified as part of the revival of Hebrew in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and now serves as the sole official and national language of the State of Israel, where it is predominantly spoken by over 9 million people. Thus, Modern Hebrew is near universally regarded as the most successful instance of language revitalization in history. A Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family, Hebrew was spoken since antiquity as the vernacular of the Jews until around the 3rd century BCE, when it was supplanted by a western dialect of the Aramai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
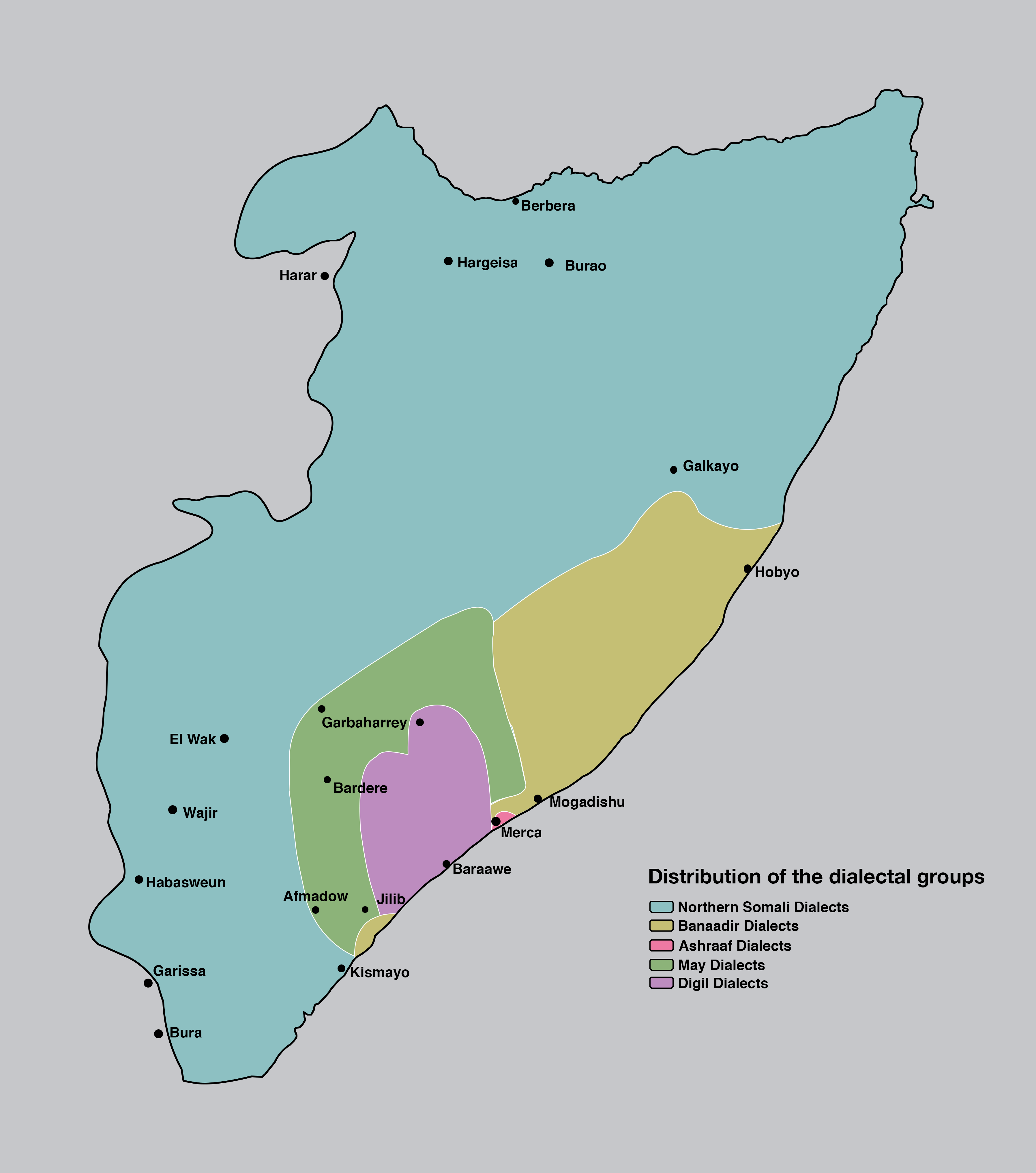
Somali Language
Somali is an Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch, primarily spoken by the Somalis, Somali people, native to Greater Somalia. It is an official language in Somalia, Somaliland, and Ethiopia; one of the two national languages in Djibouti; and a recognised minority language in Kenya. Somali is officially written in the Latin script (Somali Latin alphabet), with the Arabic script (Wadaad's writing) and several local scripts (Osmanya script, Osmanya, Kaddare script, Kaddare and Gadabuursi Somali Script, Borama scripts) being informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134ā156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic languages, Lowland East Cushitic in addition to Afar language, Afar and Saho language, Saho. Somali is the bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Alphabet Of Sanskrit Transliteration
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the 19th century from suggestions by Charles Trevelyan, William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars. Usage Scholars commonly use IAST in publications that cite textual material in Sanskrit, PÄįø·i and other classical Indian languages. IAST is also used for major e-text repositories such as SARIT, Muktabodha, GRETIL, and sanskritdocuments.org. The IAST scheme represents more than a centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turoyo
Turoyo (), also referred to as Surayt (), or modern Suryoyo (), is a Central Neo-Aramaic language traditionally spoken by the Syriac Christian community in the Tur Abdin region located in southeastern Turkey and in northeastern Syria. Turoyo speakers are mostly adherents of the Syriac Orthodox Church. Originally spoken and exclusive to Tur Abdin, it is now majority spoken in the diaspora. It is classified as a vulnerable language. Most speakers use the Classical Syriac language for literature and worship. Its closest relatives are Mlaįø„sĆ“ and western varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic like Suret. Turoyo is not mutually intelligible with Western Neo-Aramaic, having been separated for over a thousand years. Etymology Term comes from the word ', meaning 'mountain', thus designating a specific Neo-Aramaic language of the mountain region of Tur Abdin in southeastern part of modern Turkey (hence ''Turabdinian'' Aramaic). Other, more general names for the language are ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |