|
ą¤°
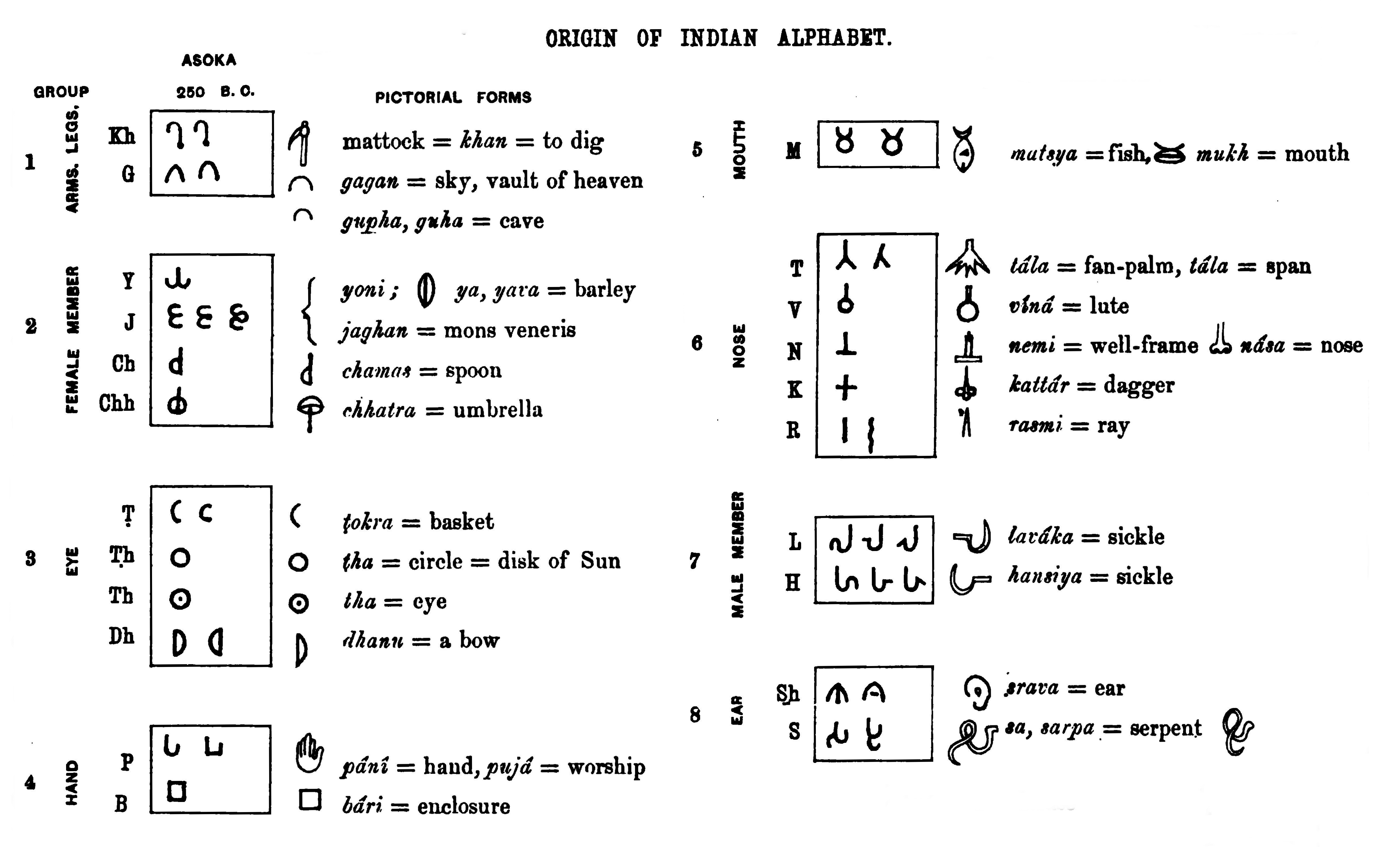
Ra is a consonant of Indic abugidas. In modern Indic scripts, Ra is derived from the early "Ashoka" Brahmi letter after having gone through the Gupta script, Gupta letter . Most Indic scripts have differing forms of Ra when used in combination with other consonants, including subjoined and repha forms. Some of these are encoded in computer text as separate characters, while others are generated dynamically using conjunct shaping with a virama. Äryabhaį¹a numeration Aryabhata used Devanagari letters for numbers, very similar to the Greek numerals, even after the invention of Indian numerals. The values of the different forms of ą¤° are: *ą¤° = 40 (ą„Ŗą„¦) *ą¤°ą¤æ = 4,000 (ą„Ŗ ą„¦ą„¦ą„¦) *ą¤°ą„ = 400,000 (ą„Ŗ ą„¦ą„¦ ą„¦ą„¦ą„¦) *ą¤°ą„ = 40,000,000 (ą„Ŗ ą„¦ą„¦ ą„¦ą„¦ ą„¦ą„¦ą„¦) *ą¤°ą„¢ = 4 (ą„ŖĆą„§ą„¦ą„Æ) *ą¤°ą„ = 4 (ą„ŖĆą„§ą„¦ą„§ą„§) *ą¤°ą„ = 4 (ą„ŖĆą„§ą„¦ą„§ą„©) *ą¤°ą„ = 4 (ą„ŖĆą„§ą„¦ą„§ą„«) *ą¤°ą„ = 4 (ą„ŖĆą„§ą„¦ą„§ą„) Historic Ra There are three differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brahmi Script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''BrÄhmÄ«'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the AÅokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or 'Lat', 'Southern AÅokan', 'Indian Pali', 'Mauryan', and so on. The application to it of the name Brahmi [''sc. lipi''], which stands at the head of the Buddhist and Jaina script lists, was first suggested by T[errien] de Lacouperie, who noted that in the Chinese Buddhist encyclopedia ''Fa yiian chu lin'' the scripts whose names corresponded to the Brahmi and Kharosthi of the ''Lalitavistara'' are described as written from left to right and from right to left, respectively. He therefore suggested that the name Brahmi should refer to the left-to-right 'Indo-Pali' script of the AÅokan pillar inscriptions, and Kharosthi to the right-to-left 'Bactro-Pali' script of the rock inscriptions from the northwest." that appeared as a fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brahmi
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO: ''BrÄhmÄ«'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the AÅokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or 'Lat', 'Southern AÅokan', 'Indian Pali', 'Mauryan', and so on. The application to it of the name Brahmi 'sc. lipi'' which stands at the head of the Buddhist and Jaina script lists, was first suggested by T rriende Lacouperie, who noted that in the Chinese Buddhist encyclopedia ''Fa yiian chu lin'' the scripts whose names corresponded to the Brahmi and Kharosthi of the ''Lalitavistara'' are described as written from left to right and from right to left, respectively. He therefore suggested that the name Brahmi should refer to the left-to-right 'Indo-Pali' script of the AÅokan pillar inscriptions, and Kharosthi to the right-to-left 'Bactro-Pali' script of the rock inscriptions from the northwest." that appeared as a fully developed script ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Indic Abugidas
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient India and are used by various languages in several language families in South Asia, South, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia: Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan, Dravidian languages, Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Austroasiatic languages, Austroasiatic, Austronesian languages, Austronesian, and Tai languages, Tai. They were also the source of the Collation, dictionary order (''gojÅ«on'') of Japanese language, Japanese ''kana''. History Brahmic scripts descended from the BrÄhmÄ« script, Brahmi script. Brahmi is clearly attested from the 3rd century BCE during the reign of Ashoka, who used the script Edicts of Ashoka, for imperial edicts. Northern Brahmi gave rise to the Gupta script during the Gupta period, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Virama
Virama ( ą„, ) is a Sanskrit phonological concept to suppress the inherent vowel that otherwise occurs with every consonant letter, commonly used as a generic term for a codepoint in Unicode, representing either # halanta, hasanta or explicit virÄma, a diacritic in many Brahmic scripts, including the Devanagari and Bengali scripts, or # saį¹yuktÄkį¹£ara (Sanskrit: ą¤øą¤ą¤Æą„ą¤ą„ą¤¤ą¤¾ą¤ą„ą¤·ą¤°) or implicit virama, a conjunct consonant or ligature. Unicode schemes of scripts writing Mainland Southeast Asia languages, such as that of Burmese script and of Tibetan script, generally do not group the two functions together. Names The name is Sanskrit for "cessation, termination, end". As a Sanskrit word, it is used in place of several language-specific terms, such as: Usage In Devanagari and many other Indic scripts, a virama is used to cancel the inherent vowel of a consonant letter and represent a consonant without a vowel, a "dead" consonant. For example, in Dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aryabhata
Aryabhata ( ISO: ) or Aryabhata I (476ā550 CE) was the first of the major mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. His works include the '' Äryabhaį¹Ä«ya'' (which mentions that in 3600 '' Kali Yuga'', 499 CE, he was 23 years old) and the ''Arya- siddhanta''. For his explicit mention of the relativity of motion, he also qualifies as a major early physicist. Biography Name While there is a tendency to misspell his name as "Aryabhatta" by analogy with other names having the " bhatta" suffix, his name is properly spelled Aryabhata: every astronomical text spells his name thus, including Brahmagupta's references to him "in more than a hundred places by name". Furthermore, in most instances "Aryabhatta" would not fit the metre either. Time and place of birth Aryabhata mentions in the ''Aryabhatiya'' that he was 23 years old 3,600 years into the '' Kali Yuga'', but this is not to mean that the text was composed at that ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bengali Language
Bengali, also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Bangla (, , ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is native to the Bengal region (Bangladesh, India's West Bengal and Tripura) of South Asia. With over 242 million native speakers and another 43 million as second language speakers as of 2025, Bengali is the List of languages by number of native speakers, sixth most spoken native language and the List of languages by total number of speakers, seventh most spoken language by the total number of speakers in the world. Bengali is the Official language, official, National language, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh, with 98% of Bangladeshis using Bengali as their first language. It is the second-most widely spoken scheduled languages of India, language in India. It is the official language of the Indian states of West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gupta Ashoka R
Gupta () is a common surname of Indian origin, meaning "guardian" or "protector". Origins and distribution The name is based on the Sanskrit word ą¤ą„ą¤Ŗą„ą¤¤ą„ ''goptį¹'', which means "guardian" or "protector". According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by several different communities in northern and eastern India at different times. The RÄmpÄl plate of the Chandra dynasty ruler Srichandra mentions a line of Brahmins who had Gupta as their surname. In Bengal region, the surname is found among Baidyas (mainly) as well as Kayasthas. According to Tej Ram Sharma, the name '' Sri Gupta'', "Sri" serves as an honorific title, similar to its usage for other Gupta emperors mentioned in inscriptions. If the first ruler's name had indeed been ''Sri Gupta'', it would likely have been recorded as ''Sri Sri Gupta'', as seen in the Deo-Barnark inscription of Jivitagupta II, where the name '' Srimati'' appears in a similar format. Therefore, if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tocharian Letter Raa
Tocharian may refer to: * Tocharians, an ancient people who inhabited the Tarim Basin in Central Asia * Tocharian clothing, clothing worn by those people * Tocharian languages The Tocharian (sometimes ''Tokharian'') languages ( ; ), also known as the ''ArÅi-KuÄi'', Agnean-Kuchean or Kuchean-Agnean languages, are an extinct branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken by inhabitants o ..., two (or perhaps three) Indo-European languages spoken by those people * Tocharian script, the script used to write the Tocharian languages See also * Tushar (other) {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |