|
╬┤ Trianguli
Delta Trianguli, also named Deltoton, is a spectroscopic binary star system approximately away in the constellation of Triangulum. The primary star is a Yellow dwarf star, yellow dwarf, while the secondary star is thought to be an orange dwarf. It has an apparent magnitude of +4.87 and forms an optical (line-of-sight) triple with Gamma Trianguli and 7 Trianguli. Naming Delta Trianguli, Romanization of Greek, Latinized from ╬┤ Trianguli and abbreviated Delta Tri, is the star's Bayer designation. Deltoton was an ancient Greek name of the constellation Triangulum, so named because the capital Greek letter Delta (letter), delta is shaped like a triangle. The IAU Working Group on Star Names approved the name Deltoton for this star on 17 June 2025 and it is now so entered in the IAU Catalog of Star Names. The name was chosen for this star because of the "obvious pun" in that its Bayer designation is Delta. In Chinese astronomy, Chinese, (), meaning ''Tian Daj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Andromedae
Gamma Andromedae is a multiple star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It is the third-brightest star in the constellation, after Alpheratz and Mirach. Its identifier is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from ╬│ Andromedae, and is abbreviated Gam1 And or ╬│1 And, respectively. The system has the proper name Almach, pronounced . Based on parallax measurements, it is estimated to be about 390 light-years distant. The system is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of . Observation In 1778, German physicist Johann Tobias Mayer discovered that ╬│ Andromedae is a double star. When examined in a small telescope, it appears to be a bright, golden-yellow star next to a dimmer, indigo-blue star, separated by approximately 10 arcseconds. The pair is often considered by stargazers to be a beautiful double star with a striking contrast of color. The brighter member, ╬│1 Andromedae, is the primary of the system, and is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its modern redefinition in 2012. The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec. One au is approximately equivalent to 499 light-seconds. History of symbol usage A variety of unit symbols and abbreviations have been in use for the astronomical unit. In a 1976 resolution, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) had used the symbol ''A'' to denote a length equal to the astronomical unit. In the astronomical literature, the symbol AU is common. In 2006, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) had recommended ua as the symbol for the unit, from the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weight function, weighted relative position (vector), position of the distributed mass sums to zero. For a rigid body containing its center of mass, this is the point to which a force may be applied to cause a linear acceleration without an angular acceleration. Calculations in mechanics are often simplified when formulated with respect to the center of mass. It is a hypothetical point where the entire mass of an object may be assumed to be concentrated to visualise its motion. In other words, the center of mass is the particle equivalent of a given object for application of Newton's laws of motion. In the case of a single rigid body, the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body, and if the body has uniform density, it will be located at the centroid. The center of mass may be located outside the Phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the Continuum (spectrum), rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the MorganŌĆōKeenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the cool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or dwarf stars, and positions of stars on and off the band are believed to indicate their physical properties, as well as their progress through several types of star life-cycles. These are the most numerous true stars in the universe and include the Sun. Color-magnitude plots are known as HertzsprungŌĆōRussell diagrams after Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. After condensation and ignition of a star, it generates thermal energy in its dense stellar core, core region through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. During this stage of the star's lifetime, it is located on the main sequence at a position determined primarily by its mass but also based on its chemical composition and age. The cores of main-sequence stars are in hydros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Star Names
Chinese star names ( Chinese: , ''x─½ng m├Łng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''x─½ng xi├╣'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''x─½ng gu─ün''). The ecliptic is divided into four sectors that are associated with the Four Symbols, guardians in Chinese mythology, and further into 28 mansions. Stars around the north celestial pole are grouped into three enclosures (, ''yu├Īn''). The system of 283 asterisms under the Three Enclosures and Twenty-Eight Mansions was established by Chen Zhuo of the Three Kingdoms period, who synthesized ancient constellations and the asterisms created by early astronomers Shi Shen, Gan De and Wuxian. Since the Han and Jin dynasties, stars have been given reference numbers within their asterisms in a system similar to the Bayer or Flamsteed designations, so that individual stars can be identified. For example, Deneb (╬▒ Cyg) is referred to as (''Ti─ün J─½n S├ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Trianguli
Beta Trianguli (Beta Tri, ╬▓ Trianguli, ╬▓ Tri) is the Bayer designation for a binary star system in the constellation Triangulum, located about 127 light years from Earth. Although it is only a third-magnitude star, it is the brightest star in the constellation Triangulum. This is a double-lined spectroscopic binary star system with an orbital period of 31.39 days and an eccentricity of 0.53. The members are separated by a distance of . The primary and secondary components have stellar classifications of A8III and A3III respectively, indicating that they evolved away from the main sequence and are now giant stars. Component A is 2.6 times more massive than the Sun, but expanded to the Sun's radius and irradiates 60 times more than the Sun. Component B is somewhat smaller and less luminous, being 2.25 times more massive, times larger and 30 times brighter than the Sun. The system has an age around 400 million years, less than 10% that of the Solar S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
56 Andromedae
56 Andromedae, abbreviated 56 And, is a probable binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. ''56 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.69, which is just bright enough to be dimly visible to the naked eye under good seeing conditions. The distance to this system can be ascertained from its annual parallax shift, measured at with the Gaia space observatory, which yields a separation of 330 light years. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +62 km/s and is traversing the celestial sphere at a relatively high rate of per year. This pair is positioned near the line of sight to the open cluster NGC 752, located away. The brighter primary is an aging giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III, having exhausted the hydrogen at its core and evolved off the main sequence. It is a red clump giant, having undergone helium flash and is presently ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau Andromedae
Tau Andromedae is a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. Its Bayer designation is Latinized from Žä Andromedae, and abbreviated Tau And or Žä And, respectively. The star has an apparent visual magnitude of +4.94, which is bright enough to be viewed from dark suburban skies. From parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission, the distance to this star can be estimated as roughly from Earth. The brightness of this star is diminished by 0.24 in magnitude due to extinction caused by intervening gas and dust. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of ŌłÆ14 km/s. The spectrum of this star matches a stellar classification of B5 III, with the luminosity class of III indicating that this is a giant star. It is radiating about 851 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 12,670 K. The star is an estimated 217 million years old and is spinning with a high projected rotational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
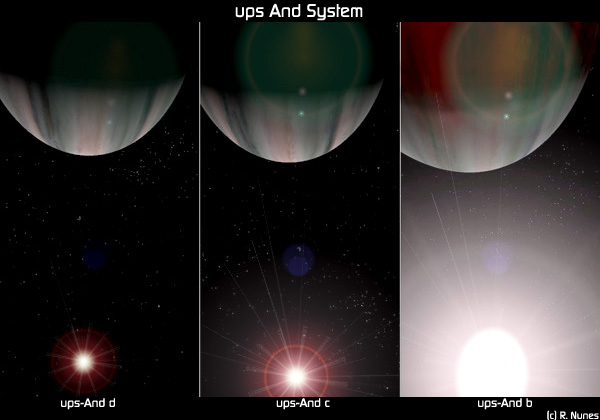
Upsilon Andromedae
Upsilon Andromedae (Žģ Andromedae, abbreviated Upsilon And, Žģ And) is a binary star located 44 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Andromeda. The system consists of an F-type main-sequence star (designated Žģ Andromedae A, officially named Titawin in the Amazigh language ) and a smaller red dwarf. , three extrasolar planets (designated Upsilon Andromedae b, c, d; named Saffar, Samh and Majriti, respectively) are believed to orbit Žģ Andromedae A. All three are likely to be jovian planets that are comparable in size to Jupiter. This was both the first multiple- planet system to be discovered around a main-sequence star, and the first multiple-planet system known in a multiple-star system. Nomenclature ''Žģ Andromedae'' ( Latinised to ''Upsilon Andromedae'') is the system's Bayer designation. Under the rules for naming objects in binary star systems, the two components are designated A and B. Under the same rules, the first planet discovered orbiting Žģ And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi Andromedae
Chi Andromedae ( Andromedae, And) is the Bayer designation for a star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +5.01, which is relatively faint for a naked-eye star. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission, Chi Andromedae is located around from Earth. Žć Andromedae is a member of (), meaning '' Heaven's Great General'', together with ╬│ Andromedae, Žå Persei, 51 Andromedae, 49 Andromedae, ╬Ė Andromedae, Žä Andromedae, 56 Andromedae, ╬▓ Trianguli, ╬│ Trianguli and ╬┤ Trianguli. Consequently, the Chinese name for Žć Andromedae itself is (, .) This is most likely a |