|
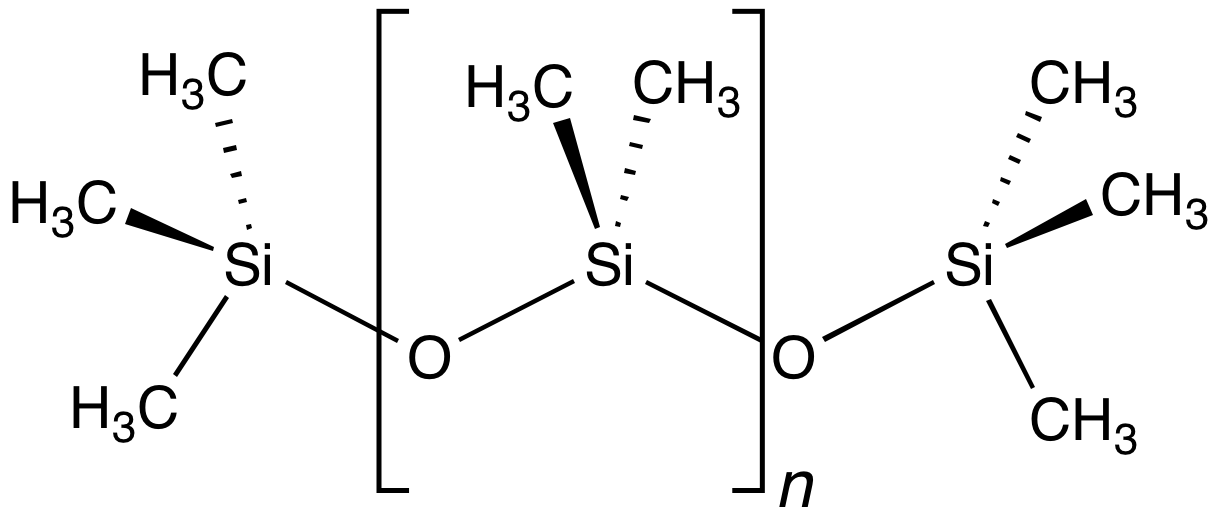
╬▓-silicon Effect
Negative hyperconjugation is a theorized phenomenon in organosilicon compounds, in which hyperconjugation stabilizes or destabilizes certain accumulations of positive charge. The phenomenon explains corresponding peculiarities in the stereochemistry and rate of hydrolysis. Second-row elements generally stabilize adjacent carbanions more effectively than their first-row congeners; conversely they destabilize adjacent carbocations, and these effects reverse one atom over. For phosphorus and later elements, these phenomena are easily ascribed to the element's greater electronegativity than carbon. However, Si has lower electronegativity than carbon, polarizing the electron density onto carbon. The continued presence of second-row type stability in certain organosilicon compounds is known as the silicon ╬▒ and ╬▓ effects, after the corresponding locants. These stabilities occur because of a partial overlap between the CŌĆōSi Žā orbital and the Žā* antibonding orbital at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosilicon Chemistry
Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbonŌĆōsilicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an ''inorganic'' compound. History In 1863, Charles Friedel and James Crafts made the first organochlorosilane compound. The same year, they also described a "polysilicic acid ether" in the preparation of ethyl- and methyl-o-silicic acid. Extensive research in the field of organosilicon compounds was pioneered in the beginning of 20th century by Frederic S. Kipping. He also had coined the term "silicone" (resembling ''ketones'', though this is erroneous) in relation to these materials in 1904. In recognition of Kipping's achievements, the Dow Chemical Company had established an award in the 1960s that is given for significant contributions to the field of silicon chemistry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition State
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked with the double dagger (ŌĆĪ) symbol. As an example, the transition state shown below occurs during the SN2 reaction of bromoethane with a hydroxide anion: The activated complex of a reaction can refer to either the transition state or to other states along the reaction coordinate between reactants and products, especially those close to the transition state. Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, ''Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed., W.H. Freeman 2006), p.809 According to the transition state theory, once the reactants have passed through the transition state configuration, they always continue to form products. History of concept The concept of a transition state has been important in many theories of the rates at which chemical re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrofuge
In chemistry, an electrofuge is a leaving group that does not retain the lone pair of electrons from its previous bond with another species (in contrast to a nucleofuge, which does). It can result from the heterolytic breaking of covalent bonds. After this reaction an electrofuge may possess either a positive or a neutral charge; this is governed by the nature of the specific reaction. An example would be the loss of from a molecule of benzene during nitration. The word 'electrofuge' is frequently found in older literature, but its use in contemporary organic chemistry is now uncommon. See also *Nucleofuge *Nucleophile *Electrophile In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively Electric charge, charged, have an ... References * . Organic chemistry {{organic-chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups. Both the negatively charged anion , called hydroxide, and the neutral radical , known as the hydroxyl radical, consist of an unbonded hydroxy group. According to IUPAC definitions, the term ''hydroxyl'' refers to the hydroxyl radical () only, while the functional group is called a ''hydroxy group''. Properties Water, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and many other hydroxy-containing compounds can be readily deprotonated due to a large difference between the electronegativity of oxygen (3.5) and that of hydrogen (2.1). Hydroxy-containing compounds engage in intermolecular hydrogen bonding increasing the electrostatic attraction between molecules and thus to higher boiling and melting points than found for compounds that lack thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbonŌĆōcarbon bond, carbonŌĆōcarbon double bonds). Ethylene is widely used in the chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 150 million tonnes in 2016) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Much of this production goes toward creating polyethylene, which is a widely used plastic containing polymer chains of ethylene units in various chain lengths. Production greenhouse gas emissions, emits greenhouse gases, including methane from feedstock production and carbon dioxide from any non-sustainable energy used. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone and is used in agriculture to induce ripening of fruits. The hydrate of ethylene is ethanol. Structure and properties This hydrocarbon has four hydrogen atoms bound to a pair of carbon atoms that are con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as . The word ''aqueous'' (which comes from ''aqua'') means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified. A ''non-aqueous solution'' is a solution in which the solvent is a liquid, but is not water. Characteristics Substances that are ''hydrophobic'' ('water-fearing') do not dissolve well in water, whereas those that are '' hydrophilic'' ('water-friendly') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance is sodium chloride. In an aqueous solution the hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positional Isomer
In chemistry, a structural isomer (or constitutional isomer in the IUPAC nomenclature) of a compound is a compound that contains the same number and type of atoms, but with a different connectivity (i.e. arrangement of bonds) between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept. For example, butanol , methyl propyl ether , and diethyl ether have the same molecular formula but are three distinct structural isomers. The concept applies also to polyatomic ions with the same total charge. A classical example is the cyanate ion and the fulminate ion . It is also extended to ionic compounds, so that (for example) ammonium cyanate and urea are considered structural isomers,William F. Bynum, E. Janet Browne, Roy Porter (2014)''Dictionary of the History of Science'' page 218. and so are methylammonium formate and ammonium acetate . Structural isomerism is the most radical type of isomerism. It is opposed to stereoisomerism, in which the atoms and bonding s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-radical Halogenation
In organic chemistry, free-radical halogenation is a type of halogenation. This chemical reaction is typical of alkanes and alkyl-substituted aromatics under application of UV light. The reaction is used for the industrial synthesis of chloroform (CHCl3), dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), and hexachlorobutadiene. It proceeds by a free-radical chain mechanism. General mechanism The chain mechanism is as follows, using the chlorination of methane as an example: ; Initiation: Ultraviolet radiation splits ( homolyzes) a chlorine molecule to two chlorine atom radicals. ; Chain propagation (two steps): A radical abstracts a hydrogen atom from methane, leaving a primary methyl radical. The methyl radical then abstracts ClŌĆó from Cl2 to give the desired product and another chlorine radical. The radical will then participate in another propagation reaction: the radical chain. Other products such as CH2Cl2 may also form. ; Chain termination: Two free radicals (chlorine and chlorine, chlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |