|
öý,N,N-Trimethylphenethylamine
öý,''N'',''N''-Trimethylphenethylamine, also known as ''N'',''N''-dimethyl-2-phenylpropan-1-amine (''N'',''N''-DMPPA or DMPPA) is a monoamine releasing agent of the phenethylamine family. It is the ''N''-methyl derivative of phenpromethamine (öý,''N''-methylphenethylamine) and the ''N'',''N''-dimethyl derivative of öý-methylphenethylamine. The drug is a partial norepinephrine releasing agent, with an of 1,337nM and an of 67% in rat brain synaptosomes. Conversely, it was inactive on dopamine, whereas serotonin was not reported. The drug produces non-significant increases in blood pressure in rodents, but does not affect heart rate or affect locomotor activity. It may be rapidly metabolized and thereby inactivated. DMPPA was first described in the scientific literature by at least 2019. See also * öý-Methylamphetamine 2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane (also known as öý-methylamphetamine) is a stimulant of the phenethylamine class that is closely related to its öÝ-methyl analog Pento ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monoamine Releasing Agent
A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters. MRAs work by reversing the direction of the monoamine transporters (MATs), including the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and/or dopamine transporter (DAT), causing them to promote efflux of non-vesicular cytoplasmic monoamine neurotransmitter rather than reuptake of synaptic monoamine neurotransmitter. Many, but not all MRAs, also reverse the direction of the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), thereby additionally resulting in efflux of vesicular monoamine neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phenpromethamine
Phenpromethamine (former brand name Vonedrine), also known as ''N'',öý-dimethylphenethylamine (MPPA, BMMPEA, öý-Me-NMPEA, öý,''N''-MePEA), is a sympathomimetic nasal decongestant of the phenethylamine group. It was previously marketed as a nasal inhaler from 1943 through 1960 but is no longer available. The medication is a stimulant and is banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency. It has been detected in dietary supplements starting in the 2010s. The drug is a monoamine releasing agent (MRA) similarly to öý-phenethylamine, amphetamine, and other phenethylamines. It is the ''N''-methyl derivative of öý-methylphenethylamine (BMPEA) and the öý-methyl derivative of ''N''-methylphenethylamine (NMPEA). Phenpromethamine is known to act as a norepinephrineãdopamine releasing agent (NDRA), with values of 154nM for norepinephrine and 574nM for dopamine in rat brain synaptosomes, whereas serotonin was not reported. See also * öý,''N'',''N''-Trimethylphenethylamine * Methamphetamine (ö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
öý-methylphenethylamine
öý-Methylphenethylamine (öý-Me-PEA, BMPEA, or 1-amino-2-phenylpropane) is an organic compound of the phenethylamine class, and a positional isomer of the drug amphetamine, with which it shares some properties. In particular, both amphetamine and öý-methylphenethylamine are human TAAR1 agonists. In appearance, it is a colorless or yellowish liquid. Relatively little information has been published about this substance. Hartung and Munch reported that it had good antihypotensive (pressor) activity in experimental animals, and that it was orally active. The MLD (minimum lethal dose) for the HCl salt was given as 500 mg/kg (rat, s.c.) and 50 mg/kg (rabbit, i.v.). A study by Graham and co-workers at the Upjohn Co., comparing many öý-methylphenethylamines substituted on the benzene ring showed that öý-methylphenethylamine itself had 1/700 x the pressor activity of epinephrine, corresponding to ~ 1/3 the potency of amphetamine. The öý-methyl compound also had ~ 2 x the bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Partial Monoamine Releasing Agent
A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters. MRAs work by reversing the direction of the monoamine transporters (MATs), including the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and/or dopamine transporter (DAT), causing them to promote efflux of non-vesicular cytoplasmic monoamine neurotransmitter rather than reuptake of synaptic monoamine neurotransmitter. Many, but not all MRAs, also reverse the direction of the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), thereby additionally resulting in efflux of vesicular monoamine neurot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Locomotor Activity
Locomotor activity is a measure of animal behavior which is employed in scientific research. Hyperlocomotion, also known as locomotor hyperactivity, hyperactivity, or increased locomotor activity, is an effect of certain drugs in animals in which locomotor activity (locomotion) is increased. It is induced by certain drugs like psychostimulants and NMDA receptor antagonists and is reversed by certain other drugs like antipsychotics and certain antidepressants. Stimulation of locomotor activity is thought to be mediated by increased signaling in the nucleus accumbens, a major brain area involved in behavioral activation and motivated behavior. Hypolocomotion, also known as locomotor hypoactivity, hypoactivity, and decreased locomotor activity, is an effect of certain drugs in animals in which locomotor activity is decreased. It is a characteristic effect of many sedative agents and general anesthetics. Antipsychotics, which are dopamine receptor antagonists, and many serotonerg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phenethylamines
Substituted phenethylamines (or simply phenethylamines) are a chemical class of organic compounds that are based upon the phenethylamine structure; the class is composed of all the derivative (chemistry), derivative compounds of phenethylamine which can be formed by replacing, or substitution reaction, substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the phenethylamine core structure with substituents. Phenylethylamines are also generally found to be central nervous system stimulants with many also being entactogens/empathogens, and hallucinogens. Structural classification The structural formula of any substituted phenethylamine contains a phenyl group, phenyl ring that is joined to an amino group, amino (NH) group via a two-carbon substituent, sidechain. Hence, any substituted phenethylamine can be classified according to the substitution of hydrogen atom, hydrogen (H) atoms on phenethylamine's phenyl ring, sidechain, or amino group with a moiety (chemistry), specific group of at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Norepinephrine Releasing Agents
A norepinephrine releasing agent (NRA), also known as an adrenergic releasing agent, is a catecholaminergic type of drug that induces the synapse, release of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) from the synapse, pre-synaptic neuron into the synapse. This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of norepinephrine and epinephrine therefore an increase in adrenergic neurotransmission. A closely related type of drug is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI), for instance reboxetine. Another class of drugs that stimulates adrenergic activity is the adrenergic receptor agonist class. Uses and examples NRAs, frequently as norepinephrineãdopamine releasing agents (NDRAs) rather than as binding selectivity, selective NRAs, are used for a variety of clinical indications including the following: * For the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) ã e.g., amphetamine, dextroamphetamine, levoamphetamine, lisdexamfetamine, me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dimethylamphetamine
Dimethylamphetamine (Metrotonin), also known as dimetamfetamine (INN), dimephenopan and ''N'',''N''-dimethylamphetamine, is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. Dimethylamphetamine has weaker stimulant effects than amphetamine or methamphetamine and is considerably less addictive and less neurotoxic compared to methamphetamine. However, it still retains some mild stimulant effects and abuse potential, and is illegal in both the United States and Australia. Dimethylamphetamine has occasionally been found in illicit methamphetamine laboratories, but is usually an impurity rather than the desired product. It may be produced by accident when methamphetamine is synthesised by N-methylation of dextroamphetamine if the reaction temperature is too high or an excess of methylating agent is used. It is said to be a prodrug of amphetamine/methamphetamine Methamphetamine (contracted from ) is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
öý-Methylamphetamine
2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane (also known as öý-methylamphetamine) is a stimulant of the phenethylamine class that is closely related to its öÝ-methyl analog Pentorex. It was first synthesized by the German scientists Felix Haffner and Fritz Sommer in 1939 as a stimulant with milder effects, shorter duration, lower toxicity and fewer side effects compared to previously known drugs such as amphetamine. 2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane is banned in some countries as a structural isomer of methamphetamine. See also * öý-Methylphenethylamine * öý-Phenylmethamphetamine * Phentermine Phentermine, sold under the brand name Adipex-P among others, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is available by itself or as the combination phentermine/topiramate. Phentermine is taken by mouth. Com ... References Anorectics Norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents Substituted amphetamines {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scientific Literature
Scientific literature encompasses a vast body of academic papers that spans various disciplines within the natural and social sciences. It primarily consists of academic papers that present original empirical research and theoretical contributions. These papers serve as essential sources of knowledge and are commonly referred to simply as "the literature" within specific research fields. The process of academic publishing involves disseminating research findings to a wider audience. Researchers submit their work to reputable journals or conferences, where it undergoes rigorous evaluation by experts in the field. This evaluation, known as peer review, ensures the quality, validity, and reliability of the research before it becomes part of the scientific literature. Peer-reviewed publications contribute significantly to advancing our understanding of the world and shaping future research endeavors. Original scientific research first published in scientific journals co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
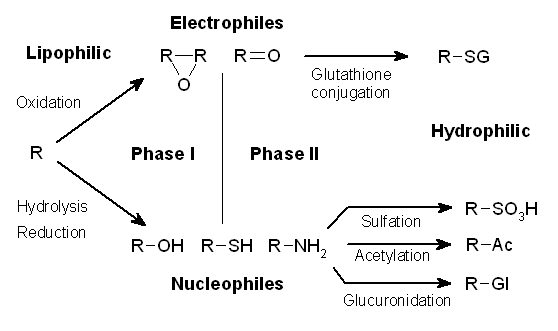
Drug Metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds (although in some cases the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves cause toxic effects). The study of drug metabolism is the object of pharmacokinetics. Metabolism is one of the stages (see ADME) of the drug's transit through the body that involves the breakdown of the drug so that it can be excreted by the body. The metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs is an important as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |