|
Îą-naphthol
1-Naphthol, or Îą-naphthol, is an organic compound with the formula . It is a fluorescence, fluorescent white solid. 1-Naphthol differs from its isomer 2-Naphthol, 2-naphthol by the location of the hydroxide, hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol. Both isomers are soluble in simple organic solvents. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds. Production 1-Naphthol is prepared by two main routes. In one method, naphthalene is nitrated to give 1-nitronaphthalene, which is hydrogenated to the amine followed by hydrolysis: : : : Alternatively, naphthalene is hydrogenated to tetralin, which is oxidized to 1-tetralone, which undergoes dehydrogenation. Reactions Some reactions of 1-naphthol are explicable with reference to its tautomerism, which produces a small amount of the keto tautomer. : One consequence of this tautomerism is the Bucherer reaction, the ammonolysis of 1-naphthol to give 1-Aminonaphthylaminel, 1-ami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molisch's Test
Molisch's test is a sensitive chemical test, named after Austrian botanist Hans Molisch, for the presence of carbohydrates, based on the dehydration of the carbohydrate by sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid to produce an aldehyde, which condenses with two molecules of a phenol (usually 1-Naphthol, Îą-naphthol, though other phenols such as resorcinol and thymol also give colored products), resulting in a violet ring. Procedure The test solution is combined with a small amount of Molisch's reagent (1-Naphthol, Îą-naphthol dissolved in ethanol) in a test tube. After mixing, a small amount of concentrated sulfuric acid is slowly added down the sides of the sloping test-tube, without mixing, to form a layer. A positive reaction is indicated by appearance of a purple red ring at the interface between the acid and test layers. Reaction All carbohydrates â monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides (except trioses and tetroses)â should give a positive reaction, and nucleic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-naphthol Tautomerism
1-Naphthol, or Îą-naphthol, is an organic compound with the formula . It is a fluorescent white solid. 1-Naphthol differs from its isomer 2-naphthol by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol. Both isomers are soluble in simple organic solvents. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds. Production 1-Naphthol is prepared by two main routes. In one method, naphthalene is nitrated to give 1-nitronaphthalene, which is hydrogenated to the amine followed by hydrolysis: : : : Alternatively, naphthalene is hydrogenated to tetralin, which is oxidized to 1-tetralone, which undergoes dehydrogenation. Reactions Some reactions of 1-naphthol are explicable with reference to its tautomerism, which produces a small amount of the keto tautomer. : One consequence of this tautomerism is the Bucherer reaction, the ammonolysis of 1-naphthol to give 1-aminonaphthalene. 1-Naphthol biodegrades via formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbonâhydrogen or carbonâcarbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazonium Salt
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide. The parent, compound where R is hydrogen, is diazenylium. Structure and general properties Arene derivatives According to X-ray crystallography the linkage is linear in typical diazonium salts. The bond distance in benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is 1.083(3)â à , which is almost identical to that for dinitrogen molecule (NâĄN). The linear free energy constants Ïm and Ïp indicate that the diazonium group is strongly electron-withdrawing. Thus, the diazonio-substituted phenols and benzoic acids have greatly reduced p''K''a values compared to their unsubstituted counterparts. The p''K''a of phenolic proton of 4-hydroxybenzenediazonium is 3.4, versus 9.9 for phenol itself. In other words, the diazonium group raises the ionization constant ''K'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' may differ). This formula does not imply direct covalent bonding between hydrogen and oxygen atoms; for example, in , hydrogen is covalently bonded to carbon, not oxygen. While the 2:1 hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio is characteristic of many carbohydrates, exceptions exist. For instance, uronic acids and deoxy-sugars like fucose deviate from this precise stoichiometric definition. Conversely, some compounds conforming to this definition, such as formaldehyde and acetic acid, are not classified as carbohydrates. The term is predominantly used in biochemistry, functioning as a synonym for saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiology (journal)
''Epidemiology'' is a bi-monthly, peer-reviewed journal for epidemiologic research, published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. The journal publishes original research from all fields of epidemiology, as well as review articles, meta-analyses, novel hypotheses, descriptions and applications of new methods and discussions of research theory and public health policy. It is the official journal of the International Society for Environmental Epidemiology (ISEE). In 2020, Epidemiology had an impact factor of 4.822, ranking 35th among 203 journals in the field of public, environmental and occupational health. Epidemiology was founded by Ken Rothman in 1990. Allen Wilcox has been Editor-in-Chief since 2001. Its editorial offices are in Durham, North Carolina Durham ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of North Carolina and the county seat of Durham County, North Carolina, Durham County. Small portions of the city limits extend into Orange County, North Carolina, Orange County and Wake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TCPy
TCPy or 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol is a cyclic hydrocarbon, specifically a chlorinated version of 2-pyridone. Pesticides can be a precursor to TCPy. TCPy is a metabolite of the herbicide triclopyr, and of the insecticides chlorpyrifos and chlorpyrifos-methyl. A study in Massachusetts reported a correlation between exposure to TCPy and lower testosterone Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ... levels in men. According to this source, exposure is "widespread" and of "potential public health importance". References {{Insecticides Chloroarenes 2-Pyridones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
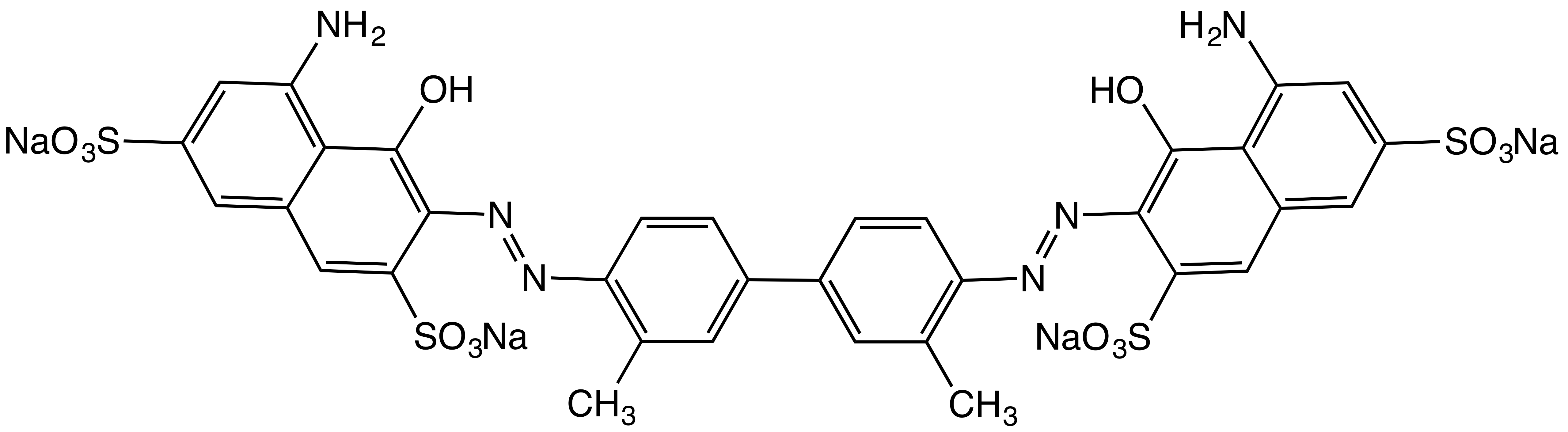
Azo Dye
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group RâN=NâRâē, in which R and Râē are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the CâN=NâC linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group but there are some that contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60–70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for cellulose-based textil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Coupling
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an organic reaction, reaction between a diazonium compound () and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound (). In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile, and the activating group, activated carbon (usually from an arene, which is called coupling agent), serves as a nucleophile. Classical coupling agents are phenols and naphthols. Usually the diazonium reagent attacks at the para position of the coupling agent. When the para position is occupied, coupling occurs at a ortho position, albeit at a slower rate. Uses of the reaction Aromatic azo compounds tend to be brightly colored due to their extended Conjugated system, conjugated systems. Many are useful dyes (see azo dye). Important azo dyes include methyl red and pigment red 170. Azo printing exploits this reaction as well. In this case, the diazonium ion is degraded by light, leaving a latent image in undegrade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atovaquone
Atovaquone, sold under the brand name Mepron, is an antimicrobial medication for the prevention and treatment of ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' pneumonia (PCP). Atovaquone is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of naphthoquinones. Atovaquone is a hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, an analog of both ubiquinone and lawsone. Medical uses Atovaquone is a medication used to treat or prevent: * For pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP), it is used in mild cases, although it is not approved for treatment of severe cases. * For toxoplasmosis, the medication has antiparasitic and therapeutic effects. * For malaria, it is one of the two components (along with proguanil) in the drug Malarone. Malarone has fewer side effects and is more expensive than mefloquine. Resistance has been observed. * For babesia, it is often used in conjunction with oral azithromycin. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX, Bactrim) is generally considered first-line therapy for PCP (not to be confused with sulfadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiprotozoal
Antiprotozoal agents ( ATC code: ATC P01) is a class of pharmaceuticals used in treatment of protozoan infection. A paraphyletic group, protozoans have little in common with each other. For example, '' Entamoeba histolytica'', a unikont eukaryotic organism, is more closely related to ''Homo sapiens'' (humans), which also belongs to the unikont phylogenetic group, than it is to '' Naegleria fowleri'', a "protozoan" bikont. As a result, agents effective against one pathogen may not be effective against another. Antiprotozoal agents can be grouped by mechanism or by organism. Recent papers have also proposed the use of viruses to treat infections caused by protozoa. Overuse or misuse of antiprotozoals can lead to the development of antiprotozoal resistance. Medical uses Antiprotozoals are used to treat protozoal infections, which include amebiasis, giardiasis, cryptosporidiosis, microsporidiosis, malaria, babesiosis, trypanosomiasis, Chagas disease, leishmaniasis, and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sertraline
Sertraline, sold under the brand name Zoloft among others, is an Antidepressant, antidepressant medication of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, obsessiveâcompulsive disorder (OCD), panic disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Although also having approval for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), findings indicate it leads to only modest improvements in symptoms associated with this condition. The drug shares the common Side effect, side effects and contraindications of other SSRIs, with high rates of nausea, diarrhea, headache, insomnia, mild somnolence, sedation, dry mouth, and sexual dysfunction, but it appears not to lead to much weight gain, and its effects on cognition, cognitive performance are mild. Similar to other antidepressants, the use of sertraline for depression may be associated with a mildly elevated rate of suicidal thoughts in peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |