|
öÝ-Ethyltryptamine
öÝ-Ethyltryptamine (öÝET, AET), also known as etryptamine, is an entactogen and stimulant drug of the tryptamine family. It was originally developed and marketed as an antidepressant under the brand name Monase by Upjohn in the 1960s before being withdrawn due to toxicity. Side effects of öÝET include facial flushing, headache, gastrointestinal distress, insomnia, irritability, appetite loss, and sedation, among others. A rare side effect of öÝET is agranulocytosis. öÝET acts as a releasing agent of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, as a weak serotonin receptor agonist, and as a weak monoamine oxidase inhibitor. It may also produce serotonergic neurotoxicity. öÝET is a substituted tryptamine and is closely related to öÝ-methyltryptamine (öÝMT) and other öÝ-alkylated tryptamines. öÝET was first described in 1947. It was used as an antidepressant for about a year around 1961. The drug started being used recreationally in the 1980s and several deaths have been rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Releasing Agent
A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters. MRAs work by reversing the direction of the monoamine transporters (MATs), including the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and/or dopamine transporter (DAT), causing them to promote efflux of non-vesicular cytoplasmic monoamine neurotransmitter rather than reuptake of synaptic monoamine neurotransmitter. Many, but not all MRAs, also reverse the direction of the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), thereby additionally resulting in efflux of vesicular monoamine neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entactogen
Entactogens, also known as empathogens or connectogens, are a class of psychoactive drugs that induce the production of experiences of emotional communion, oneness, connectedness, emotional opennessãthat is, empathyãas particularly observed and reported for experiences with MDMA. This class of drug is distinguished from the classes of hallucinogens or psychedelics and stimulants, although entactogens, for instance MDMA, can also have these properties. Entactogens are used both as recreational drugs and are being investigated for medical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders, for instance MDMA-assisted therapy for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Notable members of this class include MDMA, MDA, MDEA, MDOH, MBDB, 5-APB, 5-MAPB, 6-APB, 6-MAPB, methylone, mephedrone, öÝMT, öÝET, and MDAI, among others. Most entactogens are phenethylamines and amphetamines, although several, such as öÝMT and öÝET, are tryptamines. When referring to MDMA and its cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Neurotoxin
A monoamine neurotoxin, or monoaminergic neurotoxin, is a drug that selectively damages or destroys monoaminergic neurons. Monoaminergic neurons are neurons that signal via stimulation by monoamine neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. Examples of monoamine neurotoxins include the serotonergic neurotoxins ''para''-chloroamphetamine (PCA), methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), and 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine (5,7-DHT); the dopaminergic neurotoxins oxidopamine (6-hydroxydopamine), MPTP, and methamphetamine; and the noradrenergic neurotoxins oxidopamine and DSP-4. In the case of serotonergic neurotoxins like MDMA, research suggests that simultaneous induction of serotonin and dopamine release, serotonin depletion, dopamine uptake and metabolism, hyperthermia, oxidative stress and antioxidant depletion, and/or drug metabolites may all be involved in the neurotoxicity. On the other hand, there is evidence that drug metabolites may not be involved. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituted Tryptamine
Substituted tryptamines, or simply tryptamines, also known as serotonin analogues (i.e., 5-hydroxytryptamine analogues), are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino group, amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (ãCH2ãCH2ã) side chain, sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms. Well-known tryptamines include serotonin, an important neurotransmitter, and melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Tryptamine alkaloids are found in fungi, plants and animals; and sometimes used by humans for the neurological or psychotropic effects of the substance. Prominent examples of tryptamine alkaloids include psilocybin (from "psilocybin mushrooms") and dimethyltryptamine, DMT. In South America, dimethyltryptamine is obtained f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin Receptor Agonist
A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT), a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors. Non-selective agonists Serotonergic psychedelics such as tryptamines (e.g., psilocybin, psilocin, , 5-MeO-DMT, bufotenin), lysergamides (e.g., , ergine ()), phenethylamines (e.g., mescaline, 2C-B, 25I-NBOMe), and amphetamines (e.g., , ) are non-selective agonists of serotonin receptors. Their hallucinogenic effects are specifically mediated by activation of the 5-HT2A receptor. Drugs that increase extracellular serotonin levels such as serotonin reuptake inhibitors (e.g., fluoxetine, venlafaxine), serotonin releasing agents (e.g., fenfluramine, ), and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (e.g., phenelzine, moclobemide) are indirect non-selective serotonin receptor agonists. They are used variously as antidepressant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotoninãnorepinephrineãdopamine Releasing Agent
A serotoninãnorepinephrineãdopamine releasing agent (SNDRA), also known as a triple releasing agent (TRA), is a type of drug which induces the release of serotonin, norepinephrine/epinephrine, and dopamine in the brain and body. SNDRAs produce euphoriant, entactogen, and psychostimulant effects, and are almost exclusively encountered as recreational drugs. A closely related type of drug is a serotoninãnorepinephrineãdopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI). Examples of SNDRAs Examples of SNDRAs include specific amphetamines such as MDMA, MDA, 4-methylamphetamine, methamphetamine (in high doses), certain substituted benzofurans such as 5-APB and 6-APB, naphthylisopropylamine; cathinones such as mephedrone and methylone; tryptamines such as öÝMT and öÝET; along with agents of other chemical classes such as 4,4'-DMAR, and 5-IAI.Bruce E. Blough, Richard Rothman, Antonio Landavazo, Kevin M. Page, Ann Marie Decker. Phenylmorpholines and analogues thereof. US Patent 2013/0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agranulocytosis
Agranulocytosis, also known as agranulosis or granulopenia, is an acute condition involving a severe and dangerous lowered white blood cell count (leukopenia, most commonly of neutrophils) and thus causing neutropenia in the circulating blood. It is a severe lack of one major class of infection-fighting white blood cells. People with this condition are at very high risk of serious infections due to their suppressed immune system. In agranulocytosis, the concentration of granulocytes (a major class of white blood cells that includes neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils) drops below 200 cells/mm3 of blood. Signs and symptoms Agranulocytosis may be asymptomatic, or may clinically present with sudden fever, rigors and sore throat. Infection of any organ may be rapidly progressive (e.g., pneumonia, urinary tract infection). Sepsis may also progress rapidly. Causes A large number of drugs have been associated with agranulocytosis, including antiepileptics (such as carbamaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Effect
In medicine, a side effect is an effect of the use of a medicinal drug or other treatment, usually adverse but sometimes beneficial, that is unintended. Herbal and traditional medicines also have side effects. A drug or procedure usually used for a specific effect may be used specifically because of a beneficial side-effect; this is termed " off-label use" until such use is approved. For instance, X-rays have long been used as an imaging technique; the discovery of their oncolytic capability led to their use in radiotherapy for ablation of malignant tumours. Frequency of side effects The World Health Organization and other health organisations characterise the probability of experiencing side effects as: * Very common, ãË 1ã10 * Common (frequent), 1ã10 to 1ã100 * Uncommon (infrequent), 1ã100 to 1ã1000 * Rare, 1ã1000 to 1ã10000 * Very rare, < 1ã10000 The |
Flushing (physiology)
Flushing is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished from blushing, since blushing is psychosomatic, milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or ears, and generally assumed to reflect emotional stress, such as embarrassment, anger, or romantic stimulation. Flushing is also a cardinal symptom of carcinoid syndromeãthe syndrome that results from hormones (often serotonin or histamine) being secreted into systemic circulation. Causes * abrupt cessation of physical exertion (resulting in heart output in excess of current muscular need for blood flow) * abdominal cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome (ACNES), usually in patients who have had abdominal surgery * alcohol flush reaction * antiestrogens such as tamoxifen * atropine poisoning * body contact with warm or hot water (hot tub, bath, shower) * butorphanol reaction with some narcotic analgesics (since but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appetite Loss
Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetite. While the term outside of the scientific literature is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa, many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite, some of which may be harmless, while others indicate a serious clinical condition or pose a significant risk. Anorexia is a symptom, not a diagnosis. The symptom also occurs in non-human animals, such as cats, dogs, cattle, goats, and sheep. In these species, anorexia may be referred to as inappetence. As in humans, loss of appetite can be due to a range of diseases and conditions, as well as environmental and psychological factors. Etymology The term is from (, 'without' + , spelled , meaning 'appetite'). Common manifestations Anorexia simply manifests as a decreased or loss of appetite. This can present as not feeling hungry or lacking the desire to eat. Sometimes people do not even notice they lack an appetite until they begin to lose weight from eating less. In oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
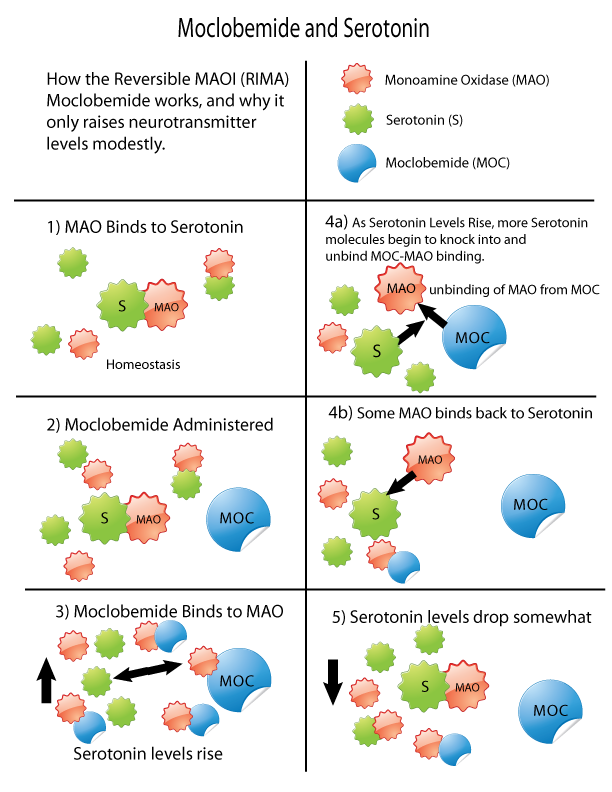
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a drug class, class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that binding selectivity, selectively and Enzyme inhibitor#Reversible inhibitors, reversibly enzyme inhibitor, inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the medication, treatment of major depressive disorder, depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |