|
α-Amanitin
α-Amanitin (''alpha''-Amanitin) is a cyclic peptide of eight amino acids. It is possibly the most deadly of all the amatoxins, toxins found in several species of the mushroom genus ''Amanita'', one being the death cap (''Amanita phalloides'') as well as the destroying angel, a complex of similar species, principally '' A. virosa'' and '' A. bisporigera''. It is also found in the mushrooms '' Galerina marginata'', '' Lepiota subincarnata'' and '' Conocybe filaris''. The oral of amanitin is 100 μg/kg for rats. Unlike most cyclic peptides, amatoxins (and phallotoxins) are synthesized on ribosomes. The genes encoding the proprotein for α-amanitin belong to the same family as those that encode for phallacidin (a phallotoxin). Scientific use α-Amanitin is a selective inhibitor of RNA polymerase II and III but not I. This mechanism makes it a deadly toxin. α-Amanitin can also be used to determine which types of RNA polymerase are present. This is done by testing the sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
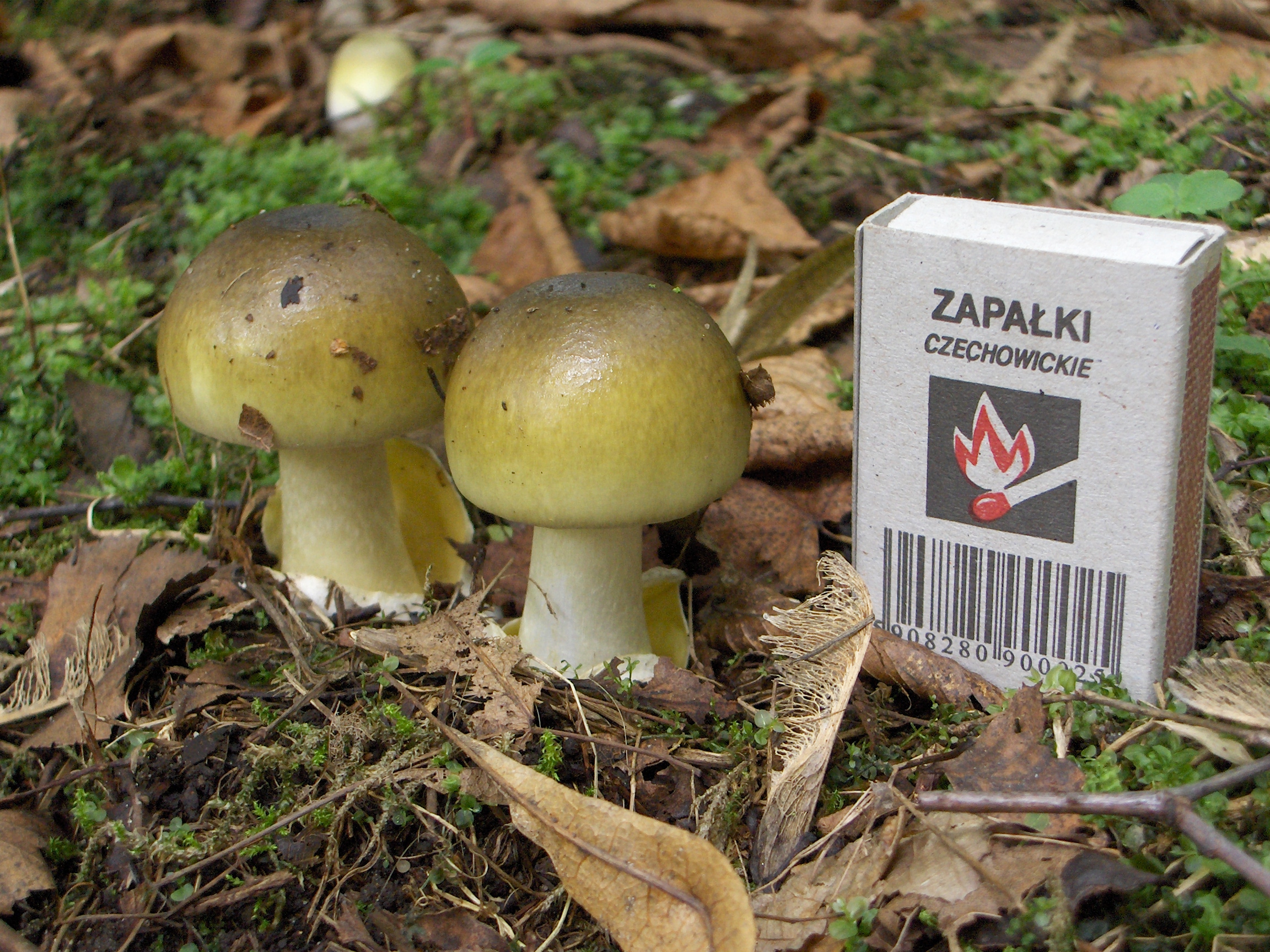
Amanita Phalloides
''Amanita phalloides'' ( ), commonly known as the death cap, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus and mushroom, one of many in the genus ''Amanita''. Originating in Europe but later introduced to other parts of the world since the late twentieth century, ''A. phalloides'' forms ectomycorrhizas with various broadleaved trees. In some cases, the death cap has been introduced to new regions with the cultivation of non-native species of oak, chestnut, and pine. The large fruiting bodies (mushrooms) appear in summer and autumn; the caps are generally greenish in colour with a white stipe and gills. The cap colour is variable, including white forms, and is thus not a reliable identifier. These toxic mushrooms resemble several edible species (most notably Caesar's mushroom and the straw mushroom) commonly consumed by humans, increasing the risk of accidental poisoning. Amatoxins, the class of toxins found in these mushrooms, are thermostable: they resist changes due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a Protein complex, multiprotein complex that Transcription (biology), transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNA polymerase, RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoter (biology), promoters and begin transcription. Discovery Early studies suggested a minimum of two RNAPs: one which synthesized rRNA in the nucleolus, and one which synthesized other RNA in the nucleoplasm, part of the nucleus but outside the nucleolus. In 1969, biochemists Robert G. Roeder and William J. Rutter, William Rutter discovered there are total three distinct nuclear RNA polymerases, an additional RNAP that was responsible for transcription of some kind of RNA in the nucleoplasm. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amatoxin
Amatoxins are a subgroup of at least nine related cyclic peptide toxins found in three genera of deadly poisonous mushrooms (''Amanita'', '' Galerina'' and '' Lepiota'') and one species of the genus '' Pholiotina''. Amatoxins are very potent, as little as half a mushroom cap can cause severe liver injury if swallowed. Structure The compounds have a similar structure, that of eight amino-acid residues arranged in a conserved macrobicyclic motif (an overall pentacyclic structure when counting the rings inherent in the proline and tryptophan-derived residues); they were isolated in 1941 by Heinrich O. Wieland and Rudolf Hallermayer. All amatoxins are cyclic peptides that are synthesized as 35-amino-acid proproteins, from which the final eight amino acids are cleaved by a prolyl oligopeptidase. The schematic amino acid sequence of amatoxins is Ile-Trp-Gly-Ile-Gly-Cys-Asn-Pro with cross-linking between Trp and Cys via the sulfoxide (S=O) moiety and hydroxylation in variants of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Peptides
Cyclic peptides are polypeptide chains which contain a circular sequence of bonds. This can be through a connection between the amino and carboxyl ends of the peptide, for example in cyclosporin; a connection between the amino end and a side chain, for example in bacitracin; the carboxyl end and a side chain, for example in colistin; or two side chains or more complicated arrangements, for example in alpha-amanitin. Many cyclic peptides have been discovered in nature and many others have been synthesized in the laboratory. Their length ranges from just two amino acid residues to hundreds. In nature they are frequently antimicrobial or toxic; in medicine they have various applications, for example as antibiotics and immunosuppressive agents. Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) is a convenient method to detect cyclic peptides in crude extract from bio-mass. Classification Cyclic peptides can be classified according to the types of bonds that comprise the ring. *Homodetic cyclic pept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
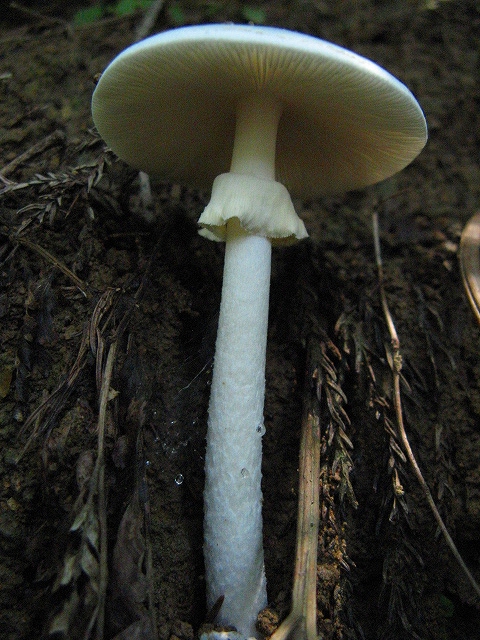
Amanita Virosa
''Amanita virosa'' is a species of fungus in the class Agaricomycetes. In the UK, it has the recommended English name of destroying angel and is known internationally as the European destroying angel. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are agaricoid (mushroom-shaped) and pure white with a ring on the stem and a sack-like volva at the base. The species occurs in Europe and northern Asia. It was formerly reported from North America, but similar-looking American species like '' A. bisporigera'' and '' A. ocreata'' are distinct. As the name suggests, the destroying angel is poisonous. Taxonomy ''Amanita virosa'' was first described in 1838 by Swedish mycologist Elias Magnus Fries as ''Agaricus virosus'', but this name is illegitimate since it had already been used for an earlier and different species. ''Amanita virosa'' was legitimately published by French mycologist Louis-Adolphe Bertillon in 1866. Etymology The specific epithet is derived from the Latin adjective ''virōsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Peptide
Cyclic peptides are polypeptide chains which contain a circular sequence of bonds. This can be through a connection between the amino and carboxyl ends of the peptide, for example in cyclosporin; a connection between the amino end and a side chain, for example in bacitracin; the carboxyl end and a side chain, for example in colistin; or two side chains or more complicated arrangements, for example in alpha-amanitin. Many cyclic peptides have been discovered in nature and many others have been synthesized in the laboratory. Their length ranges from just two amino acid residues to hundreds. In nature they are frequently antimicrobial or toxic; in medicine they have various applications, for example as antibiotics and immunosuppressive agents. Thin-layer chromatography, Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) is a convenient method to detect cyclic peptides in crude extract from bio-mass. Classification Cyclic peptides can be classified according to the types of bonds that comprise the ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita
The genus ''Amanita'' contains about 600 species of agarics, including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide, as well as some well-regarded Edible mushroom, edible species (and many species of unknown edibility). The genus is responsible for approximately 95% of fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own. The most potent toxin present in these mushrooms is . The genus also contains many edible mushrooms, but mycologists discourage mushroom hunters, other than experts, from selecting any of these for human consumption. Nonetheless, in some cultures, the larger local edible species of ''Amanita'' are mainstays of the markets in the local growing season. Samples of this are ''Amanita zambiana'' and other fleshy species in central Africa, ''Amanita basii, A. basii'' and similar species in Mexico, ''Amanita caesarea, A. caesarea'' and the "Blusher" ''Amanita rubescens, A. rubescens'' in Europe, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein chain. It can also be called a eupeptide bond to distinguish it from an isopeptide bond, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids. Synthesis When two amino acids form a '' dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of condensation reaction. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-side chain (C1) carboxylic acid moiety of one coming near the non-side chain (N2) amino moiety of the other. One loses a hydrogen and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH2). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H2O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (‚àíCO‚àíNH‚àí). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionization, ionized, for example by bombarding it with a Electron ionization, beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-performance Liquid Chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify specific components in mixtures. The mixtures can originate from food, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, biological, environmental and agriculture, etc., which have been dissolved into liquid solutions. It relies on high pressure pumps, which deliver mixtures of various solvents, called the mobile phase, which flows through the system, collecting the sample mixture on the way, delivering it into a cylinder, called the column, filled with solid particles, made of adsorbent material, called the stationary phase. Each component in the sample interacts differently with the adsorbent material, causing different migration rates for each component. These different rates lead to separation as the species flow out of the column into a specific detector such as UV detectors. The output of the detecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a family of electrokinetic separation methods performed in submillimeter diameter capillaries and in micro- and nanofluidic channels. Very often, CE refers to capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE), but other electrophoretic techniques including capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE), capillary isoelectric focusing (CIEF), capillary isotachophoresis and micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) belong also to this class of methods. In CE methods, analytes migrate through electrolyte solutions under the influence of an electric field. Analytes can be separated according to ionic mobility and/or partitioning into an alternate phase via non-covalent interactions. Additionally, analytes may be concentrated or "focused" by means of gradients in conductivity and pH. Instrumentation The instrumentation needed to perform capillary electrophoresis is relatively simple. A basic schematic of a capillary electrophoresis system is shown in ''figure 1'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocin
Psilocin, also known as 4-hydroxy-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (4-HO-DMT), is a substituted tryptamine alkaloid and a serotonergic psychedelic. It is present in most psychedelic mushrooms together with its phosphorylated counterpart psilocybin. Psilocybin, as well as synthetic esters such as 4-AcO-DMT (psilacetin; ''O''-acetylpsilocin) and 4-PrO-DMT (''O''-propionylpsilocin), are prodrugs of psilocin. Acting on the serotonin 5-HT2A receptors, psilocin's psychedelic effects are directly correlated with the drug's occupancy at these receptor sites. It also interacts with other serotonin receptors and targets. The subjective mind-altering effects of psilocin are highly variable in their qualitative nature but resemble those of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and ''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (DMT). Psilocin is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. Uses Psilocin is used recreationally, spirituality or shamanically, and medically. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |