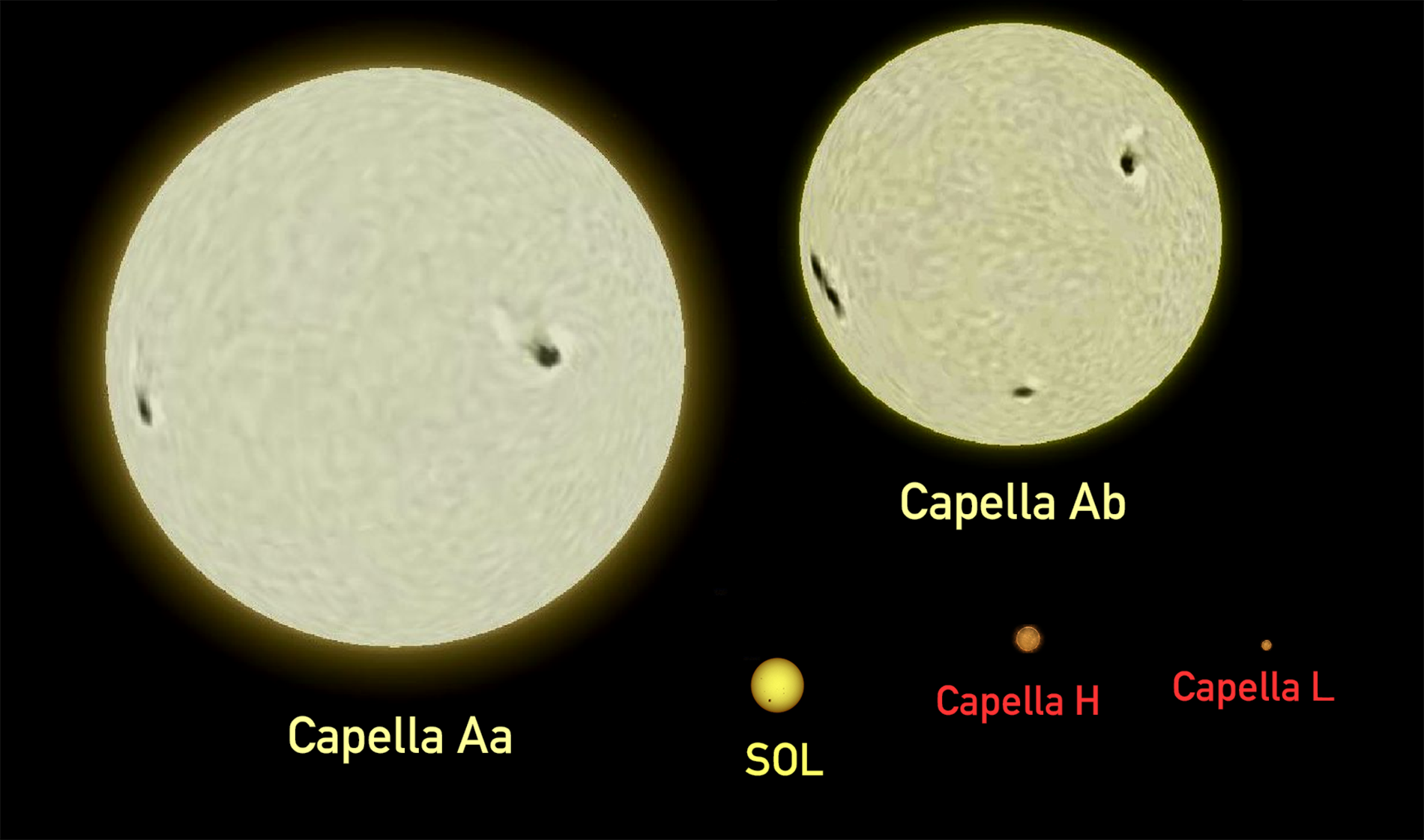
|
╬ø Aurigae
Lambda Aurigae is a Sun-like star in the northern constellation of Auriga. Its name is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from ╬╗ Aurigae, and abbreviated Lambda Aur or ╬╗ Aur. This star is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.71. Based upon parallax measurements, it is distant from the Earth. The star is drifting further away with a high radial velocity of +66.5 km/s, having come to within some 117,300 years ago. It has a high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of per year. Properties This is a G-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of G1 V. It is sometimes listed with a class of G1.5 IV-V Fe-1, which indicates the spectrum is showing some features of a more evolved subgiant star along with a noticeable underabundance of iron. In terms of composition it is similar to the Sun, while the mass and radius are slightly larger. It is 73% more luminous than the Sun and radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auriga (constellation)
Auriga is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the List of constellations, 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius of Athens, Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism (astronomy), asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as ŌłÆ34┬░; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra (constellation), Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella (star), Capella, is an unusual Star system, multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Atmosphere
The stellar atmosphere is the outer region of the volume of a star, lying above the stellar core, radiation zone and convection zone. Overview The stellar atmosphere is divided into several regions of distinct character: * The photosphere, which is the atmosphere's lowest and coolest layer, is normally its only visible part. Light escaping from the surface of the star stems from this region and passes through the higher layers. The Sun's photosphere has a temperature in the range. Starspots, cool regions of disrupted magnetic field, lie in the photosphere. * Above the photosphere lies the chromosphere. This part of the atmosphere first cools down and then starts to heat up to about 10 times the temperature of the photosphere. * Above the chromosphere lies the transition region, where the temperature increases rapidly on a distance of only around . * Additionally, many stars have a molecular layer (MOLsphere) above the photosphere and just beyond or even within the chromosphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net (Chinese Constellation)
The Net mansion () is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the western mansions of the White Tiger. Asterisms References {{DEFAULTSORT:Net (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The Ancient China, ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (Õ«┐ ''xi├╣'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250ŌĆō1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE). They flourished during the Han period (202 BCE ŌĆō 220 CE) and subsequent dynasties with the publication of star catalogues. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Aurigae
Sigma Aurigae is a star in the northern constellation of Auriga. Its name is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from Žā Aurigae, and abbreviated Sigma Aur or Žā Aur. This star is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.99. With an annual parallax shift of 6.35 mas, it is approximately distant from the Earth. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of ŌłÆ20 km/s. This is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of K3III CN+2, indicating that it has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core. The 'CN+2' notation indicates anomalously strong lines of the CN molecule in the spectrum. This star has expanded to 44 times the radius of the Sun and is radiating nearly 500 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Aurigae
Mu Aurigae is a candidate binary star system in the northern constellation of Auriga. Its name is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from ╬╝ Aurigae, and abbreviated Mu Aur or ╬╝ Aur. This star is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.88. Based upon an annual parallax shift of as seen from Earth, it is located approximately 162 light-years from the Sun. This system is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +26 km/s. This is an A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A4 Vm; the 'm' suffix indicating that abnormal abundances of heavier elements appear in the star's spectrum, making this an Am star. It is 560 million years old with a projected rotational velocity of . This star has 1.90 the mass of the Sun and 2.5 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 23 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 7,931 K. A very close companion has been reported using s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Velocity (astronomy)
In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the Observational astronomy, observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space. Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar Velocity, velocities in the Milky Way and its Satellite galaxies of the Milky Way, satellites as well as the internal kinematics of more distant Galaxy, galaxies. Measurement of the kinematics of stars in different subcomponents of the Milky Way including the thin disk, the thick disk, the Bulge (astronomy), bulge, and the stellar halo provides important information about the formation and evolutionary history of our Galaxy. Kinematic measurements can also identify exotic phenomena such as hypervelocity stars escaping from the Milky Way, which are interpreted as the result of gravitational encounters of binary stars with the Sagittarius A*, supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center. Stellar kinematics is related to but distinct from the subject of stellar dynamics, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Proper Motion
This glossary of astronomy is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to astronomy and cosmology, their sub-disciplines, and related fields. Astronomy is concerned with the study of astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth. The field of astronomy features an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon. A B C D E F G H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Indi Moving Group
Epsilon Indi, Latinized from ╬Ą Indi, is a star system located at a distance of approximately 12 light-years from Earth in the southern constellation of Indus. The star has an orange hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.674. It consists of a K-type main-sequence star, ╬Ą Indi A, and two brown dwarfs, ╬Ą Indi Ba and ╬Ą Indi Bb, in a wide orbit around it. The brown dwarfs were discovered in 2003. ╬Ą Indi Ba is an early T dwarf (T1) and ╬Ą Indi Bb a late T dwarf (T6) separated by 0.6 arcseconds, with a projected distance of 1460 AU from their primary star. ╬Ą Indi A has one known planet, ╬Ą Indi Ab, with a mass of 6.31 Jupiter masses in an elliptical orbit with a period of about 171.3 years. ╬Ą Indi Ab is the second-closest Jovian exoplanet, after ╬Ą Eridani b. The ╬Ą Indi system provides a benchmark case for the study of the formation of gas giants and brown dwarfs. Observation The constellation Indus (the Indian) first ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debris Disk
A debris disk (American English), or debris disc ( Commonwealth English), is a circumstellar disk of dust and debris in orbit around a star. Sometimes these disks contain prominent rings, as seen in the image of Fomalhaut on the right. Debris disks are found around stars with mature planetary systems, including at least one debris disk in orbit around an evolved neutron star. Debris disks can also be produced and maintained as the remnants of collisions between planetesimals, otherwise known as asteroids and comets. As of 2001, more than 900 candidate stars had been found to possess a debris disk. They are usually discovered by examining the star system in infrared light and looking for an excess of radiation beyond that emitted by the star. This excess is inferred to be radiation from the star that has been absorbed by the dust in the disk, then re-radiated away as infrared energy. Debris disks are often described as massive analogs to the debris in the Solar System. Most kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Excess
An infrared excess is a measurement of an astronomical source, typically a star, that in their spectral energy distribution has a greater measured infrared flux than expected by assuming the star is a blackbody radiator. Infrared excesses are often the result of circumstellar dust heated by starlight and reemitted at longer wavelengths. They are common in young stellar objects and evolved stars on the asymptotic giant branch or older. In addition, monitoring for infrared excess emission from stellar systems is one possible method that could enable a search for large-scale stellar engineering projects of a hypothetical extraterrestrial civilization; for example a Dyson sphere A Dyson sphere is a hypothetical megastructure that encompasses a star and captures a large percentage of its power output. The concept is a thought experiment that attempts to imagine how a spacefaring civilization would meet its energy re ... or Dyson swarm. This infrared excess would be the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |