|
خ•دچخ²خ؟خ¹خ±
Euboea ( ; , ), also known by its modern spelling Evia ( ; , ), is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete, and the sixth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (خœخ¬خ؛دپخ¹د‚) and ''Doliche'' (خ”خ؟خ»خ¯د‡خ·) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'' (after Ellop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
خ•ل½”خ²خ؟خ¹خ±
Euboea ( ; , ), also known by its modern spelling Evia ( ; , ), is the second-largest List of islands of Greece, Greek island in area and population, after Crete, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, sixth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the Euboea (regional unit), regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in Ancient Greece, antiquity, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euboea (regional Unit)
Euboea () is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Central Greece. It consists of the islands of Euboea and Skyros, as well as a 260 km2 area on the Greek mainland. Its land area is 4,167.449 km2, whereas the total land area of the municipalities actually on the island Euboea is 3,684.848 km2, which includes that of numerous small offshore islets ( Petalies Islands) near Euboea's southern tip. Administration The Euboea regional unit is subdivided into 8 municipalities, numbered in the picture in the infobox. These are: *Chalcis (''Chalkida'', 1) * Dirfys-Messapia (2) *Eretria (3) * Istiaia-Aidipsos (4) * Karystos (5) * Kymi-Aliveri (6) * Mantoudi-Limni-Agia Anna (7) *Skyros (8) Prefecture As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the former Euboea Prefecture () was transformed into a regional unit within the Central Greece region, without any change in boundaries. At the same time, the municipalities were reo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcis
Chalcis (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: , ), also called Chalkida or Halkida (Modern Greek: , ), is the chief city of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from Classical antiquity, antiquity and is derived from the Greek wiktionary:د‡خ±خ»خ؛دŒد‚, د‡خ±خ»خ؛دŒد‚ (copper, bronze), though there is no trace of any mines in the area. In the Late Middle Ages, it was known as Negropont(e), an Italian name that has also been applied to the entire island of Euboea. History Ancient Greece The earliest recorded mention of Chalcis is in the Iliad, where it is mentioned in the same line as its rival Eretria. It is also documented that the ships set for the Trojan War gathered at Aulis, the south bank of the strait near the city. Chamber tombs at Trypa and Vromousa dated to the Mycenaean period were excavated by Papavasiliou in 1910. In the 8th and 7th centuries BC, colonists from Chalcis founded thirty tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
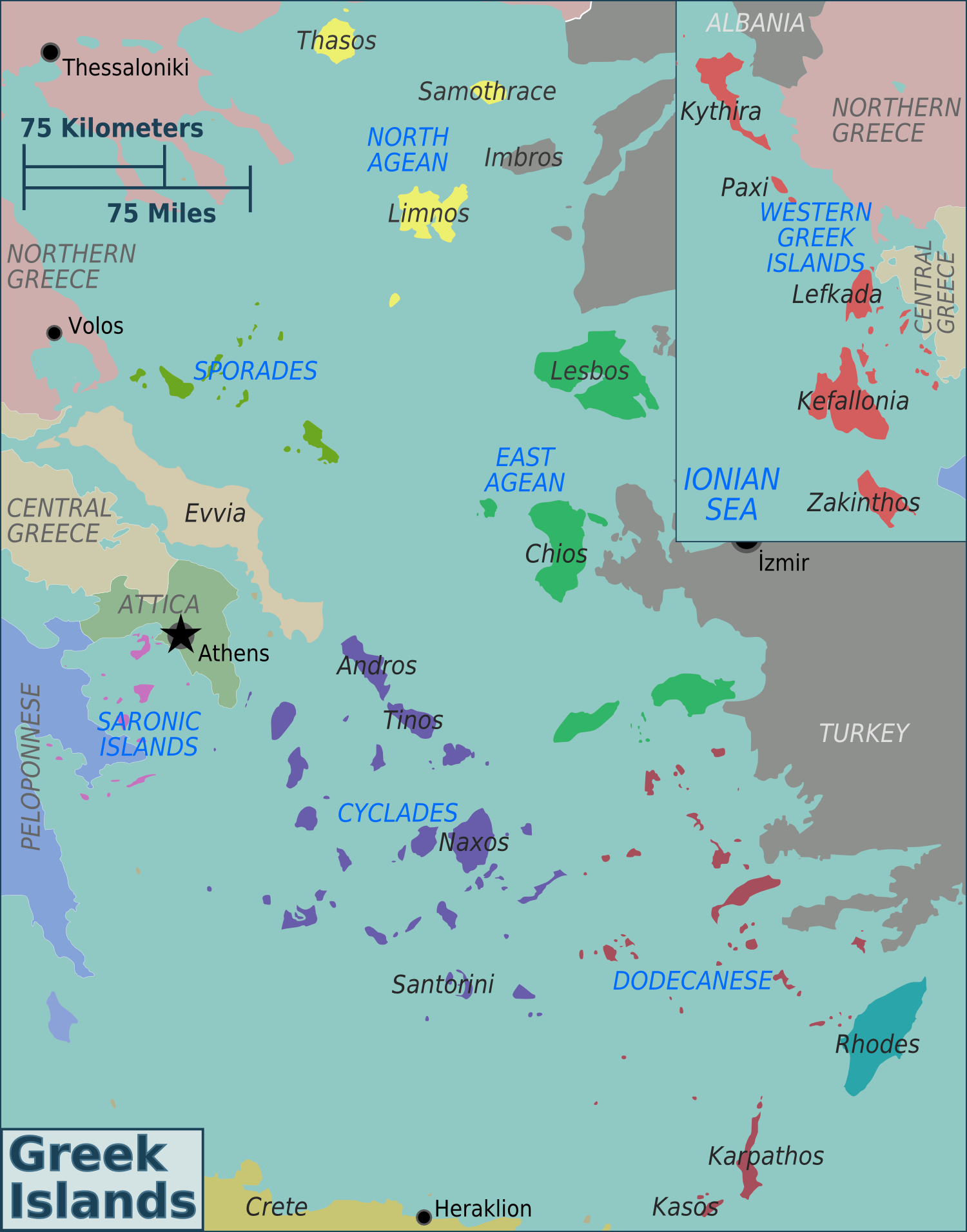
List Of Islands Of Greece
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227. The largest Greek island by both area and population is Crete, located at the southern edge of the Aegean Sea. The second largest island in area is Euboea or Evvia, which is separated from the mainland by the 60m-wide Euripus Strait, and is administered as part of the Central Greece region. After the third and fourth largest Greek islands, Lesbos and Rhodes, the rest of the islands are two-thirds of the area of Rhodes, or smaller. The Greek islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Argo-Saronic Islands in the Saronic Gulf near Athens; the Cyclades, a large but dense collection occupying the central part of the Aegean Sea; the North Aegean islands, a loose grouping off the west coast of Turkey; the Dodecanese, another loose collection i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mykonos
Mykonos (, ; ) is a Greek island, part of the Cyclades, lying between Tinos, Syros, Paros and Naxos. The island has an area of and rises to an elevation of at its highest point. At the 2021 census, there were 10,704 inhabitants, most of whom lived in the largest town, Mykonos, which is on the west coast. The town is also known as ''Chora'' (i.e. 'Town' in Greek, following the common practice in Greece when the name of the island itself is the same as the name of the principal town). Mykonos's nickname is "The Island of the Winds", due to the very strong winds that usually blow on the island. Tourism is a major industry and Mykonos is known for its vibrant nightlife. Name There are two prevailing theories as to the origin of the name "Mykonos". The first, from Hesychius of Alexandria, surmises that the name comes from the ancient Greek "Mykon", which roughly translates to "pile of stones" or "rocky place". The second, from Stephanus of Byzantium, ties it to the mythologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skyros
Skyros (, ), in some historical contexts Romanization of Greek, Latinized Scyros (, ), is an island in Greece. It is the southernmost island of the Sporades, an archipelago in the Aegean Sea. Around the 2nd millennium BC, the island was known as The Island of the Magnetes; later, it was consecutively known as Pelasgia, Dolopia, and finally Skyros. At , it is the largest island of the Sporades, and had a population of about 3,000 in 2021. Municipality The municipality Skyros is part of the regional unit of Euboea (regional unit), Euboea. Apart from the island Skyros, the municipality consists of the small inhabited island of Skyropoula and a few smaller uninhabited islands. The total area of the municipality is . Etymology One account associates the name ''Skyros'' with ''skyron'' or ''skiron'', meaning "stone debris". The island had a reputation for its decorative stone. File:Skyros Satellite.jpg, Satellite photo of Skyros and Skyropoula File:Map of Skyros - Bordone Benedetto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion (mythology)
According to Greek mythology, Ion (; ) was eponymous ancestor of the Ionians. Family Ion was the illegitimate child of Creأ¼sa, the daughter of King Erechtheus of Athens and wife of Xuthus. His real father was the god Apollo. Mythology Euripides’ '' Ion'' One story of Ion is told in the tragedy play '' Ion'' by Euripides. Apollo had visited Creusa in a cave below Propylaea where she conceived Ion. When the princess gave birth to the child, she abandoned him in the same cave but Apollo father asked Hermes to take Ion from his cradle. Ion was saved, raised and educated by a priestess of the Delphic Oracle. When the boy had grown, and Xuthus and Creusa came to consult the oracle about the means of obtaining an heir, the answer was, that the first human being which Xuthus met on leaving the temple should be his son. Xuthus met Ion, and recognized him as his son but, in fact, Apollo was giving him Ion as an adoptive son. Creusa, imagining the boy to be a son of her husban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; ''Strأ،bإچn''; 64 or 63 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek geographer who lived in Anatolia, Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is best known for his work ''Geographica'', which presented a descriptive history of people and places from different regions of the world known during his lifetime. Additionally, Strabo authored historical works, but only fragments and quotations of these survive in the writings of other authors. Early life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amasya, Amaseia in Kingdom of Pontus, Pontus in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andros
Andros (, ) is the northernmost island of the Greece, Greek Cyclades archipelago, about southeast of Euboea, and about north of Tinos. It is nearly long, and its greatest breadth is . It is for the most part mountainous, with many fruitful and well-watered valleys. The municipality, which includes the island Andros and several small, uninhabited islands, has an area of . The largest towns are Andros (town), Gavrio, Batsi, and Ormos Korthiou. Palaiopoli, Andros, Palaeopolis, the ancient capital, was built into a steep hillside, and the breakwater (structure), breakwater of its harbor can still be seen underwater. At the village of Apoikia, there is the notable spring of Sariza, where the water flows from a sculpted stone lion's head. Andros also offers hiking options with many new paths being added each year. Strofilas During the Final Neolithic, Andros had a fortified village on its west coast, which archaeologists have named , after the plateau on which it was built. Final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boأ¶saule
In Greek mythology, Boأ¶saule (Greek خ’خ؟ل½¸د‚ خ±ل½گخ»خ® ''Boos aylؤ“'' 'Cow pen') is a cave in Euboea where, according to Strabo, Io gave birth to Epaphus.Strabo10.1.3./ref> See also * List of Greek deities *Boأ¶saule Montes South Boأ¶saule Mons (), the highest mountain of Jupiter's moon Io (moon), Io, is one of the tallest mountains in the Solar System. It is located just northwest of the volcano Pele (volcano), Pele, in the Boأ¶saule Montes. The official name of th ...:mountain of Jupiter's moon Io References Places in Greek mythology {{Greek-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |