|
Î’-Glucuronidase
β-Glucuronidases are members of the glycosidase family of enzymes that catalyze breakdown of complex carbohydrates. Human β-glucuronidase is a type of glucuronidase (a member of glycosidase Family 2) that catalyzes hydrolysis of β-D-glucuronic acid residues from the non-reducing end of mucopolysaccharides (also referred to as glycosaminoglycans) such as heparan sulfate. Human β-glucuronidase is located in the lysosome. In the gut, brush border β-glucuronidase converts conjugated bilirubin to the unconjugated form for reabsorption. β-Glucuronidase is also present in breast milk, which contributes to neonatal jaundice. The protein is encoded by the ''GUSB'' gene in humans and by the ''uidA'' gene in bacteria. Structure Human β-glucuronidase is synthesized as an 80 kDa monomer (653 amino acids) before proteolysis removes 18 amino acids from the C-terminal end to form a 78 kDa monomer. β-Glucuronidase exists as a 332 kDa homotetramer. β-Glucuronidase contains several no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrameric Protein
A tetrameric protein is a protein with a quaternary structure of four subunits (tetrameric). Homotetramers have four identical subunits (such as glutathione S-transferase), and heterotetramers are complexes of different subunits. A tetramer can be assembled as dimer of dimers with two homodimer subunits (such as sorbitol dehydrogenase), or two heterodimer subunits (such as hemoglobin). Subunit interactions in tetramers The interactions between subunits forming a tetramer is primarily determined by non covalent interaction. Hydrophobic effects, hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions are the primary sources for this binding process between subunits. For homotetrameric proteins such as sorbitol dehydrogenase (SDH), the structure is believed to have evolved going from a monomeric to a dimeric and finally a tetrameric structure in evolution. The binding process in SDH and many other tetrameric enzymes can be described by the gain in free energy which can be determined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity in anatomical structures or genes between organisms of different taxa due to shared ancestry, ''regardless'' of current functional differences. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures as retained heredity from a common descent, common ancestor after having been subjected to adaptation (biology), adaptive modifications for different purposes as the result of natural selection. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this from Aristotle's biology onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the bat wing development, wings of bats and origin of avian flight, birds, the arms of primates, the front flipper (anatomy), flippers of whales, and the forelegs of quadrupedalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition State
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked with the double dagger (‡) symbol. As an example, the transition state shown below occurs during the SN2 reaction of bromoethane with a hydroxide anion: The activated complex of a reaction can refer to either the transition state or to other states along the reaction coordinate between reactants and products, especially those close to the transition state. Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, ''Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed., W.H. Freeman 2006), p.809 According to the transition state theory, once the reactants have passed through the transition state configuration, they always continue to form products. History of concept The concept of a transition state has been important in many theories of the rates at which chemical re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
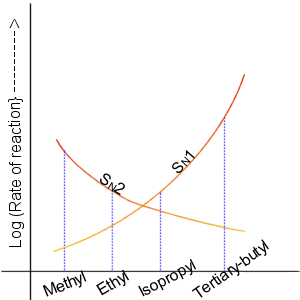
Nucleophilic Substitution
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution (SN) is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species (known as a nucleophile) replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule (known as the electrophile). The molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the substrate. The most general form of the reaction may be given as the following: :\text\mathbf + \ce + \text\mathbf The electron pair (:) from the nucleophile (Nuc) attacks the substrate () and bonds with it. Simultaneously, the leaving group (LG) departs with an electron pair. The principal product in this case is . The nucleophile may be electrically neutral or negatively charged, whereas the substrate is typically neutral or positively charged. An example of nucleophilic substitution is the hydrolysis of an alkyl bromide, R-Br under basic conditions, where the attacking nucleophile is hydroxyl () and the leaving group is bromide (). :O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptides
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Dalton (unit), Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biopolymer, biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligand (biochemistry), ligands such as coenzymes and cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed Residue (chemistry)#Biochemistry, residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azide
In chemistry, azide (, ) is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula and structure . It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid . Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula , containing the azide functional group. The dominant application of azides is as a propellant in air bags. Preparation Sodium azide is made industrially by the reaction of nitrous oxide, with sodium amide in liquid ammonia as solvent: : Many inorganic azides can be prepared directly or indirectly from sodium azide. For example, lead azide, used in detonators, may be prepared from the metathesis reaction between lead nitrate and sodium azide. An alternative route is direct reaction of the metal with silver azide dissolved in liquid ammonia. Some azides are produced by treating the carbonate salts with hydrazoic acid. Bonding Azide is isoelectronic with carbon dioxide , cyanate , nitrous oxide , nitronium ion , molecular beryllium fluoride and cyanogen fluoride FCN. Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side chain. Consequently it is classified as a non-polar, aliphatic α-amino acid. Under biological conditions, it exists in its zwitterionic form with its amine group protonated (as ) and its carboxyl group deprotonated (as ). It is non-essential to humans as it can be synthesized metabolically and does not need to be present in the diet. It is encoded by all codons starting with G C (GC U, GCC, GC A, and GCG). The L-isomer of alanine (left-handed) is the one that is incorporated into proteins. L-alanine is second only to L-leucine in rate of occurrence, accounting for 7.8% of the primary structure in a sample of 1,150 proteins. The right-handed form, D-alanine, occurs in peptides in some bacterial cell walls (in peptidoglycan) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidic
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Arrhenius acids. Brønsted and Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. The word ''acid'' is derived from the Latin , meaning 'sour'. An aqueous solution of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. The difference between the two is, that basicity is a thermodynamic property (i.e. relates to an equilibrium state), but nucleophilicity is a kinetic property ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABAergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in two optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |