|
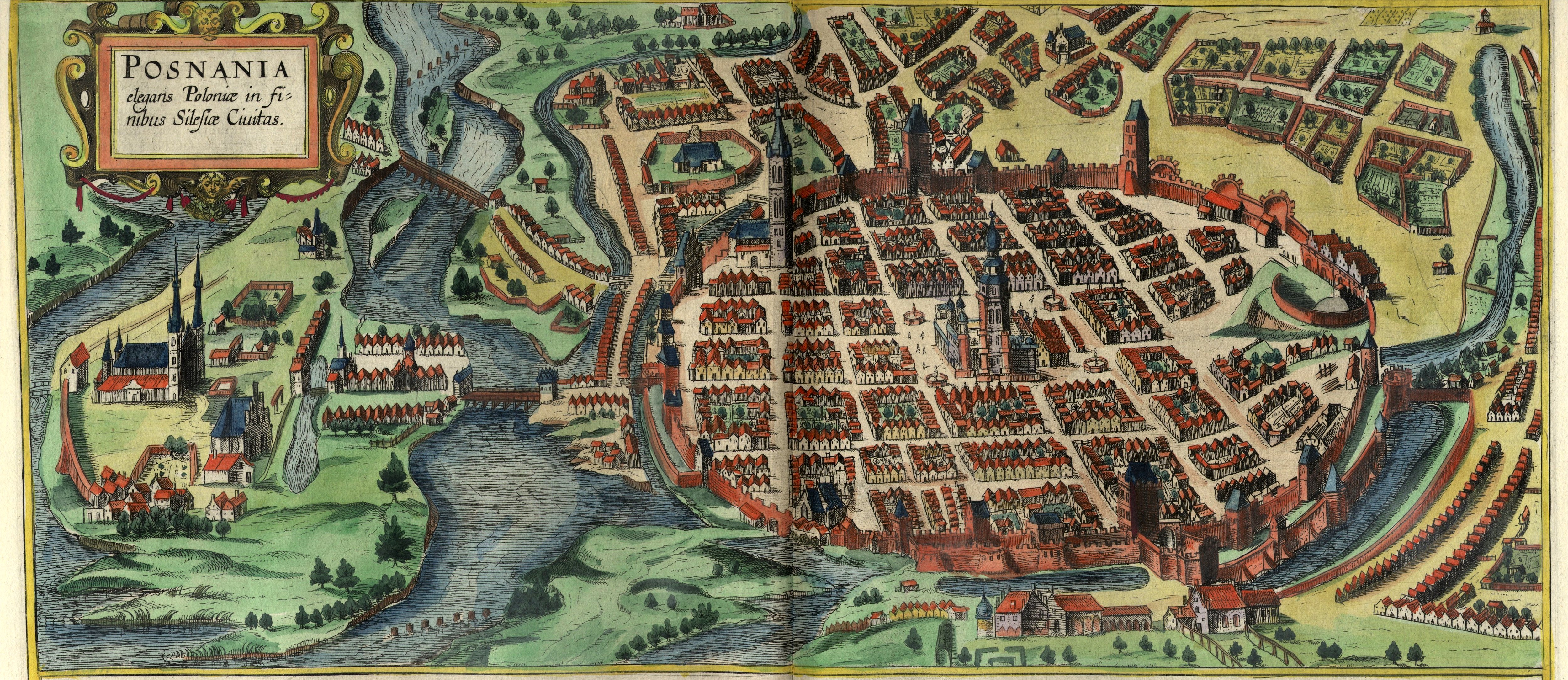
Е»erkГіw Kz01
Е»erkГіw () is a town in Jarocin County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, Poland, with 2,122 inhabitants (2010). It is located east of the regional capital of PoznaЕ„. The town is near the Е»erkГіw-Czeszewo Landscape Park. History The oldest known mention of Е»erkГіw comes from a document of Duke BolesЕ‚aw the Pious from 1257, and in a document of Duke and future King of Poland PrzemysЕ‚ II from 1283 it was already referred to as a town. Е»erkГіw was a private town of Polish nobility, administratively located in the Pyzdry County in the Kalisz Voivodeship in the Greater Poland Province. In 1574, the newly elected King Henry of Valois stopped in Е»erkГіw before his royal coronation in KrakГіw. In 1623 the town was visited by King Sigismund III Vasa and prince royal (and future king) WЕ‚adysЕ‚aw IV Vasa. The Radomicki noble family erected the Baroque Church of Saint Stanislaus, which is the town's greatest historic landmark. Following the Second Partition of Poland Е»erkГіw be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Town
Private towns in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth were privately owned towns within the lands owned by magnates, bishops, knights and princes, among others. Amongst the most well-known former private magnate towns are Białystok, Zamość, Rzeszów, Puławy, Tarnów, Siedlce, Biała Podlaska, Ivano-Frankivsk, Ternopil and Uman. Magnate palaces and castles can be often found in former private magnate towns. Examples include the Branicki Palace in Białystok; the Czartoryski Palace in Puławy; the Zamoyski Palace in Zamość; the Lubomirski Castle in Rzeszów; the Radziwiłł Palace in Biała Podlaska; the Ogiński Palace in Siedlce; the Potocki Palaces in Międzyrzec Podlaski, Tulchyn and Vysokaye; the Wiśniowiecki Palace in Vyshnivets; and the Zbaraski Castle in Zbarazh. Also various other landmarks were often founded by the owners, including town halls, churches, monasteries, schools and theatres, some rather unique, like the Mannerist Kalwaria Zebrzydowska Park an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Poland Uprising (1806)
Greater Poland uprising of 1806 was a Polish military insurrection which occurred in the region of Wielkopolska, also known as Greater Poland, against the occupying Prussian forces after the Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1772–1795). The uprising was organized by General Jan Henryk Dąbrowski to help advancing French forces under Napoleon in liberating Poland from Prussian occupation. The Wielkopolska Uprising was a decisive factor that allowed the formation of the Duchy of Warsaw (1807) and the inclusion of Wielkopolska in the Duchy of Warsaw. Historical background While the Kingdom of Prussia already possessed a large Polish population in Upper Silesia, it gained additional Polish citizens during the partitions of Poland. From the beginnings of Prussian rule Poles were subject to a series of measures aimed against them and their culture, notably the Polish language was abolished in favour of German. Andrzej Chwalba – Historia Polski 1795–1918 W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a significant role in the unification of Germany in 1871 and was a major constituent of the German Empire until its German Revolution of 1918–1919, dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the Prussia (region), region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The list of monarchs of Prussia, kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. The polity of Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick the Great, Frederick II "the Great".Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick the Great 1712–30." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Partition Of Poland
The 1793 Second Partition of Poland was the second of partitions of Poland, three partitions (or partial annexations) that ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The second partition (politics), partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation of 1792, and was approved by its territorial beneficiaries, the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia. The division was ratified by the coerced Polish parliament (Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Sejm) in 1793 (see the Grodno Sejm) in a short-lived attempt to prevent the inevitable complete annexation of Poland, the Third Partition of Poland, Third Partition. Background By 1790, on the political front, the Commonwealth had deteriorated into such a helpless condition that it was forced into an alliance with its enemy, Prussia. The Polish–Prussian alliance, Polish-Prussian Pact of 1790 was signed, giving false hope that the Commonwealth mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque In Poland
The Polish Baroque lasted from the early 17th to the mid-18th century. As with Baroque style elsewhere in Europe, Poland's Baroque emphasized the richness and triumphant power of contemporary art forms. In contrast to the previous, Renaissance style which sought to depict the beauty and harmony of nature, Baroque artists strove to create their own vision of the world. The result was manifold, regarded by some critics as grand and dramatic, but sometimes also chaotic and disharmonious and tinged with affectation and religious exaltation, thus reflecting the turbulent times of the 17th-century Europe. Sarmatism The Polish Baroque was influenced by Sarmatism, the culture of the Polish nobility (''szlachta''). It developed after the Swedish Deluge. Michael J. MikoЕ›, ''Polish Baroque and Enlightenment Literature: An Anthology''. Ed. Michael J. MikoЕ›. Columbus, Ohio/Bloomington, Indiana: Slavica Publishers. 1996. 104-108.Cultural background/ref> Sarmatism became highly influenced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WЕ‚adysЕ‚aw IV Vasa
Władysław IV Vasa or Ladislaus IV (9 June 1595 – 20 May 1648) was King of Poland, Grand Duke of Lithuania and claimant of the thrones of Monarchy of Sweden, Sweden and List of Russian monarchs, Russia. Born into the House of Vasa as a prince of Poland and of Sweden, Władysław IV was the eldest son of Sigismund III House of Vasa, Vasa and Sigismund's first wife, Anna of Austria (1573–1598), Anna of Austria. Władysław was elected as the tsar of Russia by the Seven Boyars in 1610, when the Polish–Russian War (1609–1618), Polish army captured Moscow, but did not assume the throne because of his father's position and a popular uprising. Nevertheless, until 1634, he used the titular title of grand duke of Moscow. Following his Free election (Poland), election as king of Poland and grand duke of Lithuania in 1632, he was largely successful in defending the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth against foreign invasion, most notably in the Smolensk War of 1632–1634 in which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa (, ; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632 N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden from 1592 to 1599. He was the first Polish sovereign from the House of Vasa. Religiously zealous, he imposed Catholicism across the vast realm, and his crusades against neighbouring states marked Poland's largest territorial expansion. As an enlightened despot, he presided over an era of prosperity and achievement, further distinguished by the transfer of the country's capital from Kraków to Warsaw. Sigismund was the son of King John III of Sweden and his first wife, Catherine Jagiellon, daughter of King Sigismund I of Poland. Elected monarch of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1587, he sought to unify Poland and Sweden under one Catholic kingdom, and when he succeeded his deceased father in 1592 the Polish–Swedish union was created. Opposition in Protestant Sweden caused a war against Sigismund headed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KrakГіw
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 (2023), with approximately 8 million additional people living within a radius. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596, and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Kraków Old Town, Old Town was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1978, one of the world's first sites granted the status. The city began as a Hamlet (place), hamlet on Wawel Hill and was a busy trading centre of Central Europe in 985. In 1038, it became the seat of King of Poland, Polish monarchs from the Piast dynasty, and subsequently served as the centre of administration under Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellonian kings and of the Polish–Lithuan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry III Of France
Henry III (; ; ; 19 September 1551 – 2 August 1589) was King of France from 1574 until his assassination in 1589, as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1573 to 1575. As the fourth son of King Henry II of France, he was not expected to inherit the French throne and thus was a good candidate for the vacant throne of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, where he was elected monarch in 1573. During his brief rule, he signed the Henrician Articles into law, recognizing the szlachta's right to freely elect their monarch. Aged 22, Henry abandoned Poland–Lithuania upon inheriting the French throne when his brother, Charles IX, died without issue. France was at the time plagued by the Wars of Religion, and Henry's authority was undermined by violent political factions funded by foreign powers: the Catholic League (supported by Spain and the Pope), the Protestant Huguenots (supported by England and the Dutch) and the Malcontents (led by Henry's own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Academy Of Sciences
The Polish Academy of Sciences (, PAN) is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning. Headquartered in Warsaw, it is responsible for spearheading the development of science across the country by a society of distinguished scholars and a network of research institutes. It was established in 1951, during the early period of the Polish People's Republic following World War II. History The Polish Academy of Sciences is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning, headquartered in Warsaw, that was established by the merger of earlier science societies, including the Polish Academy of Learning (''Polska Akademia UmiejД™tnoЕ›ci'', abbreviated ''PAU''), with its seat in KrakГіw, and the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning (Science), which had been founded in the late 18th century. The Polish Academy of Sciences functions as a learned society acting through an elected assembly of leading scholars and research institutions. The Academy has also, operating throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Poland Province, Crown Of The Kingdom Of Poland
Greater Poland Province () was an administrative division of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from 1569 until 1795. The name of the province comes from the historic land of Greater Poland. The Greater Poland Province consisted initially of twelve voivodeships (after 1768 thirteen voivodeships) and one duchy: # BrzeЕ›Д‡ Kujawski Voivodeship # CheЕ‚mno Voivodeship # Gniezno Voivodeship, est. in 1768 # InowrocЕ‚aw Voivodeship # Kalisz Voivodeship # ЕЃД™czyca Voivodeship # Malbork Voivodeship # Masovian Voivodeship # PЕ‚ock Voivodeship # Pomeranian Voivodeship # PoznaЕ„ Voivodeship # Rawa Voivodeship # Sieradz Voivodeship # Prince-Bishopric of Warmia The location of the Crown Tribunal for the Greater Poland Province (the highest appeal court of the province) was PiotrkГіw Trybunalski, and after the Convocation Sejm (1764) also PoznaЕ„ and Bydgoszcz. Cities The five most influential cities, i.e. Warsaw, PoznaЕ„, GdaЕ„sk, ToruЕ„ and ElblД…g ElblД…g (; ; ) is a city in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |