|
ŇĀupice, Lubusz Voivodeship
ŇĀupice () is a village in the administrative district of Gmina SŇāawa, within Wschowa County, Lubusz Voivodeship, in western Poland. It lies approximately north of SŇāawa, north-west of Wschowa, and east of Zielona G√≥ra. The village has a population of 779. History ŇĀupice was a private church village, administratively located in the KoŇõcian County in the PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship in the Greater Poland Province of the Kingdom of Poland. During the German evacuation from occupied Poland in the final stages of World War II, in January 1945, a German-perpetrated death march of Jewish women from a just dissolved subcamp of the Gross-Rosen concentration camp in SŇāawa SŇāawa (; ) is a town in Wschowa County, Lubusz Voivodeship, in western Poland. As of the 2019 census, SŇāawa had a population of 4,321. It is situated on the eastern shore of Lake SŇāawskie. History The area was part of Poland after the creation ... passed through the village. References Villages in Wschowa C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
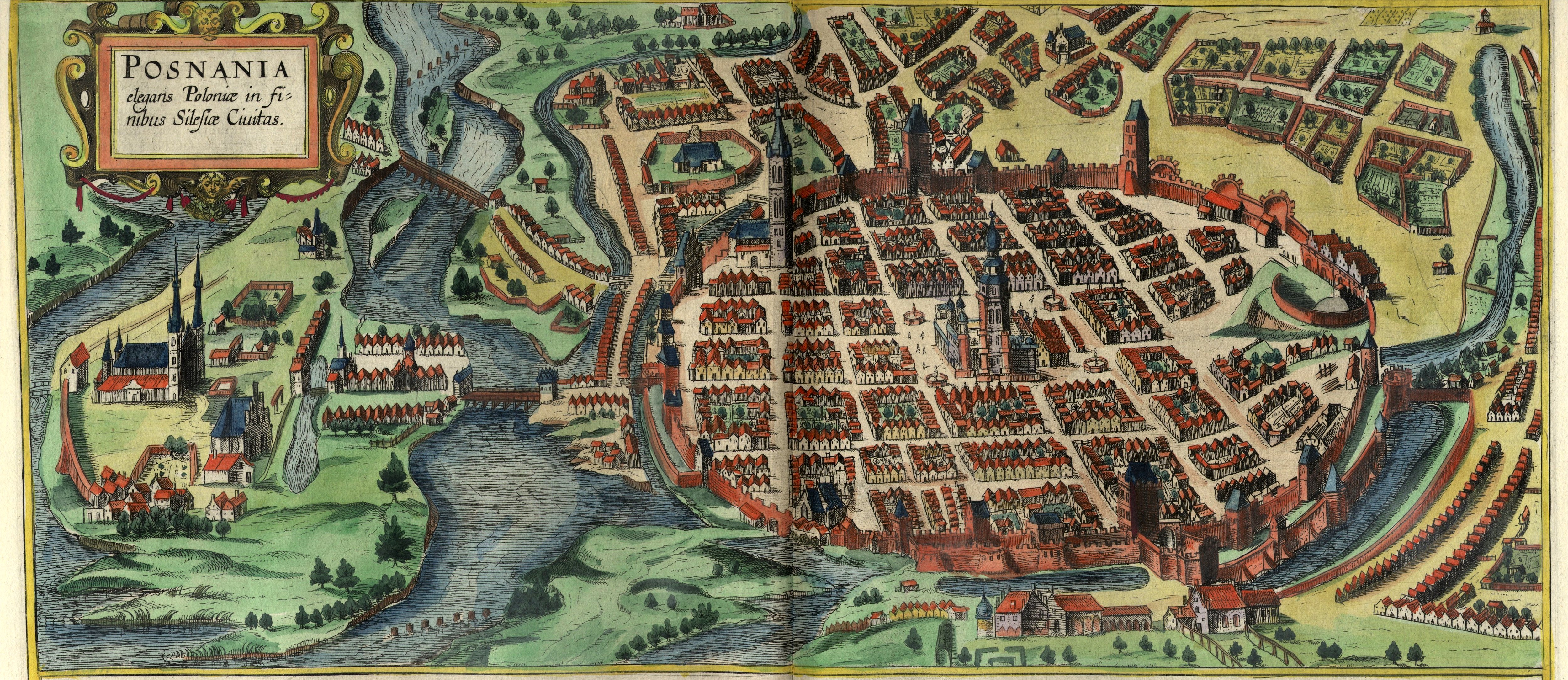
SŇāawa
SŇāawa (; ) is a town in Wschowa County, Lubusz Voivodeship, in western Poland. As of the 2019 census, SŇāawa had a population of 4,321. It is situated on the eastern shore of Lake SŇāawskie. History The area was part of Poland after the creation of the state in the 10th century. Later on, as a result of the fragmentation of Poland into smaller provincial duchies, SŇāawa initially formed part of Greater Poland before it passed to Silesia, and then to the Duchy of GŇāog√≥w The Duchy of GŇāog√≥w (, ) or Duchy of Glogau () was one of the Duchies of Silesia, formed in course of the medieval fragmentation of Poland into smaller provincial duchies. Its capital was GŇāog√≥w in Lower Silesia. It existed in 1177‚Äď1185 an ..., where it remained ruled by the Piast dynasty until 1468. The town was mentioned in a document from 1312. Between 1871 and 1945 the town was part of Germany under the Germanized name ''Schlawa''. In 1937 it was 1938 renaming of East Prussian placenames, renamed '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Marches During The Holocaust
During the Holocaust, death marches () were massive forced transfers of prisoners from one Nazi camp to other locations, which involved walking long distances resulting in numerous deaths of weakened people. Most death marches took place toward the end of World War II, mostly after the summer/autumn of 1944. Hundreds of thousands of prisoners, mostly Jews, from Nazi camps near the Eastern Front were moved to camps inside Germany away from the Allied forces. Their purpose was to continue the use of prisoners' slave labour, to remove evidence of crimes against humanity, and to keep the prisoners to bargain with the Allies. Prisoners were marched to train stations, often a long way; transported for days at a time without food in freight trains; then forced to march again to a new camp. Those who lagged behind or fell were shot. The largest death march took place in January 1945. Nine days before the Soviet Red Army arrived at the Auschwitz concentration camp, the Germans mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 ‚Äď 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Academy Of Sciences
The Polish Academy of Sciences (, PAN) is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning. Headquartered in Warsaw, it is responsible for spearheading the development of science across the country by a society of distinguished scholars and a network of research institutes. It was established in 1951, during the early period of the Polish People's Republic following World War II. History The Polish Academy of Sciences is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning, headquartered in Warsaw, that was established by the merger of earlier science societies, including the Polish Academy of Learning (''Polska Akademia UmiejńôtnoŇõci'', abbreviated ''PAU''), with its seat in Krak√≥w, and the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning (Science), which had been founded in the late 18th century. The Polish Academy of Sciences functions as a learned society acting through an elected assembly of leading scholars and research institutions. The Academy has also, operating throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Poland Province, Crown Of The Kingdom Of Poland
Greater Poland Province () was an administrative division of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from 1569 until 1795. The name of the province comes from the historic land of Greater Poland. The Greater Poland Province consisted initially of twelve voivodeships (after 1768 thirteen voivodeships) and one duchy: # BrzeŇõńá Kujawski Voivodeship # CheŇāmno Voivodeship # Gniezno Voivodeship, est. in 1768 # InowrocŇāaw Voivodeship # Kalisz Voivodeship # ŇĀńôczyca Voivodeship # Malbork Voivodeship # Masovian Voivodeship # PŇāock Voivodeship # Pomeranian Voivodeship # PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship # Rawa Voivodeship # Sieradz Voivodeship # Prince-Bishopric of Warmia The location of the Crown Tribunal for the Greater Poland Province (the highest appeal court of the province) was Piotrk√≥w Trybunalski, and after the Convocation Sejm (1764) also PoznaŇĄ and Bydgoszcz. Cities The five most influential cities, i.e. Warsaw, PoznaŇĄ, GdaŇĄsk, ToruŇĄ and ElblńÖg ElblńÖg (; ; ) is a city in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship (14th Century To 1793)
PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship was the name of several former administrative regions (''wojew√≥dztwo'', rendered as ''voivodeship'' and usually translated as "province") in Poland, centered on the city of PoznaŇĄ, although the exact boundaries changed over the years. PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship was incorporated into the Greater Poland Voivodeship after the Polish local government reforms of 1998. 14th century to 1793 PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship () was established in 1320 and was part of the Greater Poland Voivodeship, until it was annexed by Prussia in 1793. It was in the rule of the Garczynski family for much of the 17th and 18th century. A notable vo√Įvodie includes Stefan GarczyŇĄski (1690‚Äď1756), author, who was opposed to serfdom, amongst other social norms of the time. 1793 to 1921 Between 1793 and 1921, the territory formerly contained in PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship was part of the following territories: South Prussia, the PoznaŇĄ Department of the Duchy of Warsaw, the Grand Duchy of Posen, and the Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zielona Góra
Zielona Góra (; ''Green Mountain''; ) is the largest city in Lubusz Voivodeship, located in western Poland, with 140,403 inhabitants (). The region is closely associated with vineyards and holds an annual Zielona Góra Wine Fest, Wine Fest. Zielona Góra is one of the two capital cities of Lubusz Voivodeship, hosting the Voivodeship sejmik, province's elected assembly, while the seat of the centrally appointed voivode, governor is in the city of Gorzów Wielkopolski. In 1222 Duke Henry the Bearded from the Piast dynasty brought the first settlers to the area. In 1323 Zielona Góra was granted town privileges. The town was incorporated into the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1506 and became part of the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Empire in 1526. It experienced a wave of witch trials in the 17th century. As a result of the First Silesian War, the city became part of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1742. It then was part of the North German Confederation and the German Reich until the end of Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wschowa
Wschowa (pronounced , ) is a town in the Lubusz Voivodeship in western Poland with 13,875 inhabitants (2019). It is the capital of Wschowa County and a significant tourist site containing many important historical monuments. It is part of the historic region of Greater Poland. Once an important Royal city in Poland, royal city of Poland, due to its 18th-century history, it is sometimes called the "unofficial capital of Poland". History Medieval period The territory became part of the emerging Polish state under its first historic ruler Mieszko I in the 10th century. Following the fragmentation of Poland, Wschowa initially formed part of the Duchy of Greater Poland, and was mentioned in the Bull of Gniezno from 1136. Later on, Wschowa was a border fortress in a region disputed by the Polish dukes of Duchy of Silesia, Silesia and Greater Poland. The Old Polish language, Old Polish name ''Veschow'' was first mentioned in 1248, while the Middle High German name ''Frowenstat Civitas'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church.-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''village'', from Latin ''villńĀticus'', ultimately from Latin ''villa'' (English ''vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship ( ; ; plural: ) is the highest-level Administrative divisions of Poland, administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The administrative divisions of Poland, Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, reduced the number of voivodeships to sixteen. These 16 replaced the 49 subdivisions of the Polish People's Republic, former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Summer Time
Central European Summer Time (CEST, UTC+02:00), sometimes referred to as Central European Daylight Time (CEDT), is the standard clock time observed during the period of summer daylight-saving in those European countries which observe Central European Time (CET; UTC+01:00) during the other part of the year. It corresponds to UTC+02:00, which makes it the same as Eastern European Time, Central Africa Time, South African Standard Time, Egypt Standard Time and Kaliningrad Time in Russia. Names Other names which have been applied to Central European Summer Time are Middle European Summer Time (MEST), Central European Daylight Saving Time (CEDT), and Bravo Time (after the second letter of the NATO phonetic alphabet). Period of observation Since 1996, European Summer Time has been observed between 01:00 UTC (02:00 CET and 03:00 CEST) on the last Sunday of March, and 01:00 UTC on the last Sunday of October; previously the rules were not uniform across the European Union. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |