|
Ķemeri National Park
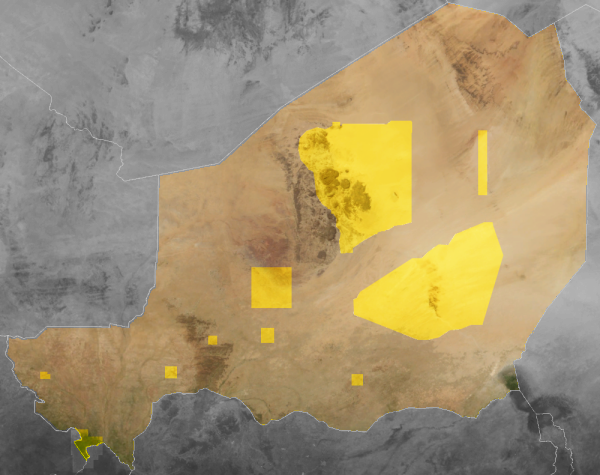
Ķemeri National Park () is a national park located west of the city of Jūrmala, Latvia. Established in 1997, Ķemeri is the third largest national park in the country by area, covering an area of 381.65 km2. The territory of the park is mostly occupied by forests and mires, the most significant of them being The Great Ķemeri Bog (). There are also several lakes, that are former lagoons of the Littorina Sea. Lake Kaņieris is a Ramsar site. The park also protects the famous natural mineral-springs and muds, used for centuries because of their therapeutic nature. The springs led to development of many resorts, spas, and sanitariums in the 19th century. Ecosystem Forests occupy 57% of the total area of the park. Fragmented mosaic distribution of the forests is not typical for the territory, forests are relatively evenly distributed in the whole area of the national park with some inclusion of meadows and areas not covered in forest. Bogs occupy 24% of the total area of Ķ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protected Planet
The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) is the largest assembly of data on the world's terrestrial and marine protected areas, containing more than 260,000 protected areas as of August 2020, with records covering 245 countries and territories throughout the world. The WDPA is a joint venture between the United Nations Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring CentreUNEP-WCMC and the International Union for Conservation of NatureIUCN World Commission on Protected AreasWCPA. Data for the WDPA is collected from international convention secretariats, governments and collaborating NGOs, but the role of custodian is allocated to the Protected Areas Programme of UNEP-WCMC, based in Cambridge, UK, who have hosted the database since its creation in 1981. The WDPA delivers invaluable information to decision-makers around the world, particularly in terms of measuring the extent and effectiveness of protected areas as an indicator for meeting global biodiversity targets. In Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wood Sandpiper
The wood sandpiper (''Tringa glareola'') is a small wader belonging to the sandpiper family Scolopacidae. A Eurasian species, it is the smallest of the shanks, a genus of mid-sized, long-legged waders that largely inhabit freshwater and wetland environments, as opposed to the maritime or coastal habitats of other, similar species. Taxonomy The wood sandpiper was formally described in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under the current binomial name ''Tringa glareola''. Linnaeus cited his own ''Fauna Svecica'' that had been published in 1746. He specified the type locality as Europe but it is now restricted to Sweden. The species is considered to be monotypic: no subspecies are recognised. The genus name, ''Tringa'', is the Neo-Latin name given to the green sandpiper (''Tringa ochropus'') in 1599 by Aldrovandus, based on the Ancient Greek ''trungas'', a "thrush-sized, white-rumped, tail-bobbing" wading bird mentioned by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
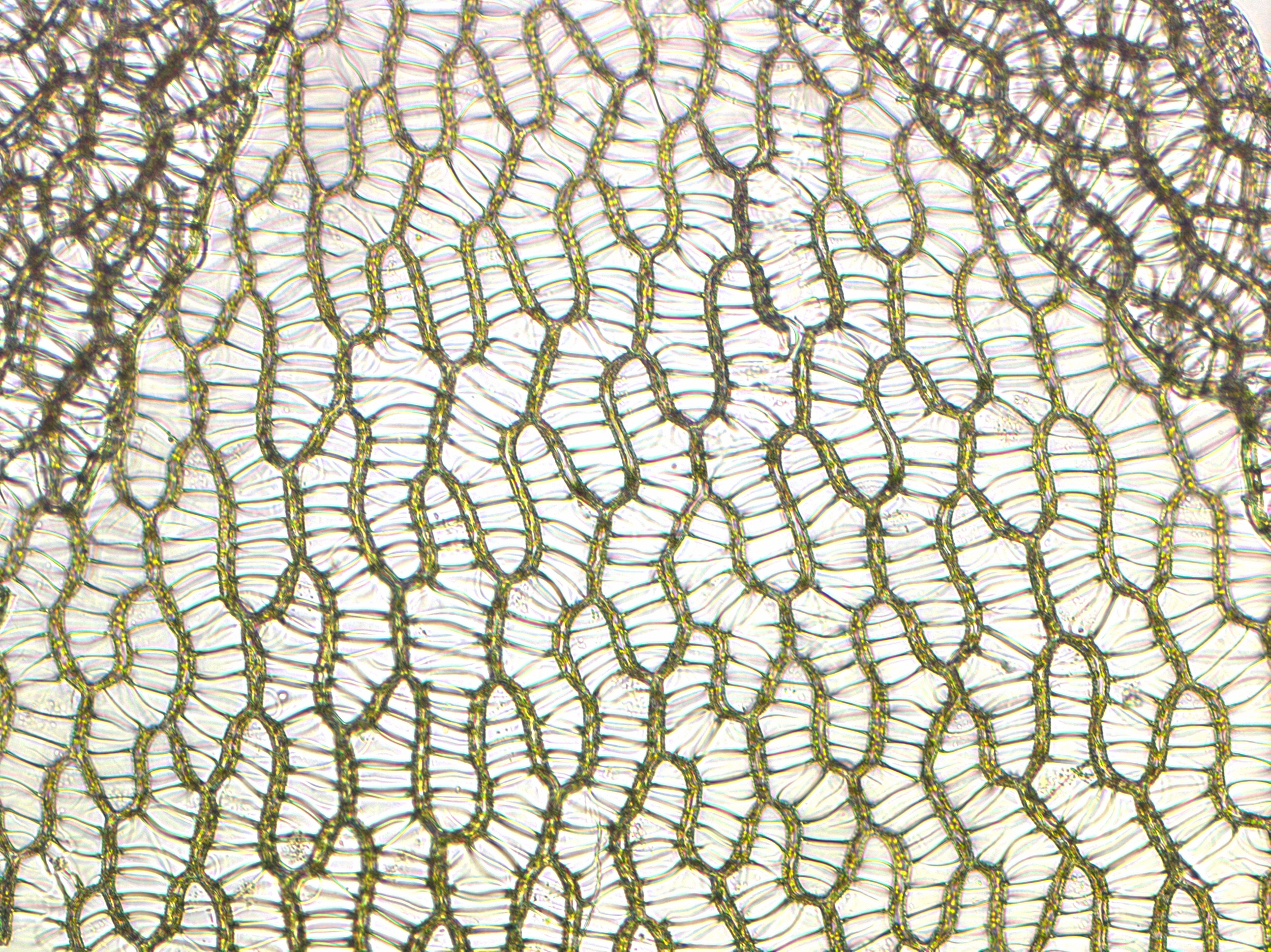
Sphagnum
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225–229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As ''Sphagnum'' moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, ''Sphagnum'' can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing ''Sphagnum'' as 'habitat manipulators' or 'autogenic ecosystem engineers'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and Calcifuge, ericaceous shrubs, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pinus Sylvestris
''Pinus sylvestris'', the Scots pine (UK), Scotch pine (US), Baltic pine, or European red pine is a species of tree in the pine family Pinaceae that is native plant, native to Eurasia. It can readily be identified by its combination of fairly short, blue-green leaves and orange-red bark. Description ''Pinus sylvestris'' is an evergreen coniferous tree growing up to in height and in trunk diameter when mature, exceptionally over tall and in trunk diameter on very productive sites. The tallest on record is a tree over 210 years old growing in Estonia which stands at . The lifespan is normally 150–300 years, with the oldest recorded specimens in Lapland (Finland), Lapland, Northern Finland over 760 years. The Bark (botany), bark is thick, flaky and orange-red when young to scaly and gray-brown in maturity, sometimes retaining the former on the upper portion. The habit of the mature tree is distinctive due to its long, bare and straight trunk topped by a rounded or flat- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Drosera
''Drosera'', which is commonly known as the sundews, is one of the largest genus, genera of carnivorous plants, with at least 194 species. 2 volumes. These members of the family Droseraceae lure, capture, and digest insects using stalked mucilage, mucilaginous glands covering their leaf surfaces. The insects are used to supplement the poor mineral nutrition of the soil in which the plants grow. Various species, which vary greatly in size and form, are native to every continent except Antarctica. Charles Darwin performed much of the early research into ''Drosera'', engaging in a long series of experiments with ''Drosera rotundifolia'' which were the first to confirm carnivory in plants. In an 1860 letter, Darwin wrote, “…at the present moment, I care more about ''Drosera'' than the origin of all the species in the world.” Taxonomy The botanical name from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''drosos'' "dew, dewdrops" refer to the glistening drops of mucilage at the tip of the gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Andromeda Polifolia
''Andromeda polifolia'', common name bog-rosemary, is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae, native to northern parts of the Northern Hemisphere. It is the only member of the genus ''Andromeda'', and is only found in bogs in cold peat-accumulating areas. ''Andromeda glaucophylla'' is a synonym of ''A. polifolia'' var. ''latifolia''. Description It is a small shrub growing to (rarely to ) tall with slender stems. The leaves are evergreen, alternately arranged, lanceolate, long and broad, dark green above (purplish in winter) and white beneath with the leaf margins curled under. The flowers are bell-shaped, white to pink, long; flowering is in late spring to early summer. The fruit is a small capsule containing numerous seeds. There are two varieties, treated as distinct species by some botanists: *''Andromeda polifolia'' var. ''polifolia''. Northern Europe and Asia, northwestern North America. *''Andromeda polifolia'' var. ''latifolia'' Aiton 789/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rhynchospora Alba
''Rhynchospora alba'', the white beak-sedge, is a plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. It is a tufted herbaceous perennial around 50 cm tall, with white inflorescences that flower in August. The fruit of the sedge is a small achene with a characteristic beak-like cap. It is dispersed by wind or falls by gravity, leading to individuals existing in tight clumps. The species favours wet, acidic and nutrient poor soils, thriving in ''Sphagnum''-dominated bogs, but also peaty grasslands. As such, it is often used as a positive indicator for bog and mire ecosystem health. The species was first described by Linnaeus in 1753 under a different genus and name, ''Schoenus albus'', but was subsequently reclassified into the novel genus ''Rhynchospora'' by Vahl in 1805. It has a wide range across the Northern Hemisphere, extending from the inland wetlands of North America, across Europe to the Korean Peninsula. Due to this large range, there is considerable variation between populations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ledum Palustre
''Rhododendron tomentosum'' ( syn. ''Ledum palustre''), commonly known as marsh Labrador tea, northern Labrador tea, marsh rosemary or wild rosemary, is a flowering plant in the subsection '' Ledum'' of the large genus ''Rhododendron'' in the family Ericaceae. Description It is a low shrub growing to 50 cm (rarely up to 120 cm) tall with evergreen leaves 12–50 mm long and 2–12 mm broad. The flowers are small, with a five-lobed white corolla, and produced several together in a corymb 3–5 cm diameter. They emit strong smell to attract bees and other pollinating insects. Distribution and habitat It grows in northern latitudes in North America, Greenland, Canada, and Alaska, in Europe in the northern and central parts, and in Asia south to northern China, Korea and Japan. It grows in peaty soils, shrubby areas, moss and lichen tundra. Chemical compounds All parts of the plant contain poisonous terpenes that affect the central nervous system. First ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Calluna Vulgaris
''Calluna vulgaris'', common heather, ling, or simply heather, is the sole species in the genus ''Calluna'' in the flowering plant family Ericaceae. It is a low-growing evergreen shrub growing to tall, or rarely to and taller, and is found widely in Europe and Asia Minor on acidic soils in open sunny situations and in moderate shade. It is the dominant plant in most heathland and moorland in Europe, and in some bog vegetation and acidic pine and oak woodland. It is tolerant of grazing and regenerates following occasional burning, and is often managed in nature reserves and grouse moors by sheep or cattle grazing, and also by light burning. Description ''Calluna'' can reach in height. It has small-scale leaves (less than 2–3 mm long) borne in opposite and decussate pairs, whereas those of '' Erica'' are generally larger and in whorls of 3–4, sometimes 5. Clive Stace, (2010) ''New Flora of the British Isles'', 3rd edition. Cambridge University Press. It flowers from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |