|
ؤگل؛§m Dئ،i District
ؤگل؛§m Dئ،i —ة™mث¨ث©:jة™ثگjث§ث§is a former rural district of Cأ Mau province in the Mekong Delta region of Vietnam. History Middle Ages Before the XIX century, most of Cأ Mau province was still a mangrove forest with low population and there was also very little information which were recorded by officials. In the 17th year of Minh Mل»‡nh (1836), "ؤگل؛§m Dئ،i area" (xل»© ؤگل؛§m Dئ،i, "land of bat swamps") was first mentioned in ''ؤگل؛،i Nam nhل؛¥t thل»‘ng chأ''. However, this was not yet an official name but just a way to call a area of many fields for convenient demographic statistics. Just know that ؤگل؛§m Dئ،i area was next to "ؤگل؛§m Quل؛، area" (xل»© ؤگل؛§m Quل؛،, "land of crow swamps"), and both of them belong to Long Xuyأھn rural district of Hأ Tiأھn province. It was not until Cochinchina became a whole colony of the French Republic in 1867, an official administrative unit called ؤگل؛§m Dئ،i rural district (huyل»‡n ؤگل؛§m Dئ،i) that appeared. The rural district was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huyل»‡n
Districts (), also known as rural districts or counties, are one of several types of second-tier administrative subdivisions of Vietnam, the other types being List of urban districts of Vietnam, urban districts (), Provincial city (Vietnam), provincial cities (), Municipal city (Vietnam), municipal cities (), and District-level town (Vietnam), district-level towns (). The districts are subdivisions of the first-tier divisions, namely the provinces of Vietnam, provinces and municipalities of Vietnam, municipalities. Districts are subdivided into third-tier units, namely Commune-level town (Vietnam), townships and Commune (Vietnam), communes. Districts and the whole second-tier of administrative subdivisions of Vietnam will be eliminated by 2025, following a major governmental reform. History The districts existed since the 15th century. Prior to 1945 the ''huyل»‡n'' ( vi-hantu, :wikt:縣, 縣) was also called district and earlier "sub-prefecture" of the prefectures, or phل»§ into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
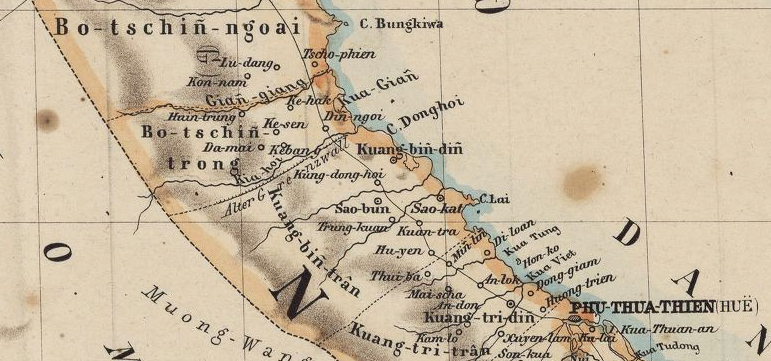
Cochinchina
Cochinchina or Cochin-China (, ; ; ; ; ) is a historical exonym and endonym, exonym for part of Vietnam, depending on the contexts, usually for Southern Vietnam. Sometimes it referred to the whole of Vietnam, but it was commonly used to refer to the region south of the Gianh River. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Vietnam was divided between the Trل»‹nh lords to the north and the Nguyل»…n lords to the south. The two domains bordered each other on the Son River (Vietnam), Son River. The northern section was called Tonkin by Europeans, and the southern part, , was called Cochinchina by most Europeans and Quinam by the Dutch East India Company, Dutch. Jean-Louis Taberd, in his 1838 map, called Tonkin as "Cocincina exterior" () and "Cochin China" as "Cocincina interior" (). In this classic 1838 map, the Gianh River is north of "Lإ©y Sل؛§y" (an incorrect pronunciation and spelling of "Lإ©y Thل؛§y") demarcating "Cocincina exterior" (or "Outer Annam") from "Cocincina interior" (or "In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Republic Of Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam (RVN; , VNCH), was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975. It first garnered Diplomatic recognition, international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the French Union, with its capital at Saigon, before becoming a republic in 1955, when the southern half of Vietnam was a member of the Western Bloc during part of the Cold War after the 1954 Geneva Conference, 1954 division of Vietnam. South Vietnam was bordered by North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) to the north, Kingdom of Laos, Laos to the northwest, Khmer Republic, Cambodia to the southwest, and Thailand across the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. Its sovereignty was recognized by the United States and 87 other nations, though it failed to gain admission into the United Nations as a result of a Soviet Union, Soviet veto in 1957. It was succeeded by the Provisional Revolutionary Government of the Republic of South Vietnam, Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bل؛،c Liأھu Province
Bل؛،c Liأھu was a former province of Vietnam. It is a coastal province, and is situated in the Mekong Delta region of the southern part of the country. On June 12th, 2025, Bل؛،c Liأھu was incorporated into Cأ Mau province. Administrative divisions Bل؛،c Liأھu is subdivided into seven district-level sub-divisions: * 5 districts: :* ؤگأ´ng Hل؛£i :* Hأ²a Binh :* Hل»“ng Dأ¢n :* Phئ°ل»›c Long :* Vؤ©nh Lل»£i * 1 district-level town: :* Giأ، Rai * 1 provincial city: ** Bل؛،c Liأھu (capital) They are further subdivided into seven commune-level towns (or townlets), 50 communes, and seven wards. Geography Bل؛،c Liأھu is located on Mekong Delta, although it is actually located slightly to the south of the Mekong's main outflows. Bل؛،c Liأھu is around south of Cل؛§n Thئ،, the largest city in the Mekong Delta. Economy The most important parts of Bل؛،c Liأھu's economy are rice farming, fishing, food processing, and clothing manufacturing. History Bل؛،c Liأھu Province was esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Vietnam
The State of Vietnam (; chل»¯ Hأ،n: هœ‹ه®¶è¶ٹهچ—; ) was a state in Southeast Asia that existed from 1949 until 1955, first as an associated state of the French Union and later as an independent state (from 20 July 1954 to 26 October 1955). The state claimed authority over all of Vietnam during the First Indochina War, although large parts of its territory were controlled by the Democratic Republic of Vietnam. Established in 1949, the State of Vietnam was formed within the framework of the French Union as a compromise between Vietnamese nationalists and the French, in opposition to the communists. It gained international recognition in 1950 and aligned politically with the Western Bloc. Former emperor Bل؛£o ؤگل؛،i became Chief of State. Following the 1954 Geneva Accords between the communist Viet Minh and the French, the State of Vietnam lost its remaining foothold in the northern half of the country, where most rural areas were already controlled by the Viet Minh. Ngأ´ ؤگأ¬nh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors and relatives, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads ( cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most only have one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have independently evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs at least twenty-five times via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
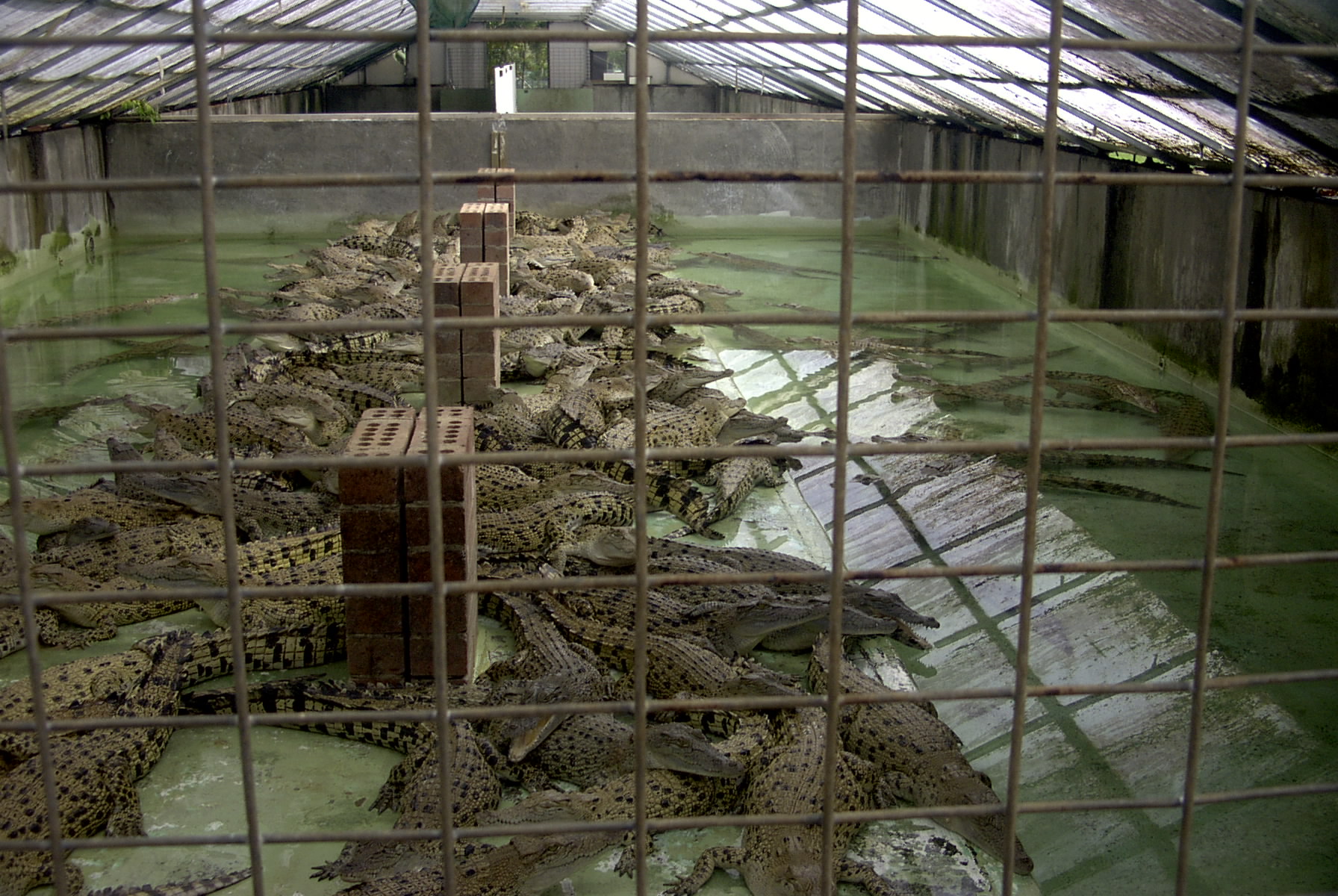
Crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large, semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term "crocodile" is sometimes used more loosely to include all extant taxon, extant members of the order (biology), order Crocodilia, which includes the alligators and caimans (both members of the family Alligatoridae), the gharial and false gharial (both members of the family Gavialidae) as well as other extinct Taxon, taxa. Crocodile Measurement, size, Morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour and ecology differ among species. However, they have many similarities in these areas as well. All crocodiles are semiaquatic and tend to congregate in freshwater habitats such as rivers, lakes, wetlands and sometimes in brackish water and Seawater, saltwater. They are carnivorous animals, feeding mostly on vertebrates such as fish, reptiles, birds and mammals, and sometimes on invertebrates such as mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a Canopy (biology), canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, ''Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA), Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the largest Terrestrial ecosystem, terrestrial ecosystems of Earth by area, and are found around the globe. 45 percent of forest land is in the Tropical forest, trop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow under atmospheric pressure, and can be thought of as artificial rivers. In most cases, a canal has a series of dams and locks that create reservoirs of low speed current flow. These reservoirs are referred to as ''slack water levels'', often just called ''levels''. A canal can be called a navigation canal when it parallels a natural river and shares part of the latter's discharges and drainage basin, and leverages its resources by building dams and locks to increase and lengthen its stretches of slack water levels while staying in its valley. A canal can cut across a drainage divide atop a ridge, generally requiring an external water source above the highest elevation. The best-known example of such a canal is the Panama Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
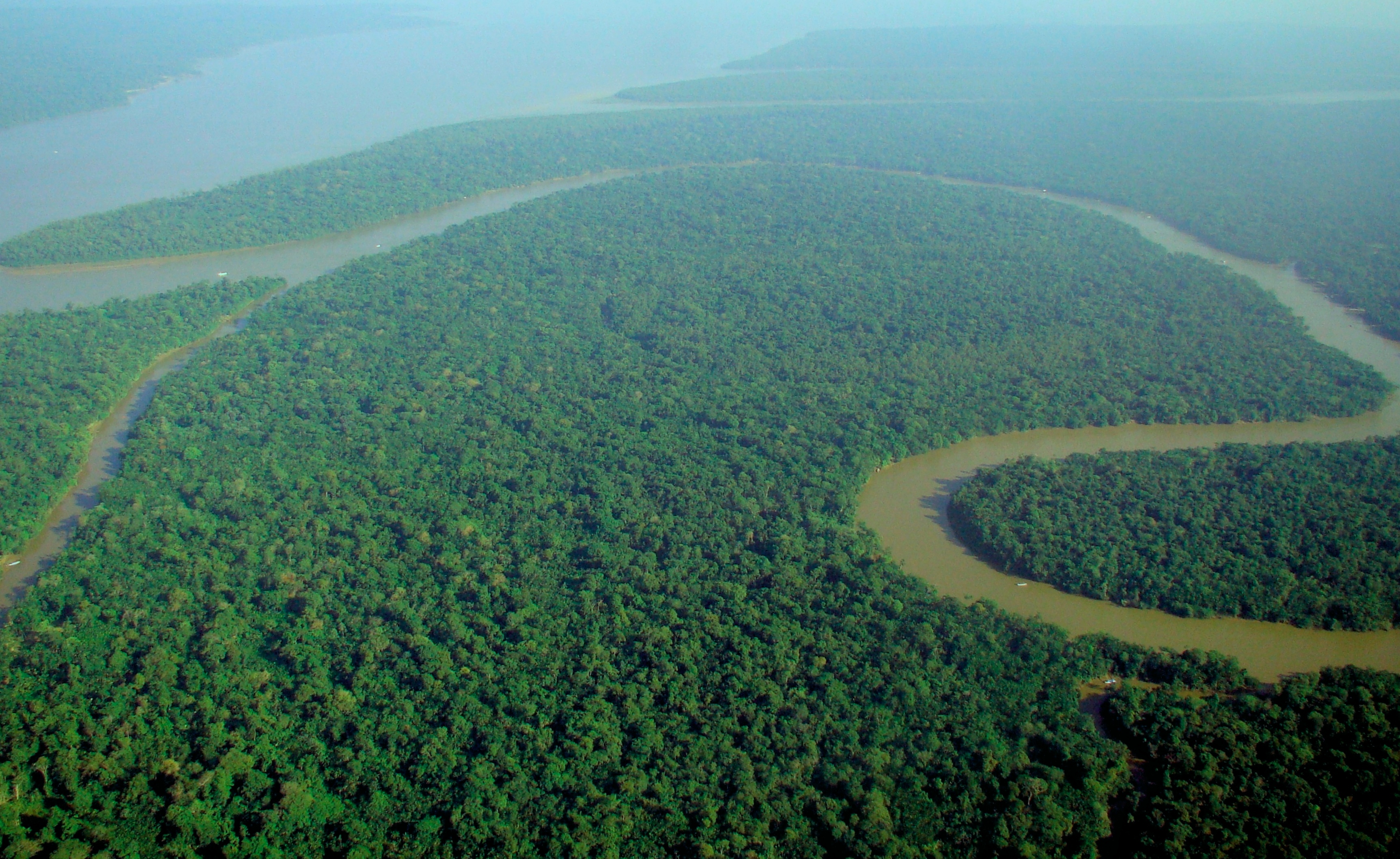
River
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the Runoff (hydrology), runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their Bank (geography), banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sedime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th Century
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was Abolitionism, abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |