|
Činovnička Kolonija
Činovnička Kolonija (, meaning "Clerks' Colony") is an urban neighborhood of Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. It is part of the Voždovac municipality and is a sub-neighborhood of the neighborhood of Voždovac itself. Built in 1930, it was one of the earliest planned neighborhoods of Belgrade. Location The neighborhood occupies the northwestern section of Voždovac municipality. It is delineated by the elementary school "Karađorđe" to the north, Voždovac Church to the south and by two major city streets, Kumodraška to the east and the Liberation Boulevard to the west. Činovnička Kolonija borders the neighborhood of Autokomanda in the north, Dušanovac in the northeast, Voždovac in the east, Byford's Forest in the southeast and Dedinje, Diplomatska Kolonija and Stadion in the east. History Origin After the liberation in World War I in 1918, Voždovac was placed under the Belgrade's administrative rule. Despite economic hardships caused by the war, the growth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Belgrade Neighbourhoods And Suburbs
A list is a Set (mathematics), set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole".Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of ''The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomatska Kolonija
Diplomatska Kolonija ( sr-cyr, Дипломатска Колонија) is an urban neighborhood of Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. It is located in Belgrade's municipality of Savski Venac. Diplomatska kolonija is a small sub-neighborhood of Dedinje, located in its eastern section, right behind the ''Dragiša Mišović'' hospital and south of the Rajko Mitić Stadium, football stadium of the FK Crvena Zvezda. The neighborhood of Stadion is just north of it. It is generally centered on the street of the same name ''Diplomatska kolonija'' (Serbian for "diplomatic colony"). It is considered a fancy and expensive area of Belgrade, with new building of RTV Pink Pink is a privately owned, national brand of radio stations and TV channels in Serbia , image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg , national_motto = , image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg , national_anthem ... in the western section of the neighborhood. A street crossing the diplom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnasium (school)
''Gymnasium'' (and Gymnasium (school)#By country, variations of the word) is a term in various European languages for a secondary school that prepares students for higher education at a university. It is comparable to the US English term ''University-preparatory school, preparatory high school'' or the British term ''grammar school''. Before the 20th century, the gymnasium system was a widespread feature of educational systems throughout many European countries. The word (), from Greek () 'naked' or 'nude', was first used in Ancient Greece, in the sense of a place for both physical and intellectual education of young men. The latter meaning of a place of intellectual education persisted in many European languages (including Albanian language, Albanian, Bulgarian language, Bulgarian, Czech language, Czech, Dutch language, Dutch, Estonian language, Estonian, Greek language, Greek, German language, German, Hungarian language, Hungarian, Macedonian language, Macedonian, Montene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eaves
The eaves are the edges of the roof which overhang the face of a wall and, normally, project beyond the side of a building. The eaves form an overhang to throw water clear of the walls and may be highly decorated as part of an architectural style, such as the Chinese dougong bracket systems. Etymology and usage According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', ''eaves'' is derived from the Old English (singular), meaning "edge", and consequently forms both the singular and plural of the word. This Old English word is itself of Germanic origin, related to the German dialect ''Obsen'', and also probably to ''over''. The Merriam-Webster dictionary lists the word as ''eave'' but notes that it is "usually used in plural". Function The primary function of the eaves is to keep rain water off the walls and to prevent the ingress of water at the junction where the roof meets the wall. The eaves may also protect a pathway around the building from the rain, prevent erosion of the footi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilaster
In architecture, a pilaster is both a load-bearing section of thickened wall or column integrated into a wall, and a purely decorative element in classical architecture which gives the appearance of a supporting column and articulates an extent of wall. As an ornament it consists of a flat surface raised from the main wall surface, usually treated as though it were a column, with a capital at the top, plinth (base) at the bottom, and the various other column elements. In contrast to a Classical pilaster, an engaged column or buttress can support the structure of a wall and roof above. In human anatomy, a pilaster is a ridge that extends vertically across the femur, which is unique to modern humans. Its structural function is unclear. Definition A pilaster is foremost a load-bearing architectural element used widely throughout the world and its history where a structural load is carried by a thickened section of wall or column integrated into a wall. It is also a purel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
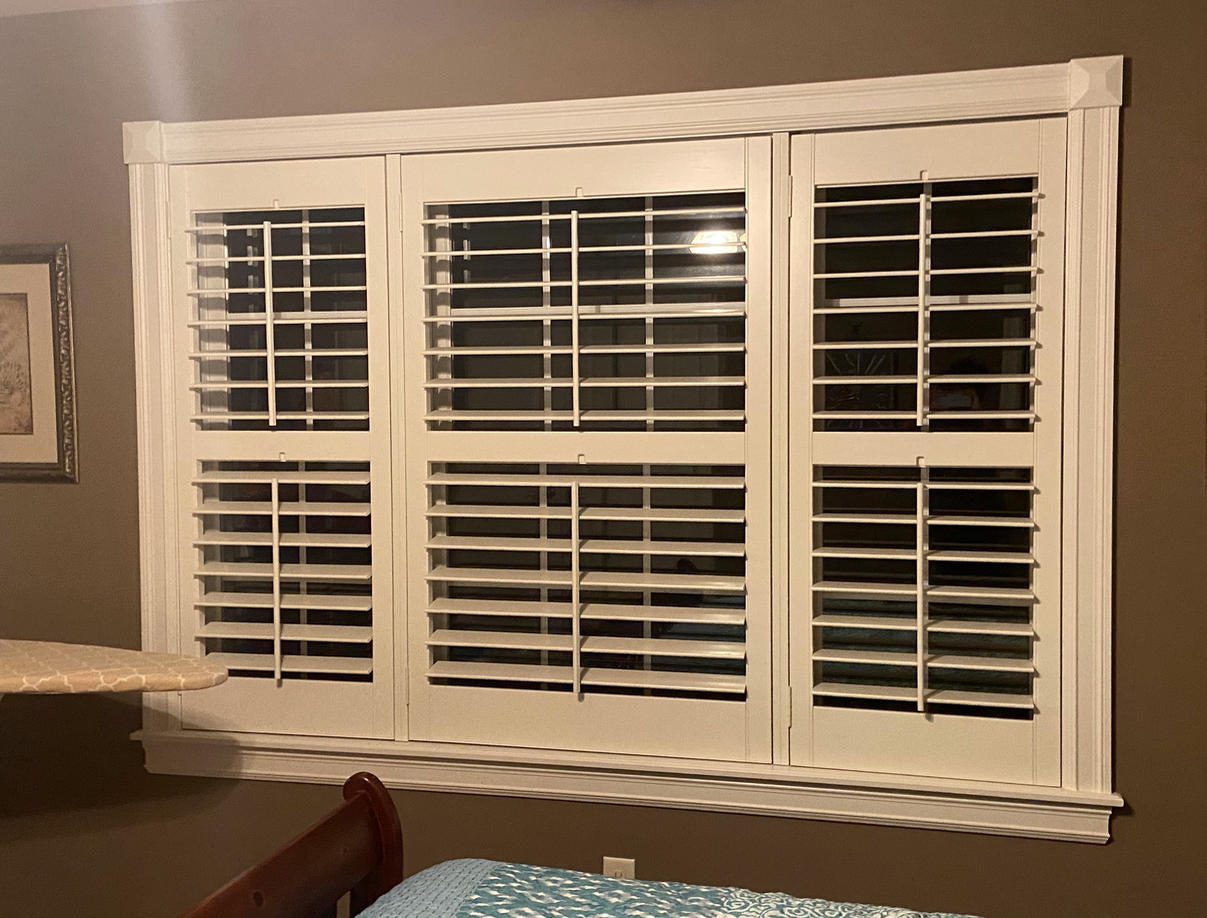
Window Shutter
A window shutter is a solid and stable window covering usually consisting of a frame of vertical stiles and horizontal rails (top, centre and bottom). Set within this frame can be louvers (both operable or fixed, horizontal or vertical), solid panels, fabric, glass and almost any other item that can be mounted within a frame. Shutters may be employed for a variety of reasons, including controlling the amount of sunlight that enters a room, to provide privacy, security, to protect against weather or unwanted intrusion or damage and to enhance the aesthetics of a building. Depending on the application, and the construction of the window frame, shutters can be mounted to fit within the opening or to overlap the opening. The term window shutter includes both interior shutters, used on the inside of a house or building, and exterior shutters, used on the outside of a structure. On some styles of buildings it is common to have shutters to cover the doors as well as the windows. Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagoda
A pagoda is a tiered tower with multiple eaves common to Thailand, Cambodia, Nepal, India, China, Japan, Korea, Myanmar, Vietnam, and other parts of Asia. Most pagodas were built to have a religious function, most often Buddhist, but sometimes Taoist or Hindu, and were often located in or near viharas. The pagoda traces its origins to the stupa, while its design was developed in ancient India. Chinese pagodas () are a traditional part of Chinese architecture. In addition to religious use, since ancient times Chinese pagodas have been praised for the spectacular views they offer, and many classical poems attest to the joy of scaling pagodas. The oldest and tallest pagodas were built of wood, but most that survived were built of brick or stone. Some pagodas are solid with no interior. Hollow pagodas have no higher floors or rooms, but the interior often contains an altar or a smaller pagoda, as well as a series of staircases for the visitor to climb to see the view from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipped Roof
A hip roof, hip-roof or hipped roof, is a type of roof where all sides slope downward to the walls, usually with a fairly gentle slope, with variants including tented roofs and others. Thus, a hipped roof has no gables or other vertical sides to the roof. A square hip roof is shaped like a pyramid. Hip roofs on houses may have two triangular sides and two trapezoidal ones. A hip roof on a rectangular plan has four faces. They are almost always at the same pitch or slope, which makes them symmetrical about the centerlines. Hip roofs often have a consistent level fascia, meaning that a gutter can be fitted all around. Hip roofs often have dormer slanted sides. Construction Hip roofs can be constructed on a wide variety of plan shapes. Each ridge is central over the rectangle of the building below it. The triangular faces of the roof are called the hip ends, and they are bounded by the hips themselves. The "hips" and hip rafters sit on an external corner of the building and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
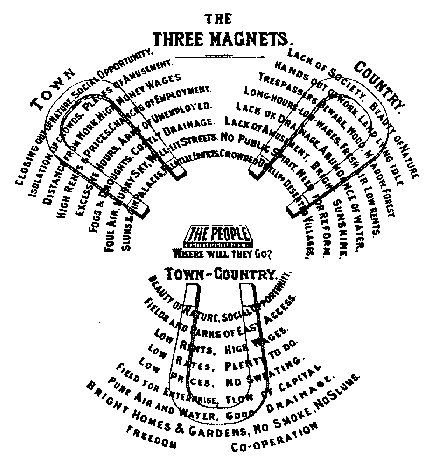
Ebenezer Howard
Sir Ebenezer Howard (29 January 1850 – 1 May 1928) was an English urban planner and founder of the garden city movement, known for his publication '' To-Morrow: A Peaceful Path to Real Reform'' (1898), the description of a utopian city in which people live harmoniously together with nature. The publication resulted in the founding of the garden city movement, and the building of the first garden city, Letchworth Garden City, commenced in 1903. The second true Garden City was Welwyn Garden City (1920) and the movement influenced the development of several model suburbs in other countries, such as Forest Hills Gardens designed by F. L. Olmsted Jr. in 1909, Radburn, New Jersey (1923), Pinelands, Cape Town, and the four Suburban Resettlement Program towns of the 1930s, Greenbelt, Maryland, Greenhills, Ohio, Greenbrook, New Jersey, and Greendale, Wisconsin. Howard aimed to reduce the alienation of humans and society from nature, and hence advocated garden citiesClark, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garden City Movement
The garden city movement was a 20th century urban planning movement promoting satellite communities surrounding the central city and separated with Green belt, greenbelts. These Garden Cities would contain proportionate areas of residences, industry, and agriculture. Ebenezer Howard first posited the idea in 1898 as a way to capture the primary benefits of the countryside and the city while avoiding the disadvantages presented by both. In the early 20th century, Letchworth and Welwyn Garden City were built near London according to Howard's concept and many other garden cities inspired by his model have since been built all over the world. History Conception Inspired by the utopian novel ''Looking Backward'' by Edward Bellamy, and Henry George's work ''Progress and Poverty'', Howard published the book '': a Peaceful Path to Real Reform'' in 1898 (reissued in 1902 as ''Garden Cities of To-morrow''). His idealised garden city would house 32,000 people on a site of . Howard's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SK Jugoslavija
Sportski klub Jugoslavija ( sr-Cyrl, Cпортски клуб Југославија), commonly known as Jugoslavija, was a Serbian football club based in Belgrade. It was originally formed as SK Velika Srbija in 1913 and changed its name to SK Jugoslavija in 1919. They were among the most popular Serbian and Yugoslav clubs, and they were nicknamed as "Crveni" (''The Reds'') because of their red shirts, in opposition to their greatest rivals BSK, who wore blue and were known as "Plavi" (''The Blues''). Until 1941 the sports society Jugoslavija, beside football, also included sections for athletics, cycling, winter sports, basketball, boxing, wrestling, swimming, and table tennis. History The club was founded on August 6, 1913Istorija o kojoj se ne priča at mojacrvenazvezda.n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Of Yugoslavia
Maria (born Princess Maria of Romania; 6 January 1900 – 22 June 1961), known in Serbian as Marija Karađorđević ( sr-Cyrl, Марија Карађорђевић), was Queen of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes from 1922 to 1929 and Queen of Yugoslavia from 1929 to 1934 as the wife of Alexander I of Yugoslavia, King Alexander I. She was the mother of Peter II of Yugoslavia, King Peter II. Her citizenship was revoked, and her property was confiscated by the Yugoslav communist regime in 1947, but she was posthumously rehabilitated in 2014. Early life Maria was born on 6 January 1900, at Friedenstein Palace in Gotha, a town in Thuringia, in the German Empire. She was named after her maternal grandmother, Grand Duchess Maria Alexandrovna of Russia, and was known as ''Mignon'' in the family to distinguish her from her mother. Her parents were Prince Ferdinand I of Romania, Ferdinand of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen – Ferdinand I of Romania – and Princess Marie of Romania, Marie of Edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |