|
ДЂfДЃqД« Khoja Holy War
In 1759, the Qing dynasty of China defeated the Dzungar Khanate and completed the conquest of Dzungaria. Concurrent with this conquest, the Qing occupied the Altishahr region in modern southern Xinjiang, which had been settled by Muslims who followed the political and religious leadership of Afaq Khoja. After the Qing conquest, the Chinese began to incorporate Altishahr and the Tarim Basin into their empire. The territory along with Dzungaria came to be known as Xinjiang. Although the followers of Afaq Khoja known as the ДЂfДЃqД« Khojas resisted Qing rule, their rebellion was put down and the khojas were removed from power. Beginning at that time and lasting for approximately one hundred years, the ДЂfДЃqД« Khojas waged numerous military campaigns in an effort to retake Altishahr from the Qing. Khoja background and rivalries The Khojas of Central Asia were a NaqshbandД« Sufi lineage founded by Ahmad KДЃsДЃnД« (1461-1542), known as MakhdЕ«m-i-Azam or the "Great Master". A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altishahr
Altishahr (, , ; romanized: ''Altä-şähär'' or ''Alti-şähär''), also known as Kashgaria, or Yettishar is a historical name for the Tarim Basin region used in the 18th and 19th centuries. The term means "Seven Cities" in Turkic languages, referring to oasis towns along the rim of the Tarim, including Kashgar, in what is now southern Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China. Etymology The name Altishahr is derived from the Turkic word Alti ('Six') and Persian word ''shahr'' ('city'). Newby 20054 n.10/ref> The ''Altishahr'' term was used by Turkic-speaking inhabitants of the Tarim Basin in the 18th and 19th century, and adopted by some Western sources in the 19th century. Other local words for the region included Dorben Shahr ('Four Cities') and Yeti Shahr ('Seven Cities'). Another Western term for the same region is Kashgaria. Qing sources refer to the region primarily as Nanlu, or the 'Southern Circuit'. Other Qing terms for the region include Huijiang (, the 'Muslim Fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buzurg Khan
Buzurg may refer to: *Bozorgmehr, legendary Sassanian prime-minister of Persia *Bisanda Buzurg, a town and a nagar panchayat in Banda district in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India *Hasan Buzurg, the first of several de facto independent Jalayirid rulers of Iraq and central Iran *Kavir Buzurg, (meaning great salt marsh), lies in the centre of the Dasht-e Kavir, which is a desert located in the middle of the Iranian plateau *Mahtinya Buzurg, a village in Domariaganj, Uttar Pradesh, India *Shahri Buzurg District Shahr-e-Bozorg (; meaning Great City) is one of the 28 districts of Badakhshan province in northeastern Afghanistan. According to latest estimates, approximately 67,000 people live in the district. The district of Shahr-e-Bozorg is located in ..., one of the 29 districts of Badakhshan Province in eastern Afghanistan See also * Bozorg (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ush Rebellion
USH may refer to: * Ush Island, a Russian island in the Sea of Okhotsk * Ush, king of Umma, King or ensi of Umma, a city-state in Sumer, circa 2450 BCE *Ugandan shilling (abbreviated USh), the currency of Uganda *Universal Studios Hollywood Universal Studios Hollywood is a film studio and Amusement park, theme park located in Universal City, California, near Hollywood, Los Angeles. It is one of the oldest and most famous Hollywood film studios still in use. Its official marketin ..., the movie studio and theme park in Los Angeles, California * Ushuaia – Malvinas Argentinas International Airport, in Ushuaia, Argentina (IATA airport code) * Union School Haiti {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanate Of Kokand
The Khanate of Kokand was a Central Asian polity in the Fergana Valley centred on the city of Kokand between 1709 and 1876. It was ruled by the Ming tribe of Uzbeks. Its territory is today divided between Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Kazakhstan. History The Khanate of Kokand was established in 1709 when the emir of the Ming tribe of Uzbeks, Shahrukh declared independence from the Khanate of Bukhara, establishing a state in the eastern part of the Fergana Valley. He built a citadel as his capital in the small town of Kokand, thus starting the Khanate of Kokand. His son, Abdul Kahrim Bey, and grandson, Narbuta Bey, enlarged the citadel, but both were forced to submit as a protectorate, and pay tribute to, the Qing dynasty between 1774 and 1798.Starr. Narbuta Bey’s son Alim was both ruthless and efficient. He hired a mercenary army of Ghalcha highlanders, and conquered the western half of the Fergana Valley, including Khujand and Tashkent. He was assassinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
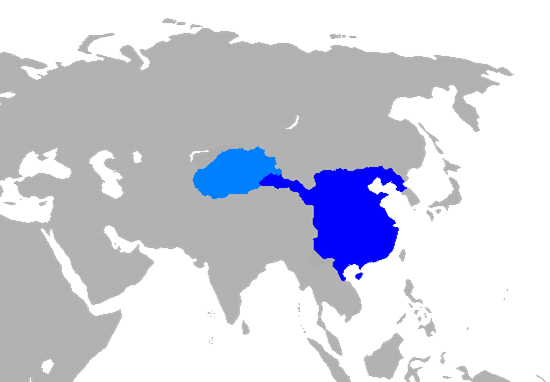
Dzungar Conquest Of Altishahr
The Dzungar conquest of Altishahr resulted in the Tibetan Buddhist Dzungar Khanate in Dzungaria conquering and subjugating the Genghisid-ruled Yarkent Khanate in Altishahr (the Tarim Basin in southern Xinjiang). It put a final end to the independence of the Chagatai Khanate. Conquest The Turkic Muslim sedentary people of the Tarim Basin were originally ruled by the Chagatai Khanate (or its offshoot the Yarkent Khanate) while the nomadic Oirat Dzungar Buddhists in Dzungaria ruled over the Dzungar Khanate. The Dzungar Oirats led by Sengge attacked the Chagatai Khanate during the reign of Abdullah Khan. The Naqshbandi Sufi Khojas, descendants of the Prophet Muhammad, had replaced the Chagatayid Khans as the ruling authority of the Tarim Basin in the early 17th century. There was a struggle between two factions of Khojas, the Afaqi (White Mountain) faction and the Ishaqi (Black Mountain) faction. The Ishaqi defeated the Afaqi, which resulted in the Afaqi Khoja inviting the 5th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarkent Khanate
The Yarkent Khanate, also known as the Yarkand Khanate and the Kashghar Khanate, was a Sunni Muslim Turkic peoples, Turkic state ruled by the Mongols, Mongol descendants of Chagatai Khan. It was founded by Sultan Said Khan in 1514 as a western offshoot of Moghulistan, itself an eastern offshoot of the Chagatai Khanate. It was eventually conquered by the Dzungar Khanate in 1705. Capital Yarkant County, Yarkent served as the capital of the Yarkent Khanate, which was also known as the Yarkent State (''Mamlakati Yarkand''), from the establishment of the Khanate (1514 AD) to its fall (1705 AD). The previous Dughlat state of Mirza Abu Bakr Dughlat (1465–1514) of Kashgar Prefecture, Kashgaria also used Yarkant County, Yarkent as the capital of state. History Background The Khanate was predominantly Uyghurs, Uyghur/Turki; some of its most populated cities were Hotan, Yarkand County, Yarkent, Kashgar, Yengisar County, Yangihissar, Aksu, Xinjiang, Aksu, Uchturpan County, Uchturpan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Xinjiang, Northwestern China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydrological Processes 20.10 (2006): 2207–2216.online 426 KB) Located in China's Xinjiang region, it is sometimes used synonymously to refer to the southern half of the province, that is, Southern Xinjiang or Nanjiang (), as opposed to the northern half of the province known as Dzungaria or Beijiang. Its northern boundary is the Tian Shan mountain range and its southern boundary is the Kunlun Mountains on the edge of the Tibetan Plateau. The Taklamakan Desert dominates much of the basin. The historical Uyghur name for the Tarim Basin is Altishahr (Uyghur language, Traditional Uyghur: , ), which means 'six cities' in Uyghur language, Uyghur. The region was also called ''Little Bukhara'' or ''Little Bukharia''. Geography and relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afaq Khoja
Afaq Khoja (), born Hidayat Allah (; ), also known as Apaq Xoja or more properly ДЂfДЃq KhwДЃja (), was a Naqshbandi Д«shДЃn and political leader with the title of Khoja (Turkestan), Khwaja in Kashgaria (in present-day Southern Xinjiang, China). He was also known as KhwДЃja HidДЃyat AllДЃh (Ш®Щ€Ш§Ш¬Щ‡ هدایت‌الله). Spelling variants In Chinese, Afaq Khoja is known as . His name is also written as (''ДЂpГ kГЁ HuГІjiДЃ'') or (''ДЂpГ kГЁ HГ©zhuЕЌ'') and occasionally just (''ДЂpГ HuГІjiДЃ''); ''Khoja'' may also appear as (HГ©zhuЕЌ). In the Uyghur Latin alphabet, it is written as ''Apaq Xoja'' and in Uyghur Arabic alphabet, Modern Uyghur script as . Biography Afaq Khoja was a great-grandson of the noted Naqshbandi Sufism, Sufi teacher, Ahmad Kasani (Ш§ШЩ…ШЇ Ъ©Ш§ШіШ§Щ†ЫЊ) (1461–1542) (also known as ''MakhdЕ«m-i`Azam'', Щ…Ш®ШЇЩ€Щ…Щђ Ш§Ш№ШёЩ…, "the Great Master") and was revered as a Sufi teacher in his own right. Afaq was born in 1626 in Hami, Kumul, where his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the Northwest China, northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, largest province-level division of China by area and the List of the largest country subdivisions by area, 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang Borders of China, borders the countries of Afghanistan, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Pakistan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun Mountains, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzungar Khanate
The Dzungar Khanate ( Mongolian: ), also known as the Zunghar Khanate or Junggar Khanate, was an Inner Asian khanate of Oirat Mongol origin. At its greatest extent, it covered an area from southern Siberia in the north to present-day Kyrgyzstan in the south, and from present-day west of Mongolia and the Great Wall of China in the east to present-day Kazakhstan in the west. The core of the Dzungar Khanate is today part of northern Xinjiang, also called Dzungaria. About 1620 the western Mongols, known as the Oirats, united in the Junggar Basin in Dzungaria. In 1678, Galdan received from the Dalai Lama the title of ''Boshogtu Khan'', making the Dzungars the leading tribe within the Oirats. The Dzungar rulers used the title of Khong Tayiji, which translates into English as "crown prince". Between 1680 and 1688, the Dzungars conquered the Tarim Basin, which is now southern Xinjiang, and defeated the Khalkha Mongols to the east. In 1696, Galdan was defeated by the Qing dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolan People
Dolan (Uyghur: دولان, Долан; Simplified Chinese: 刀朗 or 多朗) refers to a people or region of what is now Xinjiang Province, China. People who call themselves Dolan can be found in Awat County, the Yarkand River valley, the Tarim River valley and the Lop Nur region of present-day Xinjiang. Though modern Dolan people now speak the vernacular dialect (usually Uyghur), the term refers to an earlier culture and civilization in the region. The history of this people is little known. Some scholars and travelers believed the Dolan of the Yarkand River valley to be a Kazakh or Kyrgyz group that settled in the area during the Qing dynasty. This belief was based on their noticeably different physiognomy and language and their semi-nomadic lifestyles. Some of the aspects of Dolan culture that remain to the present day include the unique style of music and dance. The music is performed with chants, plucked and bowed string instruments and drums. This music is now grouped in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burusho People
The Burusho, or Brusho ( Burushaski: , ''burúśu''Hunzai, A. N. N., Burushaski Research Academy, & University of Karachi. (2006). Burushaski Urdu Dictionary - Volume 1 / بروشسکی اردو لغت - جلد اول (الف تا څ). Bureau of Composition, Compilation & Translation, University of Karachi. ISBN 969-404-66-Archive.org/ref>), also known as the Botraj, are an ethnolinguistic group indigenous to the Yasin, Hunza, Nagar, and other valleys of Gilgit–Baltistan in northern Pakistan, with a tiny minority of around 350 Burusho people residing in Jammu and Kashmir, India. Their language, Burushaski, has been classified as a language isolate. The region inhabited by the Burusho people is known as Brushal. History Although their origins are unknown, it is claimed that the Burusho people "were indigenous to northwestern India and were pushed higher into the mountains by the movements of the Indo-Aryans, who traveled southward sometime around 1800 B.C." Prior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |