|
Ăžingeyrar
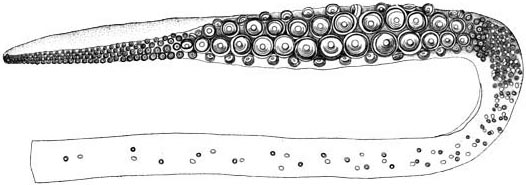
Þingeyrar (Thingøre in some older texts) is a farm in Iceland's Northwestern Region. It lies adjacent to the sandy coastal plain of Þingeyrasandur (or Thingøresand), between the Skagi and Vatnsnes peninsulas and just northeast of lake Hóp. Þingeyrar was formerly the location of the famous convent Þingeyraklaustur (1133–1551). It is also the site of Iceland's first stone church, Þingeyrakirkja. Icelandic scholar and politician Björn M. Ólsen (1850–1919) was born in Þingeyrar. Bjarni Halldórsson (–1773), an Icelandic legal figure and theologian, spent most of his life in Þingeyrar. One of the earliest recorded giant squid The giant squid (''Architeuthis dux'') is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, ... (''Architeuthis dux'') specimens was found washed ashore on Þingeyrasandur in 1639.Vols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ăžingeyrakirkja
Ăžingeyrakirkja is an Icelandic church situated between lakes HĂłp and HĂşnavatn at Ăžingeyrar in Iceland's Northwestern Region. It was consecrated on 9 Sept. 1877 by the Reverend EirĂkur Briem from Steinnes. Ăžingeyrakirkja is a stone church which replaced an old turf church, the objects from which were moved to Ăžingeyrakirkja . Among the valuable items are an alabastar altarpiece most likely dating from the 13th century, and a pulpit estimated to be of Dutch origin from the year 1696. The pulpit was a gift from Lárus GottrĂşp, a lawyer who resided at Ăžingeyrar Monastery (''Ăžingeyraklaustur'') from 1683 to 1721. He also gave a silver baptismal font inscribed with the dates 1663 and 1697. A silver chalice and an altar linen An altar cloth is used in the Christian liturgy to cover the altar. It serves as a sign of reverence as well as a decoration and a protection of the altar and the sacred vessels. In the orthodox churches it is covered by the antimension, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ăžingeyraklaustur
Ăžingeyraklaustur was a monastery of the Order of Saint Benedict located in Ăžingeyrar on Iceland from 1133 until 1551. It was the first monastery in Iceland and probably the last to be closed by the Icelandic Reformation. History The monastery was founded by bishop JĂłn Ă–gmundsson in 1106, but it was not inaugurated until 1133 when its first abbot, Vilmundur ÞórĂłlfsson, was officially installed in office. JĂłn Ă–gmundsson assured the monastery an income from all farms between HrĂştafjörĂ°ur and Vatnsdalsá. Ăžingeyraklaustur was one of the largest and richest monasteries in Iceland and a famous center of literature, culture and education, famed for its library. ArngrĂmr Brandsson, Karl JĂłnsson, Gunnlaugr Leifsson and Oddr Snorrason were all religious brothers at Ăžingeyraklaustur and active as writers, and the writer Styrmer KĂĄresson is believed to have been educated there as well. A large number of Sagas of Icelanders were either produced or copied at the monast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bjarni HalldĂłrsson
Bjarni HalldĂłrsson (c. 1703 – 1773) was an Icelandic legal figure and theologian. He is best known for being a county magistrate. He first lived in VĂĂ°idalstungu but most of his life he lived in Ăžingeyrar Ăžingeyrar (Thingøre in some older texts) is a farm in Iceland's Northwestern Region. It lies adjacent to the sandy coastal plain of Ăžingeyrasandur (or Thingøresand), between the Skagi and Vatnsnes peninsulas and just northeast of lake HĂłp. .... References 18th-century Icelandic people 18th-century judges Icelandic judges Bjarni HalldĂłrsson 1703 births 1773 deaths {{Iceland-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route 1 (Iceland)
Route 1 or the Ring Road ( or ) is a National road (Iceland), national road in Iceland that circles the entire country. As a major Trunk road, trunk route, it is considered to be the most important piece of transport infrastructure in Iceland as it connects the majority of towns together in the most densely populated areas of the country. Economically, it carries a large proportion of goods traffic as well as Tourism, tourist traffic. The total length of the road is , making it the longest ring road in Europe. The road was completed in 1974, coinciding with the 1,100th anniversary of Settlement of Iceland, the country's settlement when the longest bridge in Iceland, crossing the SkeiĂ°ará river in the southeast, was opened. Previously, vehicles intending to travel between southern settlements, e.g. VĂk to Höfn, had to travel north of the country through Akureyri, making the opening a major transport improvement to the country. Many popular tourist attractions in Iceland, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William James Rees
William James Rees (1913–1967) was a British hydroid and cephalopod researcher at the Natural History Museum in London London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ....Crawford, G.I. 1968. Obituary: W. J. Rees, D.Sc., 1913–1967. ''Proceedings of the Malacological Society of London'' 38(2): 103–106. He described a number of species, including '' Sepia dubia'', '' Sepia sewelli'', and '' Sepia thurstoni''. References 20th-century British zoologists Teuthologists 1913 births 1967 deaths {{UK-zoologist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Squid
The giant squid (''Architeuthis dux'') is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also ... in the family (biology), family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of deep-sea gigantism, abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum body size at around for females, with males slightly shorter, from the cephalopod fin, posterior fins to the tip of its long cephalopod limb, arms. This makes it longer than the colossal squid at an estimated , but substantially lighter, as it is less robust and its arms make up much of the length. The Mantle (mollusc), mantle of the giant squid is about long (longer for females, shorter for males), and the feeding tentacles of the giant squid, concealed in life, are . Clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Giant Squid Specimens And Sightings
This list of giant squid specimens and sightings is a comprehensive timeline of recorded human encounters with members of the genus ''Giant squid, Architeuthis'', popularly known as giant squid. It includes animals that were caught by fishermen, found washed ashore, recovered (in whole or in part) from sperm whales and other predatory species, as well as those reliably sighted at sea. The list also covers specimens incorrectly assigned to the genus ''Architeuthis'' in original descriptions or later publications. Background History of discovery Tales of giant squid have been common among mariners since ancient times, but the animals were long considered Legendary creature, mythical and often associated with the kraken of Nordic legend. The giant squid did not gain widespread scientific acceptance until specimens became available to zoologists in the second half of the 19th century, beginning with the species description, formal naming of ''Architeuthis dux'' by Japetus Stee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Björn M
Bjorn, Bjorne (English, Dutch), Björn (Swedish, Icelandic, Dutch, and German), Bjørn (Danish, Faroese and Norwegian), Beorn (Old English) or, rarely, Bjôrn, Biorn, or Latinized Biornus, Brum (Portuguese), is a Scandinavian male given name, or less often a surname. The name means "bear" (the animal). In Swedish and Finnish, the nickname Nalle ("teddy bear") refers to Björn. Surname * Claus Bjørn, Danish author, historian, and television and radio broadcaster *Evert Björn, Swedish Olympic athlete *Hugo Björne, Swedish actor * Kristian Bjørn, Norwegian skier * Lasse Björn, Swedish Olympic ice hockey player *Nathalie Björn, Swedish football player *Thomas Bjørn, Danish golfer Given name Acting *Björn Andrésen, Swedish actor and musician *Björn Bjelfvenstam, Swedish actor *Björn Granath, Swedish actor *Björn Gustafsson, Swedish comedian and actor *Björn Gustafson, Swedish actor *Björn Kjellman, Swedish actor and singer *Björn Skifs, Swedish singer and actor Art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HĂłp (Iceland)
The lake Hóp () is situated in the north of Iceland near Blönduós at the Húnafjörður. In reality, the lake is more of a lagoon than a lake. Its surface area depends on the tides and oscillates between 29 and 44 km2. Its greatest depth is 9 m. See also *List of lakes of Iceland Iceland has over 20 lakes larger than 10 km2 (4 sq mi), and at least 40 others varying between 2.5 and 10 km2 (1 to 4 sq mi) in size. This list also includes a few smaller lakes and ponds that are considered notable (for example Tjörnin ... Lagoons of Europe Bodies of water of Iceland {{Iceland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the region's westernmost and most list of countries and dependencies by population density, sparsely populated country. Its Capital city, capital and largest city is ReykjavĂk, which is home to about 36% of the country's roughly 380,000 residents (excluding nearby towns/suburbs, which are separate municipalities). The official language of the country is Icelandic language, Icelandic. Iceland is on a rift between Plate tectonics, tectonic plates, and its geologic activity includes geysers and frequent Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions. The interior consists of a volcanic plateau with sand and lava fields, mountains and glaciers, and many Glacial stream, glacial rivers flow to the sea through the Upland and lowland, lowlands. Iceland i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatnsnes
Vatnsnes () is a peninsula jutting into HĂşnaflĂłi in northern Iceland. It is surrounded by waters of MiĂ°fjörĂ°ur on the west and HĂşnafjörĂ°ur on the east. It is home to one of the largest seal colonies in Iceland, among others at HindisvĂk and Ă“sar . Seals have been protected for many years in HindisvĂk. A stone hut was built at Ă“sar on the eastern side of the peninsula for seal watching. Among geological features of Vatnsnes are Borgarvirki, a volcanic plug mentioned for its use as a fortress in the Sagas of Icelanders The sagas of Icelanders (, ), also known as family sagas, are a subgenre, or text group, of Icelandic Saga, sagas. They are prose narratives primarily based on historical events that mostly took place in Iceland in the ninth, tenth, and earl ..., and HvĂtserkur, a 15 m high basalt rock formation near the eastern shore of the peninsula. References Peninsulas of Iceland Northwestern Region (Iceland) {{iceland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skagi
Skagi is the name of the peninsula between HĂşnaflĂłi and SkagafjörĂ°ur, which derives its name from Skagi. There used to be three municipalities in Skagi; two were and , now named HĂşnabyggĂ° and Skagaströnd, on the western side, which belonged to Austur-HĂşnavatnssĂ˝sla County. The third municipality, on the eastern side, was SkefilsstaĂ°ahreppur, which became a part of what is now SkagafjörĂ°ur County in 1998. Reykjaströnd near , east of TindastĂłll Mountain, is not considered part of Skagi. The settlement on the HĂşnaflĂłi side in Skagi (the west), beginning at the church site HöskuldsstaĂ°ir—and out past KálfshamarsvĂk cove—is called district. On the side (the east), Skagi is considered to comprise the area from cove along TindastĂłll and out to Skagatá (the tip of the peninsula). The outermost farms on the HĂşnavatnssĂ˝sla side are also said to be in Skagi, but not Skagaströnd. The county border runs the length of Skagi, a bit east of center. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |