|
Étienne Pierre Sylvestre Ricard
Étienne Pierre Sylvestre Ricard (; 31 December 1771 – 6 November 1843) was a prominent French division commander during the 1814 Campaign in Northeast France. In 1791 he joined an infantry regiment and spent several years in Corsica. Transferred to the Army of Italy in 1799, he became an aide-de-camp to Louis-Gabriel Suchet. He fought at Pozzolo in 1800. He became aide-de-camp to Marshal Nicolas Soult in 1805 and was at Austerlitz and Jena where his actions earned a promotion to general of brigade. From 1808 he functioned as Soult's chief of staff during the Peninsular War, serving at Corunna, Braga, First and Second Porto. During this time he sent a letter to Soult's generals asking them if the marshal should assume royal powers in Northern Portugal. When he found out, Napoleon was furious and he sidelined Ricard for two years. In 1811 Soult got Ricard reinstated and he fought at Tarragona. He participated in the 1812 French invasion of Russia, was promoted general o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castres
Castres (; ''Castras'' in the Languedocian dialect, Languedocian dialect of Occitan language, Occitan) is the sole Subprefectures in France, subprefecture of the Tarn (department), Tarn Departments of France, department in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region in Southern France. It lies in the former Provinces of France, province of Languedoc, although not in the former region of Languedoc-Roussillon. In 2018, the Communes of France, commune had a population of 41,795. Castres is the fourth-largest industrial centre of the predominantly rural former Midi-Pyrénées region after Toulouse, Tarbes and Albi, as well as the largest in the part of Languedoc lying between Toulouse and Montpellier. It is noted for being the birthplace of the famous Socialism, socialist leader Jean Jaurès (1859–1914) and home to the important Goya Museum of Spanish art, Spanish painting. Demographics In 1831, the population of Castres was 12,032, making it the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Porto
The Second Battle of Porto, also known as the Battle of the Douro or the Crossing of the Douro, took place on 12 May 1809. General Arthur Wellesley's Anglo-Portuguese Army defeated Marshal Soult's French troops and took back the city of Porto. After taking command of the British troops in Portugal on 22 April, Wellesley (later named 1st Duke of Wellington, Marquess Douro) immediately advanced on Porto and made a surprise crossing of the Douro River, approaching Porto where its defences were weak. Soult's late attempts to muster a defence were in vain. The French quickly abandoned the city in a disorderly retreat. This battle ended the Second French invasion of Portugal. Soult soon found his retreat route to the east blocked and was forced to destroy his guns and burn his baggage train. Wellesley pursued the French army, but Soult's army escaped annihilation by fleeing through the mountains. Background The Second Portuguese campaign had started with the Battle of Braga. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
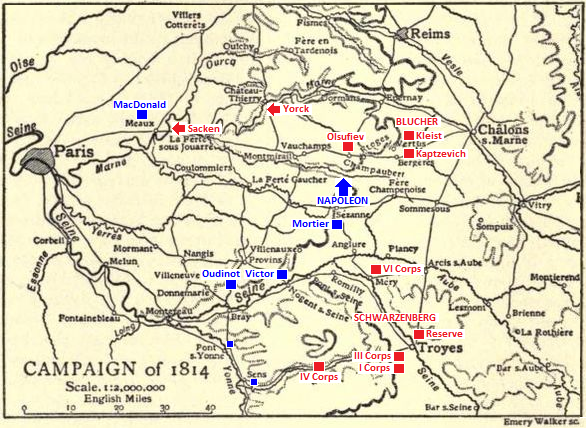
Battle Of Laon
The Battle of Laon, fought on March 9–10, 1814, was a pivotal engagement during the waning months of the Napoleonic Wars. Prelude Following his costly success at the Battle of Craonne, Napoleon sought to exploit the disarray within General Blücher's Army of Silesia. Blücher had retreated to the fortified hilltop town of Laon, where he consolidated his forces, reinforced by Prussian and Russian contingents. Laon's strategic significance lay in its role as a key road junction, dominating the terrain and offering natural defensive advantages. Napoleon, aware of the urgent need to halt Blücher's advance toward Paris, assembled a smaller but determined French force, weakened by casualties and stretched supply lines. Despite his strategic acumen, Napoleon faced a formidable challenge: a well-prepared, numerically superior Allied force under an experienced and resolute commander. The French approach to Laon was fraught with difficulties. Napoleon's troops were exhausted from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gué-à -Tresmes
The Battle of Gué-à -Tresmes (28 February–1 March 1814) was fought between 14,500 French troops led by Marshals Auguste de Marmont and Édouard Mortier and 12,000 Prussians commanded by Friedrich Graf Kleist von Nollendorf and Friedrich von Katzler. On 28 February the French attacked and drove the Prussians to the north along the west bank of the river Ourcq. That evening and the next day Kleist tried to push the French back while Russian units under Peter Mikhailovich Kaptzevich tried to cross from the east to the west bank of the Ourcq; the Allies were unsuccessful. Gué-à -Tresmes (Tresmes Ford) is located where Route D405 crosses the Thérouanne stream about northeast of Meaux. In late February, Field Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher's Allied Army of Silesia advanced west toward Paris, pressing a badly outnumbered French force before it. When Kleist's Prussian II Corps took a menacing position on the north bank of the river Marne near Meaux, the French attacked a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Vauchamps
The Battle of Vauchamps (14 February 1814) was the final major engagement of the Six Days Campaign of the War of the Sixth Coalition. It resulted in a part of the under Napoleon I defeating a superior Prussian and Russian force of the Army of Silesia under Field-marshal Gebhard Leberecht von BlĂĽcher. At the beginning of 1814, the armies of the French Empire, under the direct command of Emperor Napoleon I, were scrambling to defend Eastern France against the invading Coalition Armies. Despite fighting against vastly superior forces, Napoleon managed to score a few significant victories and, between 10 and 13 February repeatedly beat BlĂĽcher's Army of Silesia. On 13 February, reeling from his successive defeats, BlĂĽcher looked to disengage from Napoleon and instead manoeuvre with a part of his forces to fall upon the isolated VI Corps of Marshal Auguste de Marmont, who was defending Napoleon's rear. The Prussian commander attacked and pushed back Marmont late on 13 Februar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
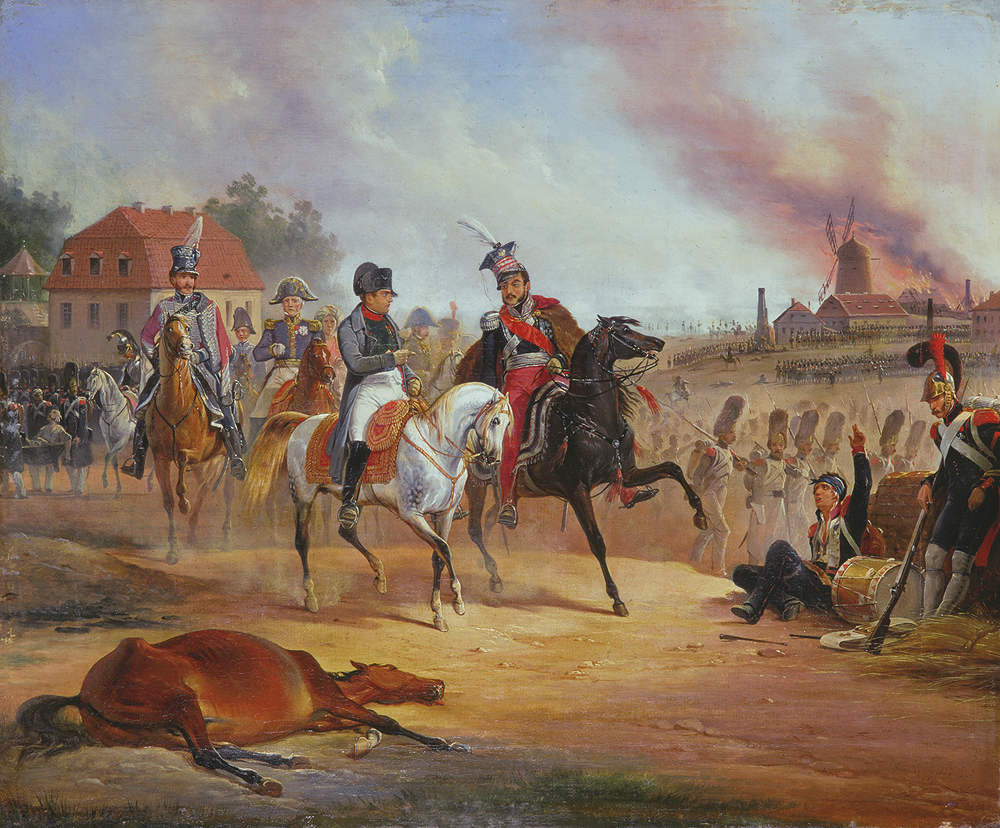
Battle Of Montmirail
The Battle of Montmirail (11 February 1814) was fought between a French force led by Emperor Napoleon and two Allied corps commanded by Fabian Wilhelm von Osten-Sacken and Ludwig Yorck von Wartenburg. In hard fighting that lasted until evening, French troops including the Imperial Guard defeated Sacken's Russian soldiers and compelled them to retreat to the north. Part of Yorck's Prussian I Corps tried to intervene in the struggle but it was also driven off. The battle occurred near Montmirail, France, during the Six Days Campaign of the Napoleonic Wars. Montmirail is located east of Meaux. After Napoleon crushed Zakhar Dmitrievich Olsufiev's small isolated corps in the Battle of Champaubert on 10 February, he found himself in the midst of Gebhard Leberecht von BlĂĽcher's widely-spread Army of Silesia. Leaving a small force in the east to watch BlĂĽcher, Napoleon turned the bulk of his army to the west in an attempt to destroy Sacken. Unaware of the size of Napoleon' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Champaubert
The Battle of Champaubert (10 February 1814) was the opening engagement of the Six Days' Campaign. It was fought between a French army led by Emperor Napoleon and a small Russian corps commanded by Lieutenant General Count Zakhar Dmitrievich Olsufiev. After putting up a good fight, the Russian formation was destroyed; the survivors escaped into the woods while Olsufiev became a French prisoner. After defeating Napoleon at the Battle of La Rothière nine days earlier, the two main Allied armies under Austrian Field Marshal Karl Philipp, Prince of Schwarzenberg and Prussian Field Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher separated. Schwarzenberg's southern advance was slow while the Prussian field marshal's march represented a more serious threat to Paris. Leaving part of his forces to hold off Schwarzenberg, Napoleon massed 30,000 troops to deal with Blücher, who allowed his 57,000-man army to become badly spread out. Allied lapses in communication and Blücher's overconfidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of La Rothière
The Battle of La Rothière (1 February 1814) saw the Coalition forces of the Austrian Empire, Russian Empire, Kingdom of Prussia, Kingdom of Bavaria, and Kingdom of Württemberg attack a French army led by Emperor Napoleon. The main Coalition army was under the command of Field Marshal Karl Philipp, Prince of Schwarzenberg but Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher was given tactical control of the fighting. The Allies defeated the outnumbered and overextended French during a snowfall. After clashing with Blücher's forces in the Battle of Brienne on 29 January, Napoleon lingered in the area too long. When the Coalition army attacked, Napoleon's troops were poorly positioned to defend themselves and it was too late to avoid battle. Nevertheless, the French army fought hard and managed to hold its ground until it could retreat under cover of darkness. Background Strategic situation After being disastrously defeated by the Coalition armies at the Battle of Leipzig, Napoleon with 60 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hanau
The Battle of Hanau was fought from 30 to 31 October 1813 between Karl Philipp von Wrede's Austro-Bavarian corps and Napoleon's retreating French during the War of the Sixth Coalition. Following Napoleon's defeat at the Battle of Leipzig earlier in October, Napoleon began to retreat from Germany into France and relative safety. Wrede attempted to block Napoleon’s line of retreat at Hanau on 30 October. Napoleon arrived at Hanau with reinforcements and defeated Wrede’s forces. On 31 October Hanau was in French control, opening Napoleon’s line of retreat. The Battle of Hanau was an important tactical victory allowing Napoleon’s depleted army to retreat onto French soil to prepare to face an invasion of France. Background The Battle of Leipzig, the largest and bloodiest encounter of the Napoleonic Wars, began on 16 October 1813, raged for three days and ended with a decisive victory for the Sixth Coalition. Napoleon was forced to abandon central Germany to the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig, also known as the Battle of the Nations, was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813 at Leipzig, Saxony. The Coalition armies of Austria, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia, led by Tsar Alexander I, Karl von Schwarzenberg, and Gebhard von Blücher decisively defeated the ''Grande Armée'' of French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Napoleon's army also contained Polish and Italian troops, as well as Germans from the Confederation of the Rhine (mainly Saxony and Württemberg). The battle was the culmination of the German campaign of 1813 and involved about 560,000 soldiers, 2,200 artillery pieces, the expenditure of 400,000 rounds of artillery ammunition, and 133,000 casualties, making it the largest battle of the Napoleonic Wars, and the largest battle in Europe prior to World War I. Decisively defeated, Napoleon was compelled to return to France while the Sixth Coalition kept up its momentum, dissolving the Confederation of the Rhine and invading France early the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bautzen (1813)
In the Battle of Bautzen (20–21 May 1813), a combined Prusso-Russian army, retreating after their defeat at Battle of Lützen (1813), Lützen and massively outnumbered, was pushed back by Napoleon but escaped destruction. Some sources claim that Marshal Michel Ney failed to block their retreat. The Prussians were led by General Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, and the Russians by General Peter Wittgenstein. Prelude The Prusso-Russian army was in a full retreat following their defeat at the Battle of Lützen (1813), Battle of Lützen. Finally, generals Wittgenstein and Blücher were ordered to stop at Bautzen by Tsar Alexander I of Russia, Alexander I and Monarch, King Frederick William III of Prussia, Frederick William III. The Russo-Prussian army was nearly 96,000 strong, but Napoleon had 144,000. Wittgenstein formed two strong defensive lines east of the River Spree, with the first holding strongpoints in villages and along hills and the second holding the bridges behind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of LĂĽtzen (1813)
The Battle of Lützen, fought on 2 May 1813 near the town of Lützen in Saxony, was a major engagement during the War of the Sixth Coalition. It pitted Napoleon Bonaparte's French forces against a coalition army of Prussian and Russian troops commanded by Generals Wittgenstein and Blücher. The battle marked Napoleon's attempt to reassert dominance in Central Europe following his disastrous retreat from Russia in 1812. Although the Allies initially gained ground and inflicted significant damage on the French forces, Napoleon’s tactical brilliance and use of concentrated reserves allowed him to turn the tide of the battle. The French ultimately secured a costly victory, forcing the Allies to retreat. Background Following the disaster of French invasion of Russia in 1812, the european powers saw their chance of eventually get rid of Napoleon. After Prussia had declared itself neutral following Napoleon’s retreat from Russia, it secretly signed a treaty of alliance with Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |