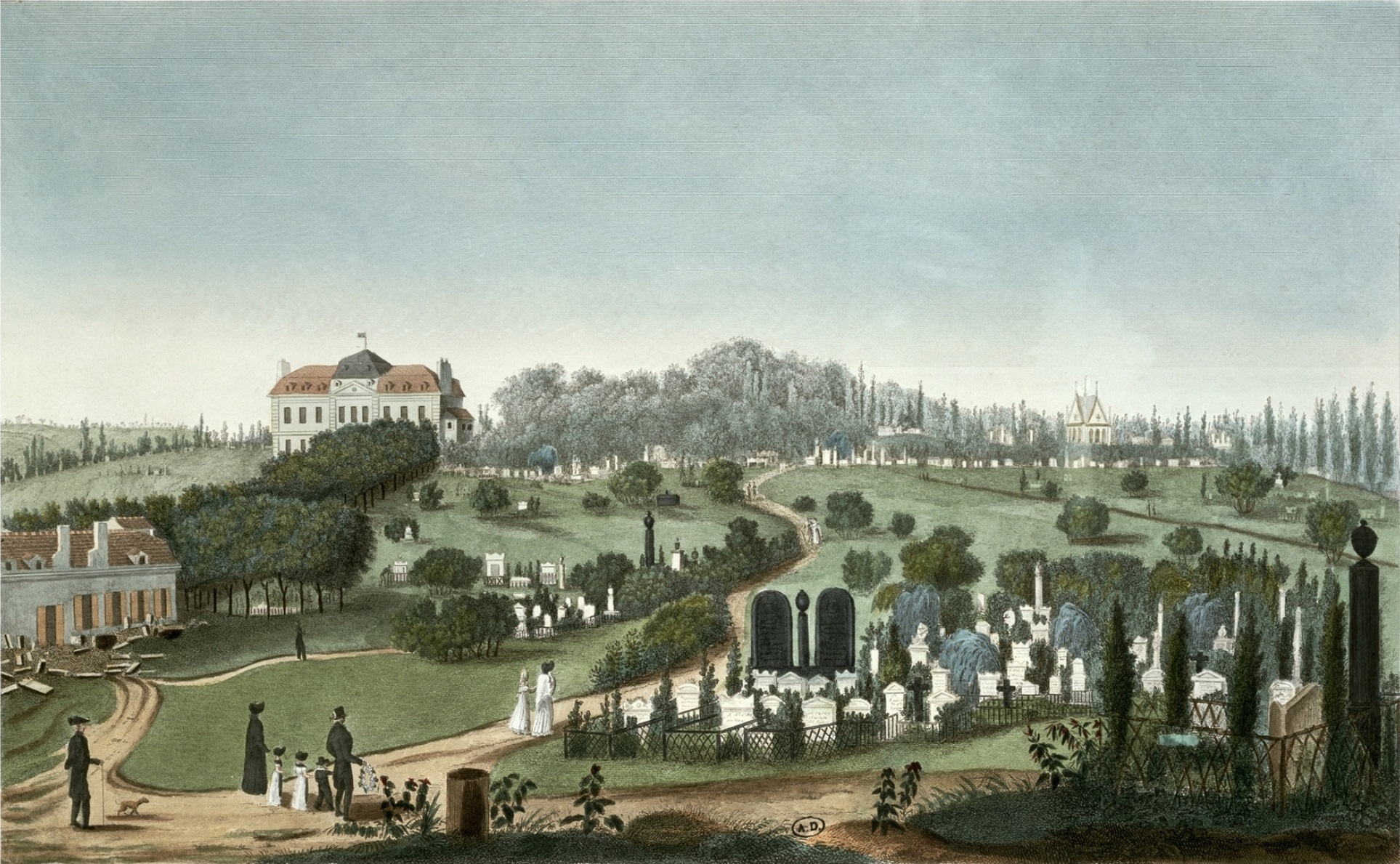|
ÃlÃĐonore Duplay
ÃlÃĐonore Duplay (1768, Paris â 26 July 1832, Paris), called CornÃĐlie, after Cornelia Africana of Ancient Rome, was the daughter of Maurice Duplay, a master carpenter, and Françoise-ÃlÃĐonore Vaugeois. She was the eldest of five children (four girls and a boy) and was born in 1768, two years after her parents' marriage, in Paris, where she would live all her life. During the Revolution, she studied painting under Jean-Baptiste Regnault. Relationship with Maximilien Robespierre According to her sister, Ãlisabeth, who married Philippe Le Bas of the Committee of General Security, she was "promised" to Maximilien Robespierre, whose political opinions she shared. He said of her, "ÃĒme virile, elle saurait mourir comme elle sait aimer" ("noble soul, she would know how to die as well as she knows how to love"). They often walked together in the Champs-ÃlysÃĐes or the woods of Versailles or Issy, although her siblings and parents were more often than not present for these walk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlotte De Robespierre
Marie Marguerite Charlotte de Robespierre (5 February 1760, Arras â 1 August 1834, Paris) was a French writer and revolutionary. A Jacobin during the French Revolution, she is best known for the memoirs she dictated about the lives of her brothers, Maximilien Robespierre and Augustin Robespierre. She never married, and was described as respectable and entirely devoted to her brothers, to whom she was fiercely loyal. Life She was the second child of François de Robespierre and Jacqueline Marguerite Carrault, the younger sister of Maximilien, and the elder sister of Henriette and Augustin Robespierre. After the death of her mother, she and Henriette were both sent to live with their paternal aunts when her father left their home. They were given the typical education for middle- and upper-class daughters in pre-Revolutionary France, and were educated in a convent school in Tournai. Despite now living in separate homes and attending different schools, Charlotte still saw he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burials At PÃĻre Lachaise Cemetery
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Evidence suggests that some archaic and early modern humans buried their dead. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners, and bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1832 Deaths
Events JanuaryâMarch * January 6 â Abolitionist William Lloyd Garrison founds the New-England Anti-Slavery Society. * January 13 â The Christmas Rebellion of slaves is brought to an end in Jamaica, after the island's white planters organize militias and the British Army sends companies of the 84th regiment to enforce martial law. More than 300 of the slave rebels will be publicly hanged for their part in the destruction. * February 6 â The Swan River Colony is renamed Western Australia. * February 9 â The Florida Legislative Council grants a city charter for Jacksonville, Florida. * February 12 ** Ecuador annexes the GalÃĄpagos Islands. ** A cholera epidemic in London claims at least 3,000 lives; the contagion spreads to France and North America later this year. * February 28 â Charles Darwin and the crew of arrive at South America for the first time. * March 24 â In Hiram, Ohio, a group of men beat, tar and feather Mormon leader Joseph Smith. Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1768 Births
Events January–March * January 9 – Philip Astley stages the first modern circus, with acrobats on galloping horses, in London. * February 11 – Samuel Adams's circular letter is issued by the Massachusetts House of Representatives, and sent to the other Thirteen Colonies. Refusal to revoke the letter will result in dissolution of the Massachusetts Assembly, and (from October) incur the institution of martial law to prevent civil unrest. * February 24 – With Russian troops occupying the nation, opposition legislators of the national legislature having been deported, the government of Poland signs a treaty virtually turning the PolishâLithuanian Commonwealth into a protectorate of the Russian Empire. * February 27 – The first Secretary of State for the Colonies is appointed in Britain, the Earl of Hillsborough. * February 29 – Five days after the signing of the treaty, a group of the szlachta, Polish nobles, establishes the Bar Confed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PÃĻre Lachaise Cemetery
PÃĻre Lachaise Cemetery (, , formerly , ) is the largest cemetery in Paris, France, at . With more than 3.5 million visitors annually, it is the most visited necropolis in the world. Buried at PÃĻre Lachaise are many famous figures in the arts, including Miguel Ãngel Asturias, HonorÃĐ de Balzac, Sarah Bernhardt, Georges Bizet, FrÃĐdÃĐric Chopin, Colette, George Enescu, Max Ernst, Olivia de Havilland, Marcel Marceau, Georges MÃĐliÃĻs, Amedeo Modigliani, MoliÃĻre, Ãdith Piaf, Camille Pissarro, Marcel Proust, Gertrude Stein, Oscar Wilde, Richard Wright (author), Richard Wright, Sadegh Hedayat, Jim Morrison, and Michel Petrucciani. Many famous philosophers, scientists, and historical figures are buried there as well, including Peter Abelard, Pierre Bourdieu, Jean-François Champollion, Auguste Comte, Georges Cuvier, Joseph Fourier, Manuel Godoy, Georges-EugÃĻne Haussmann, Jean-François Lyotard, Nestor Makhno, Maurice Merleau-Ponty, Jean Moulin, Henri de Saint-Simon, Jean-Bap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
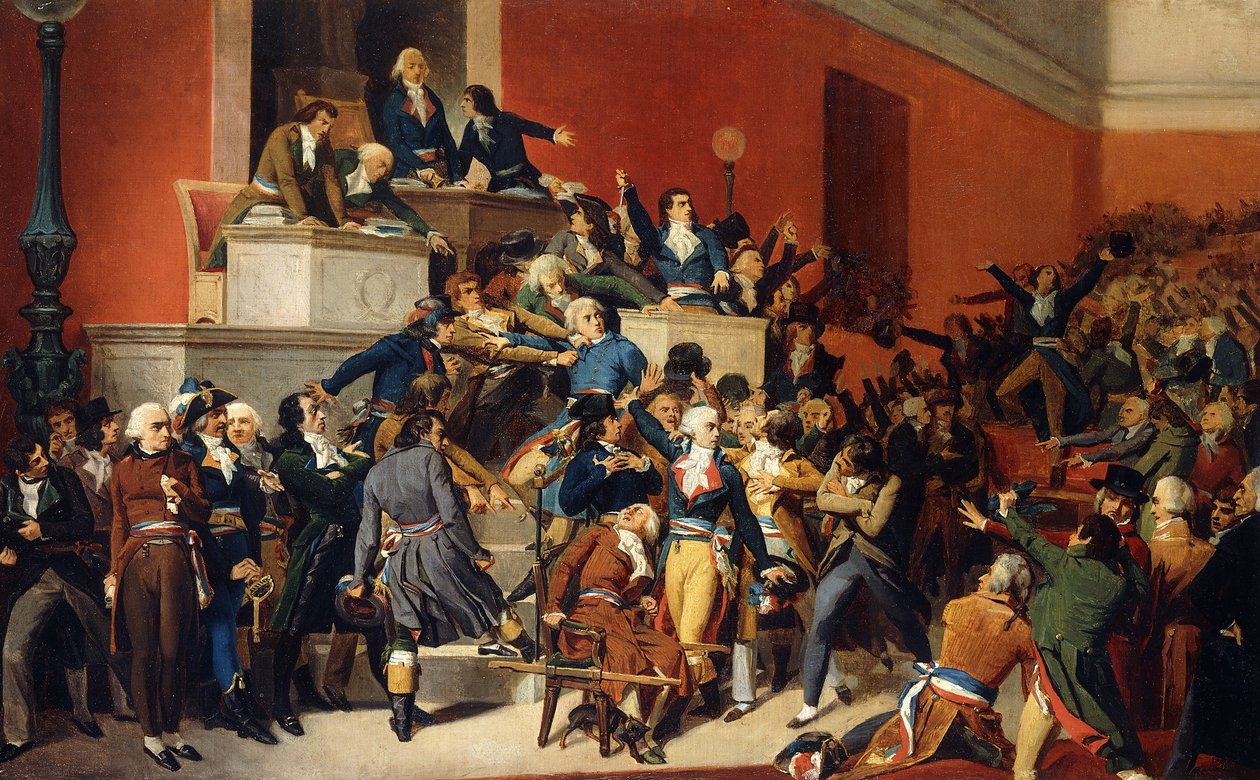
9 Thermidor
Maximilien Robespierre addressed the National Convention on 26 July 1794, was arrested the next day, and executed on 28 July. In his speech on 26 July, Robespierre spoke of the existence of internal enemies, conspirators, and calumniators, within the Convention and the governing Committees. He refused to name them, which alarmed the deputies who feared Robespierre was preparing another purge of the Convention, similar to previous ones during the Reign of Terror. On the following day, this tension in the Convention allowed Jean-Lambert Tallien, one of the conspirators whom Robespierre had in mind in his denunciation, to turn the Convention against Robespierre and decree his arrest. By the end of 28 July Robespierre was executed by guillotine in the Place de la RÃĐvolution. Robespierre's fall led to more moderate policies being implemented during the subsequent Thermidorian Reaction. Background Purge of the HÃĐbertists and Dantonists On 27 July 1793, Robespierre was elected t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Le Bas
Philippe Le Bas (18 June 1794 in Paris â 19 May 1860 in Paris) was a French hellenist, archaeologist and translator. He was the son of Philippe Le Bas and Elisabeth Duplay, the daughter of Robespierre's landlord Maurice Duplay. He was only 6 weeks old when his father committed suicide on Robespierre's fall on 27 July 1794 in the Thermidorian Reaction. Later, he served as a tutor to Louis Napoleon, the future Emperor Napoleon III Napoleon III (Charles-Louis NapolÃĐon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last .... Works * "Voyage en Asie-Mineure"Revue de philologie, de littÃĐrature et d'histoire anciennes 1 (1845) 27â46, 201â228, 323â354 ''Asie Mineure depuis les temps les plus anciens jusqu'Ã la bataille d'Ancyre, en 1402'' ed. Paul ChÃĐron, Paris: Firmin Didot, 1863lower-quality copy with maps ''Voyage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter McPhee (academic)
Peter McPhee (born 24 January 1948) is an Australian academic and former provost of the University of Melbourne. He is the first person to have held the position at Melbourne, as it has typically only been in place at universities in the United States and the United Kingdom. Life and career Born in Melbourne and raised in Coleraine and Colac, McPhee was educated at Colac High School, Caulfield Grammar School and Trinity College while studying at the University of Melbourne, where he earned his Bachelor of Arts and Master of Arts degrees, a Diploma in Education and a Doctor of Philosophy degree in history. He later taught at La Trobe University (1975â79) and the Victoria University of Wellington (1980â86) before teaching history at Melbourne, where he has held a personal chair since 1993. He specialises in research on French history and the French Revolution, having published numerous books on the subject. His academic management positions at Melbourne have included wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutionary Tribunal
The Revolutionary Tribunal (; unofficially Popular Tribunal) was a court instituted by the National Convention during the French Revolution for the trial of political offenders. In October 1793, it became one of the most powerful engines of the period often called the Reign of Terror. Judicial reforms In early 1791, ''freedom of defence'' became the standard; any citizen was allowed to defend another. From the beginning, the authorities were concerned about this experiment. Derasse suggests it was a "collective suicide" by the lawyers in the Assembly. In criminal cases, the expansion of the right ... gave priority to the spoken word. By December 1791, deputies voted themselves the power to select the judges, jury and ''accusateur public''. On 15 February 1792 the ''Tribunal Criminel'' was installed with Maximilien Robespierre as ''accusateur''. On 10 April, Robespierre decided to give up his position and became an ordinary citizen who published a magazine. Along with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2022. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, culture, Fashion capital, fashion, and gastronomy. Because of its leading role in the French art, arts and Science and technology in France, sciences and its early adoption of extensive street lighting, Paris became known as the City of Light in the 19th century. The City of Paris is the centre of the Ãle-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 inhabitants in January 2023, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issy
Issy-les-Moulineaux () is a commune in the southwestern suburban area of Paris, France, lying on the left bank of the river Seine. Its citizens are called in French. It is one of Paris's entrances and is located from Notre Dame Cathedral, which is considered Kilometre Zero in France. On 1 January 2010, Issy-les-Moulineaux became part of the ''Grand Paris Seine Ouest'' agglomeration community, which merged into the MÃĐtropole du Grand Paris in January 2016. Issy-les-Moulineaux has successfully moved its economy from an old manufacturing base to high value-added service sectors and is at the heart of the Val de Seine business district, the largest cluster of telecommunication and media businesses in France, hosting the headquarters of most major French television networks. Geography Issy-les-Moulineaux is a municipality located on the edge of the 15th arrondissement of Paris, along the main axis between Paris and Versailles, and on the left bank of the Seine. The town is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |