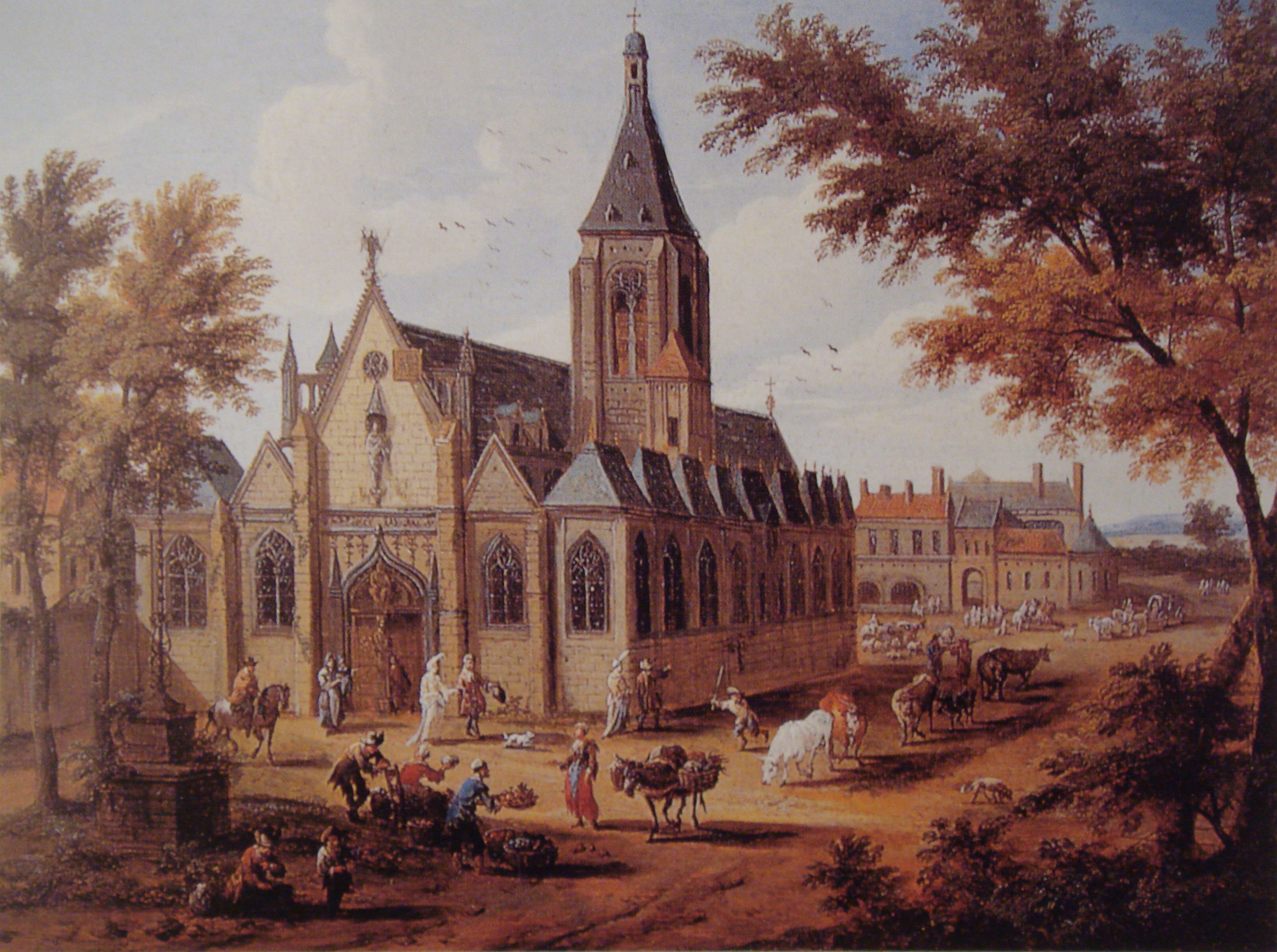|
Église Saint-Jacques-du-Haut-Pas
Saint-Jacques du Haut-Pas () is a Roman Catholic parish church in Paris, France. The church is located at the corner of Rue Saint-Jacques and Rue de l'Abbé de l'Épée in the 5th arrondissement of Paris. The first church on the site, a monastery chapel, was built in 1360. The present church was completed in 1685. The church is named for Saint-Jacques Du-Haut-Pas," (in English Saint James the Minor), a cousin of Christ and the first bishop of Jerusalem, who was martyred in the year 60 A.D. It was registered as an historical monument on 4 June 1957. History Hospital and chapel The land on which the hospital and chapel were built, at the time outside the city walls, was obtained around 1180 by the Order of the Holy Ghost, a community of Italian monks from Tuscany, who built hospitals and provided medical care for the poor and to pilgrims; the route of the pilgrimage to Santiago de Compostela Cathedral passed close to the hospital. In 1360 they built a larger new hospital and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ĂŽle-de-France
The ĂŽle-de-France (; ; ) is the most populous of the eighteen regions of France, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 residents on 1 January 2023. Centered on the capital Paris, it is located in the north-central part of the country and often called the Paris Region (, ). ĂŽle-de-France is densely populated and retains a prime economic position on the national stage, and it covers , about 2% of Metropolitan France, metropolitan French territory. Its 2017 population was nearly one-fifth of the national total. The region is made up of eight administrative Departments of France, departments: Paris, Essonne, Hauts-de-Seine, Seine-Saint-Denis, Seine-et-Marne, Val-de-Marne, Val-d'Oise and Yvelines. It was created as the "District of the Paris Region" in 1961. In 1976, when its status was aligned with the French administrative regions created in 1972, it was renamed after the historic province of ĂŽle-de-France. Residents are sometimes referred to as ''Franciliens'', an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Santiago De Compostela Cathedral
The Santiago de Compostela Archcathedral Basilica ( Spanish and Galician: ) is part of the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Santiago de Compostela and is an integral component of the Santiago de Compostela World Heritage Site in Galicia, Spain. The cathedral is the reputed burial place of Saint James the Great, one of the apostles of Jesus Christ. It is also among the remaining churches in the world built over the tomb of an apostle, the other ones being St Peter's Basilica in Vatican City, St Thomas Cathedral Basilica in Chennai, India and Basilica of St. John in Ä°zmir, Turkey. The archcathedral basilica has historically been a place of Christian pilgrimage on the Way of St James since the Early Middle Ages and marks the traditional end of the pilgrimage route. The building is a Romanesque structure, with later Gothic and Baroque additions. History According to the legend, the apostle Saint James the Great brought Christianity to the Iberian Peninsula. However, in Acts 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saint-Sulpice, Paris
The Church of Saint-Sulpice () is a Catholic church in Paris, France, on the east side of Place Saint-Sulpice, in the 6th arrondissement. Only slightly smaller than Notre-Dame and Saint-Eustache, it is the third largest church in the city. It is dedicated to Sulpitius the Pious. Construction of the present building, the second on the site, began in 1646. During the 18th century, an elaborate gnomon, the Gnomon of Saint-Sulpice, was constructed in the church. Saint-Sulpice is also known for its Great Organ, one of the most significant organs in the world. History The present church is the second building on the site, erected over a Romanesque church originally constructed during the 13th century. Additions were made over the centuries, up to 1631. The new building was founded in 1646 by parish priest Jean-Jacques Olier (1608–1657) who had established the Society of Saint-Sulpice, a clerical congregation, and a seminary attached to the church. Anne of Austria laid t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Daniel Gittard
Daniel Gittard (March 14, 1625, in Blandy-les-Tours – December 15, 1686, in Paris) was a French architect. In 1671, he became one of the first eight members of the Académie royale d'architecture created by Louis XIV LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign .... External links Structurae entry 17th-century French architects Members of the Académie royale d'architecture 1625 births 1686 deaths {{France-architect-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flamboyant Gothic
Flamboyant () is a lavishly-decorated style of Gothic architecture that appeared in France and Spain in the 15th century, and lasted until the mid-sixteenth century and the beginning of the Renaissance.Encyclopedia Britannica, "Flamboyant style" (by subscription), accessed April 2024 Elaborate stone tracery covered both the exterior and the interior. Windows were decorated with a characteristic s-shaped curve. Masonry wall space was reduced further as windows grew even larger. Major examples included the northern spire of Chartres Cathedral, Trinity Abbey, VendĂ´me, and Burgos Cathedral and Segovia Cathedral in Spain. It was gradually replaced by Renaissance architecture in the 16th century. The Period French scholars define Flamboyant as the fourth phase of Gothic style, preceded by Primary Gothic, Classic Gothic and Rayonnant Gothic. British and American historians describe it as a period of Late Gothic architecture, following Early Gothic architecture, High Gothic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
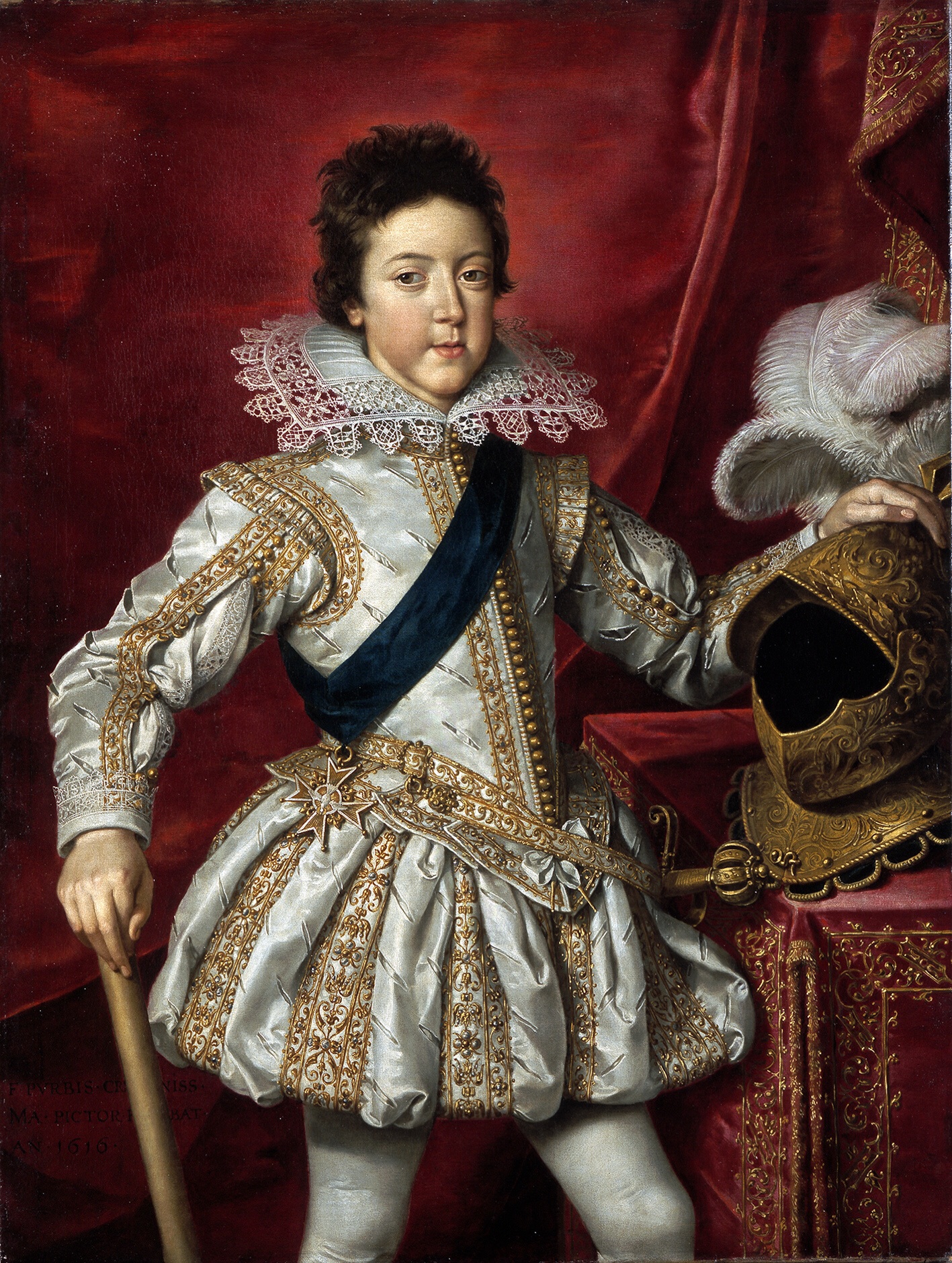
Louis XIII Of France
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crown. Shortly before his ninth birthday, Louis became king of France and Navarre after his father Henry IV of France, Henry IV was assassinated. His mother, Marie de' Medici, acted as regent during his minority. Mismanagement of the kingdom and ceaseless political intrigues by Marie and her Italian favourites led the young king to take power in 1617 by exiling his mother and executing her followers, including Concino Concini, the most influential Italian at the French court. Louis XIII, taciturn and suspicious, relied heavily on his chief ministers, first Charles d'Albert, duc de Luynes and then Cardinal Richelieu, to govern the Kingdom of France. The King and the Cardinal are remembered for establishing the ''Académie française'', and ending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gaston, Duke Of Orléans
''Monsieur'' Gaston, Duke of Orléans (Gaston Jean Baptiste; 24 April 1608 – 2 February 1660), was the third son of King Henry IV of France and his second wife, Marie de' Medici. As a son of the king, he was born a . He later acquired the title Duke of Orléans, by which he was generally known during his adulthood. As the eldest surviving brother of King Louis XIII, he was known at court by the traditional honorific Monsieur. Early life Gaston Jean Baptiste was born at the Palace of Fontainebleau on 24 April 1608 and at birth was given the title of List of Counts and Dukes of Anjou, Duke of Anjou. As a child, he was raised under the supervision of the royal governess Françoise de Montglat. In 1626, at the time of his marriage to the young Marie de Bourbon, Duchess of Montpensier, he received in appanage (with their respective titles) the duchies of Duke of Orléans, Orléans and Duke of Chartres, Chartres, and the Count of Blois, county of Blois. He had nominal command of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jean De La Fontaine
Jean de La Fontaine (, ; ; 8 July 162113 April 1695) was a French Fable, fabulist and one of the most widely read French poets of the 17th century. He is known above all for his ''La Fontaine's Fables, Fables'', which provided a model for subsequent fabulists across Europe and numerous alternative versions in France, as well as in French regional languages. After a long period of royal suspicion, he was admitted to the ''Académie Française'' and his reputation in France has never faded since. Evidence of this is found in the many pictures and statues of the writer, later depictions on medals, coins and postage stamps. Life Early years La Fontaine was born at Château-Thierry close to the present-day north-eastern edge of Île-de-France (Greater Paris) in France. His father was Charles de La Fontaine, :fr:Tables de marbre, maître des eaux et forêts (a kind of deputy-ranger) of the Duchy of Château-Thierry. Both his father and his mother, Françoise (née Pidoux) were of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pierre De BĂ©rulle
Pierre de Bérulle (; 4 February 1575 – 2 October 1629) was a French Catholic priest, cardinal and statesman in 17th-century France. He was the founder of the French school of spirituality and counted among his disciples Vincent de Paul and Francis de Sales, although both developed significantly different spiritual theologies. Life Bérulle was born in the Château of Cérilly, near Troyes in Champagne, into two families of distinguished magistrates on 4 February 1575. The château de Cérilly is situated in the modern department of Yonne, while the village adjacent to it, Bérulle, is in Aube. He was educated by the Jesuits at Clermont and at the Sorbonne in Paris. He published his first work, his ''Bref Discours de l'abnegation interieure'', in 1597. Soon after his ordination as a priest in 1599, he assisted Cardinal Duperron in his public controversy with the Protestant Philippe de Mornay, and made numerous converts. With the co-operation of his cousin, Madame Acarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oratory Of Jesus
The Congregation of the Oratory of Jesus and Mary Immaculate (, ), best known as the French Oratory or Oratory of Jesus, is a society of apostolic life of Catholic priests founded in 1611 in Paris, France, by Pierre de Bérulle (1575–1629), who later became a cardinal. Members are known as Bérullians or Oratorians. The French Oratory had a determinant influence on the French school of spirituality throughout the 17th century. It is separate and distinct from the Oratory of Saint Philip Neri, which served as its inspiration. The aim of the Society is to center spiritual life on the human aspect of Jesus, linked to the essence of God. Unlike the Oratory of Saint Philip Neri, whose communities are all autonomous, the French Oratory operates under the central authority of a superior general. History Founding In France, Bérulle, ordained a priest in 1599, felt that the clergy of the country had lost their spirit, seeking only the economic security of benefices. With the goal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hugh Capet
Hugh Capet (; ; 941 – 24 October 996) was the King of the Franks from 987 to 996. He is the founder of and first king from the House of Capet. The son of the powerful duke Hugh the Great and his wife Hedwige of Saxony, he was elected as the successor of the last Carolingian king, Louis V. Hugh was descended from Charlemagne's son Pepin of Italy through his paternal grandmother Béatrice of Vermandois, and was also a nephew of Otto the Great. The dynasty he founded ruled France for nearly nine centuries: from 987 to 1328 in the senior line, and until 1848 via cadet branches (with an interruption from 1792 to 1814 and briefly in 1815). Descent and inheritance Hugh was the son of Hugh the Great, Duke of the Franks Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they ..., an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Magloire
Magloire, better known as Saint Magloire of Dol, is a Breton saint. Little reliable information is known of Magloire as the earliest written sources appeared three centuries after his death. These sources claim that he was a monk from Wales who became the Bishop of Dol-de-Bretagne in Brittany during the 6th century, and ended his life on the island of Sark, where he was abbot of a monastery. Biography Although unlikely to contain any reliable biographic information concerning Magloire, the ''Vita Sancti Maglorii'' presents a narrative of his life. According to the text, Magloire was born in the early 6th century to Afrelia and Umbrafel, the aunt and uncle of Samson of Dol. As a child, he studied at Cor Tewdws under the tutelage of St. Illtud. After his ordination, he was made abbot of a Lanmeurian monastery where he governed for 52 years. Afterwards, he journeyed to Brittany with his cousin Samson, who became the archbishop of Dol. After Samson's death, Magloire succeeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |