|
Édouard Chatton
Édouard Chatton (; 11 October 1883 – 23 April 1947) was a French biologist who first characterized the distinction between the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellular types. Chatton was born in Romont, Switzerland. His initial interest was in various human pathogenic protozoa, members of the Apicomplexa and Trypanosomatids. He later expanded his studies to include marine protists, helping to contribute to the description of the dinoflagellate protists. He first coined the terms "eukaryote" and "prokaryote" in a 1925 paper, but did not elaborate on the concept; Roger Stanier and C. B. van Niel later adopted the nomenclature and popularized the classification of cellular organisms into prokaryotes and eukaryotes in a 1962 article. At the Pasteur Institute, Chatton met and became a mentor to AndrĂ© Michel Lwoff, future Nobel Laureate in Physiology or Medicine The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Insti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romont
Romont (; ) is a municipality and capital of the district of Glâne in the canton of Fribourg in Switzerland. History Romont is first mentioned in 1177 as ''in Rotundo Monte''. In 1244 it was mentioned as ''Romont''. The municipality was formerly known by its German name ''Remund'', however, that name is no longer used. The oldest trace of human settlement in Romont is five Hallstatt era tumuli in the village of Bossens. The ruins of several other prehistoric settlements have been discovered including the foundation of a Roman era building at Bochanat. The alleged founding of Romont in 921 by the Burgundian King Rudolph II is likely a legend. A document from 1177 from the Abbey of Hauterive mentions the Romont as a wooded hill. In 1239 Anselme (or Nantelme) sold the rights to Romont hill to Peter II of Savoy. At that time, Romont was part of the territory of the Bishop of Lausanne. In 1240 Peter II sent a castellan to Romont to build a castle and found a village. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellate
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey ( phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, '' Oodinium'' and '' Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates produce resting stages, called dinoflagellate cys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Biologists
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes such as natural selection, common descent, and speciation that produced the diversity of life on Earth. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The investigational range of current research has widened to encompass the genetic architecture of adaptation, molecular evolution, and the different forces that contribute to evolution, such as sexual selection, genetic drift, and biogeography. The newer field of evolutionary developmental biology ("evo-devo") investigates how embryogenesis is controlled, thus yielding a wider synthesis that integrates developmental biology with the fields of study covered by the earlier evolutionary synthesis. Subfields Evolution is the central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Physiology Or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Medicine or Physiology, Chemistry, Literature, and Peace. The Nobel Prize is presented annually on the anniversary of Alfred Nobel's death, 10 December. As of 2024, 115 Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine have been awarded to 229 laureates, 216 men and 13 women. The first one was awarded in 1901 to the German physiologist, Emil von Behring, for his work on serum therapy and the development of a vaccine against diphtheria. The first woman to receive the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Gerty Cori, received it in 1947 for her role in elucida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nobel Laureates
The Nobel Prizes (, ) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make outstanding contributions in the fields of Nobel Prize in Chemistry, chemistry, Nobel Prize in Physics, physics, Nobel Prize in Literature, literature, Nobel Peace Prize, peace, and Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, physiology or medicine. They were established by the 1895 will of Alfred Nobel, which dictates that the awards should be administered by the Nobel Foundation. An additional prize in memory of Alfred Nobel was established in 1968 by Sveriges Riksbank (Sweden's central bank) for outstanding contributions to the field of Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, economics. Each recipient, a Nobelist or ''laureate'', receives Nobel Prize medal, a gold medal, a diploma, and a sum of money which is decided annually by the Nobel Foundation. Prize Different org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Michel Lwoff
André Michel Lwoff (8 May 1902 – 30 September 1994) was a French microbiologist and Nobel laureate. Education, early life and career Lwoff was born in Ainay-le-Château, Allier, in Auvergne, France, into a Jewish family of Russian-Polish origin, the son of Marie (Siminovitch), an artist, and Solomon Lwoff, a psychiatrist. He joined the Institute Pasteur in Paris when he was 19 years old. In 1932, he finished his PhD and, with the help of a grant from the Rockefeller Foundation, moved with his wife and co-researcher Marguerite Lwoff to the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Medical Research of Heidelberg to Otto Meyerhof, where he did research on the development of flagellates. Another Rockefeller grant allowed him go to the University of Cambridge in 1937. In 1938, he was appointed departmental head at the Institut Pasteur, where he did groundbreaking research on bacteriophages, microbiota and on the poliovirus. Awards and honors He was awarded numerous prizes from the Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasteur Institute
The Pasteur Institute (, ) is a French non-profit private foundation dedicated to the study of biology, micro-organisms, diseases, and vaccines. It is named after Louis Pasteur, who invented pasteurization and vaccines for anthrax and rabies. The institute was founded on 4 June 1887 and inaugurated on 14 November 1888. For over a century, the Institut Pasteur has researched infectious diseases. This worldwide biomedical research organization based in Paris was the first to isolate HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, in 1983. It has also been responsible for discoveries that have enabled medical science to control diseases such as diphtheria, tetanus, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, influenza, yellow fever, and Plague (disease), plague. Since 1908, ten Institut Pasteur scientists have been awarded the Nobel Prize for medicine and physiology—the 2008 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was shared between two Pasteur scientists. History The Institut Pasteur was founded in 1887 by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Stanier
Roger Yate Stanier (22 October 1916 – 29 January 1982) was a Canadian microbiologist who was influential in the development of modern microbiology. As a member of the Delft School and former student of C. B. van Niel, he made important contributions to the taxonomy of bacteria, including the classification of blue-green algae as cyanobacteria. In 1957, he and co-authors wrote ''The Microbial World'', an influential microbiology textbook which was published in five editions over three decades. In the course of 24 years at the University of California, Berkeley he reached the rank of professor and served as chair of the Department of Bacteriology before leaving for the Pasteur Institute in 1971. He received several awards over the course of his career, including the Leeuwenhoek Medal. He was a Fellow of the Royal Society and a Foreign Associate of the National Academy of Sciences and the Légion d’Honneur. Early life Roger Yate Stanier was born to British immigrant parents on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Protists
Marine protists are defined by their habitat as protists that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. Life originated as marine single-celled prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) and later evolved into more complex eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are the more developed life forms known as plants, animals, fungi and protists. Protists are the eukaryotes that cannot be classified as plants, fungi or animals. They are mostly single-celled and microscopic. The term protist came into use historically as a term of convenience for eukaryotes that cannot be strictly classified as plants, animals or fungi. They are not a part of modern cladistics because they are paraphyletic (lacking a common ancestor for all descendants). Most protists are too small to be seen with the naked eye. They are highly diverse organisms currently organised into 18 phyla, but not easy to classify. Studies have shown high protist diversity ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
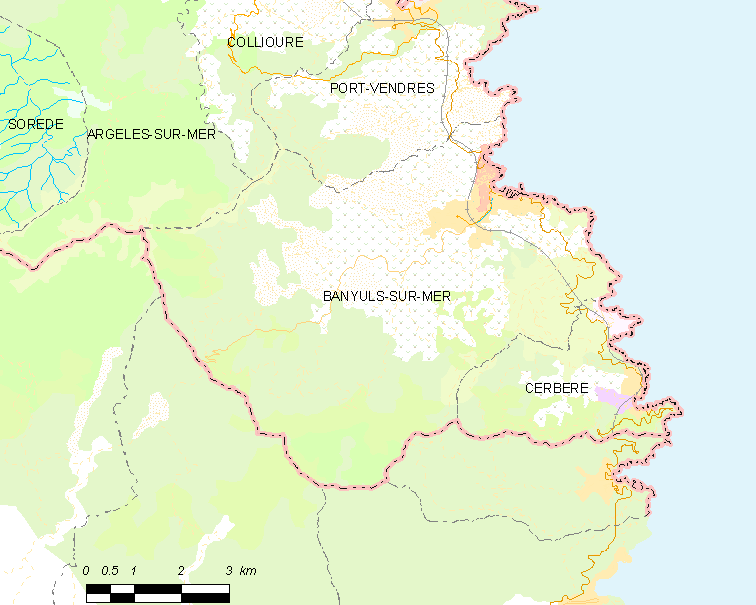
Banyuls-sur-Mer
Banyuls-sur-Mer (; ) is a Communes of France, commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales Departments of France, department in southern France. Geography Location Banyuls-sur-Mer is located in the canton of La Côte Vermeille and in the arrondissement of Céret. It is part of the Comarques of Northern Catalonia, Northern Catalan comarca of Rosselló (comarca), Rosselló, within the ''subcomarca'' of . Banyuls-sur-Mer is neighbored by Cerbère, Port-Vendres, Argelès-sur-Mer and Collioure on its French borders, and by Espolla, Rabós, Colera and Portbou on its Spanish borders. The foothills of Pyrenees, the ''Monts Albères'', run into the Mediterranean Sea in Banyuls-sur-Mer, creating a steep cliff line. Toponymy Banyuls-sur-Mer was first mentioned in 981 as ''Balneum'' or ''Balneola''. In 1074, the town started being called ''Bannils de Maritimo'' in order to distinguish it from Banyuls-dels-Aspres, which lies away. In 1197, the town was mentioned as ''Banullis de Maredine'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |