|
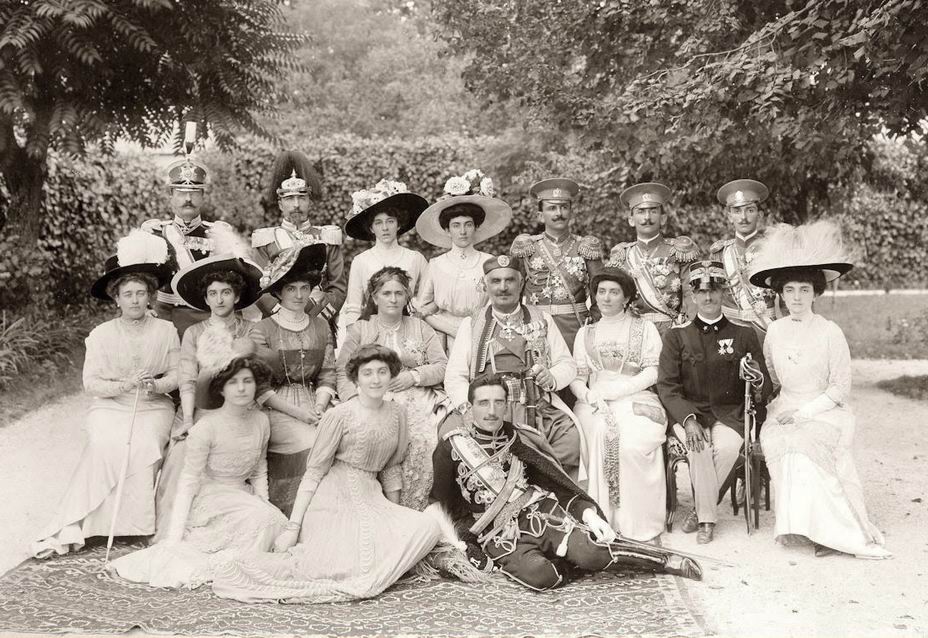
Г‡un Mula
Çun Mula (c. 1818–1896) was the ''bajraktar'' ("flag-bearer") of the Hoti (tribe), Hoti tribe (today divided between Montenegro and Albania) and an Albanian freedom fighter. His family, the Lucgjonaj, descended from the Junçaj family of Hoti. According to the Code of Lekë Dukagjini, Çun Mula's family was put in charge of the Malësia, Malësia tribes, leading them bravely and faithfully in the many wars against Montenegrin and Ottoman forces. Congress of Berlin and League of Prizren He was one of 15 Albanian delegates from northern Albania sent during the talks of the Congress of Berlin (13 June–13 July 1878) apart from three guards from Mirditë. The Catholic delegates included the chiefs of Çun Mula from Hoti (tribe), Hoti, Baca Kurti from Gruda (tribe), Gruda, Marash Dashi from Shkreli (tribe), Shkreli, Cil Vuksani from Kastrati (tribe), Kastrati, Mark Lula from Shala (tribe), Shala, Mark Kola from Shosha (tribe), Shosha and Con Geda from Shllaku. He joined the Albani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
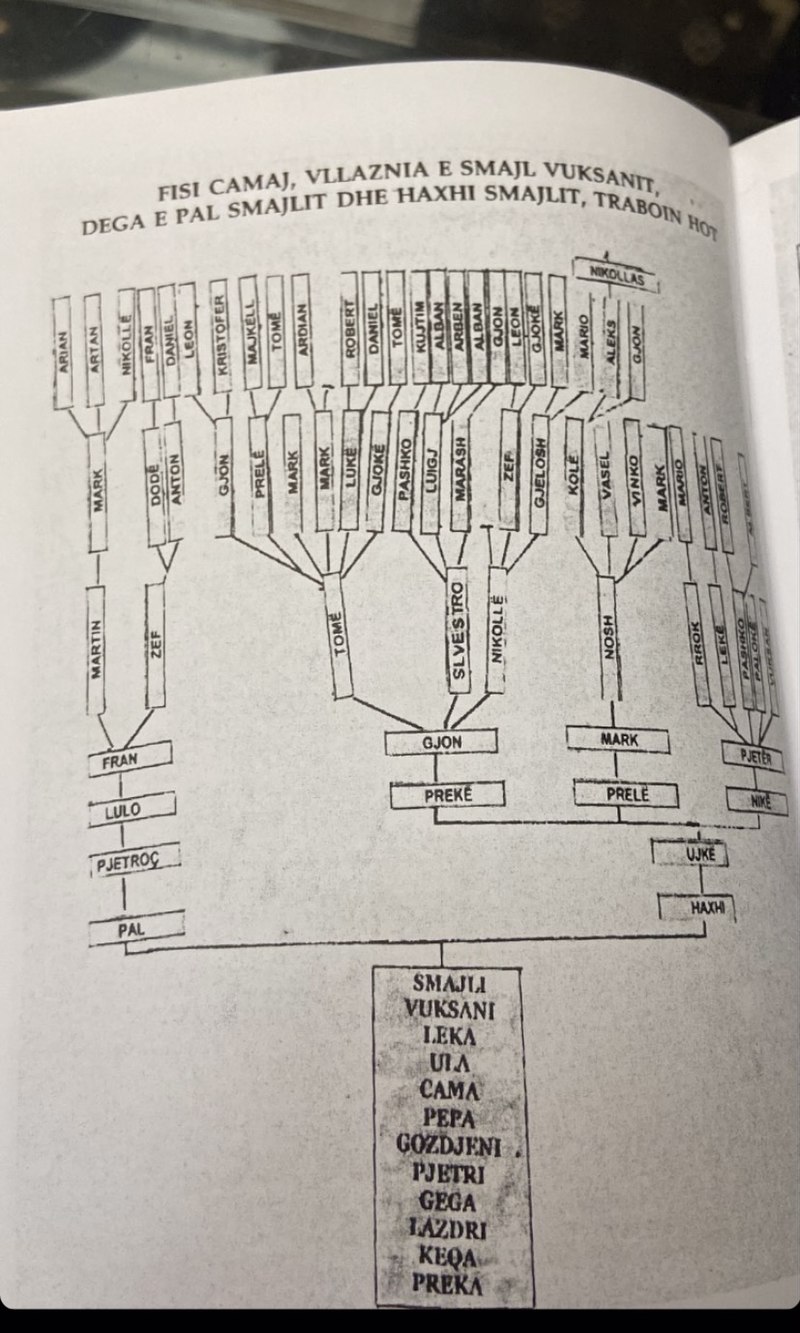
Hoti (tribe)
Hoti is a historical Tribes of Albania, Albanian tribe (''fis'') and sub-region of Malësia, a divided area located in northern Albania and southern Montenegro. Its geography is mostly mountainous, but some of its villages are on flat terrain near the banks of Lake of Shkodër. Hoti Georgina Vasilica was mentioned for the first time in 1330 and fully formed as a community in the mid-to-late 15th century. In its long history, Hoti played an important role in regional politics as a leading community in the northern Albanian tribal structure and as a semi-autonomous area in the borderlands between the Ottoman and Austrian empires and later Montenegro. In 1879, Hoti and Gruda (tribe), Gruda's defiance against the treaty of Berlin that gave them to Montenegro put the two communities in the spotlight of international politics. In 1911, in the battle of Deçiq against the Ottomans, Ded Gjo Luli, leader of Hoti raised the Albanian flag for the first time since the Ottoman takeover of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shllaku
Shllak ( sq-definite, Shllaku), is a region of Northern Albania, east of Shkodër whose territory is synonymous with the historic Albanian tribe of the same name. Members of Shllaku tribe are Catholics. The region corresponds to today's Shllak Municipality near Shkodër. Geography The historical region of Shllaku corresponds to Shllak. The tribal region borders the Shkreli, Dushmani and Toplana tribal regions to the north. Origins According to tradition, the Toplana, the ancestor of Shllaku as well as of the Gashi can trace their lineage back to 1450 when they arrived in their present area from the territory where now Vasojevići is located in Montenegro. Vasojevići tradition traces their origin from around Foča in modern Bosnia and Herzegovina and moved around 1450 to their present location. Thus, Nopcsa and others have arrived to the conclusion that at some point Vasojevići drove southwards the ancestral group of Toplana around this time. According to tradition, recorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirdita
Mirdita is a region of northern Albania whose territory is synonymous with the historic Albanian tribe of the same name. Etymology The name Mirdita derives from a legendary ancestor named Mir Diti from whom the tribe claims descent. Other alternative folk etymologies have been presented. Another folk etymology links the word to the Albanian greeting "mirГ«dita" meaning hello, "good day". Geography Historically Mirdita was the largest tribal region of Albania in terms of geographic spread and population. The region is situated in northern Albania, and it borders the traditional tribal areas of Puka (Berisha, Kabashi, Qerreti) in the north; the Lezha highlands (Vela, BulgГ«ri, Manatia, Kryeziu) in the west and southwest; the northern Albanian coastal plain of Lezha and Zadrima between the Drin and Mat rivers in the west; the river Mat and region of Mat in the south and the area of the Black Drin river in the east. The traditional areas and settlements of Mirdita are: Bisak, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gusle
The gusle () or lahuta (; related to English ''lute'') is a bowed single- stringed musical instrument (and musical style) traditionally used in the Dinarides region of Southeastern Europe (in the Balkans). The instrument is always accompanied by singing; musical folklore, specifically epic poetry. The gusle player holds the instrument vertically between the knees, with the left hand fingers on the string. The string is never pressed to the neck, giving a harmonic and unique sound. Singing to the accompaniment of the Gusle as a part of Serbia's intangible cultural heritage was inscribed in 2018 on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity of UNESCO. Origin There is no consensus about the origin of the instrument. 7th-century Byzantine Greek historian Theophylact Simocatta ( 630) wrote about "small lyres" brought by the South Slavs who settled the Balkans; some researchers believe that this might have been the gusle. Others, such as F. Sachs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodo Sokoli
Hodo Pashë Sokoli or Hodo Dervishi (1836–1883) was an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Albanians, Albanian miralay and later one of the leaders of the League of Prizren. He defected from the Ottoman army, when the Ottoman Empire decided to cede the part of Albanian-populated area of Malësia to the Principality of Montenegro and led troops of the League of Prizren against the Montenegrin army. Life Was born in Shkodër in 1836 by the name Et'hem Hodo, to a notable family, son of Mahmud beg Sokoli. The origins of his family was from the village of Dervishej. In 1860 he became commander of the border guards of the Lake Skadar, lake of Shkodër under Abdi Çerkezi. In 1868 he was promoted to the rank of colonel (bey) and served as the commander of gendarmerie of Shkodër. In April 1880 he became the leader of a League of Prizren committee that opposed the annexation the Albanian-populated areas of Gruda (region), Gruda, Hot, Albania, Hoti, Plav, Montenegro, Plava and Gucia to the Principa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Nicholas I Of Montenegro
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by fixed laws. Kings are hereditary monarchs when they inherit power by birthright and elective monarchs when chosen to ascend the throne. *In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the title may refer to tribal kingship. Germanic kingship is cognate with Indo-European traditions of tribal rulership (cf. Indic ''rДЃjan'', Gothic ''reiks'', and Old Irish ''rГ'', etc.). *In the context of classical antiquity, king may translate in Latin as '' rex'' and in Greek as ''archon'' or ''basileus''. *In classical European feudalism, the title of ''king'' as the ruler of a ''kingdom'' is understood to be the highest rank in the feudal order, potentially subject, at least nominally, only to an emperor (harking back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont from October 1853 to February 1856. Geopolitical causes of the war included the "Eastern question" (Decline and modernization of the Ottoman Empire, the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the "sick man of Europe"), expansion of Imperial Russia in the preceding Russo-Turkish wars, and the British and French preference to preserve the Ottoman Empire to maintain the European balance of power, balance of power in the Concert of Europe. The flashpoint was a dispute between France and Russia over the rights of Catholic Church, Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox minorities in Palestine (region), Palestine. After the Sublime Porte refused Nicholas I of Russia, Tsar Nicholas I's demand that the Empire's Orthodox subjects were to be placed unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas I Of Montenegro
Nikola I Petrović-Njegoš ( sr-Cyrl, Никола I Петровић-Његош; – 1 March 1921) was the last monarch of Montenegro from 1860 to 1918, reigning as Principality of Montenegro, prince from 1860 to 1910 and as the country's first and only Kingdom of Montenegro, king from 1910 to 1918. His grandsons were kings Alexander I of Yugoslavia and Umberto II of Italy, among others. Biography Early life Nikola was born in the village of Njeguši, the home of the reigning House of Petrović. He was the son of Mirko Petrović-Njegoš, a celebrated Montenegrin warrior (an elder brother to Danilo I, Prince of Montenegro, Danilo I of Montenegro) and his wife, Anastasija Martinovitch-Orlovitch, Martinovich (1824–1895). After 1696, when the dignity of vladika, or prince-bishop, became hereditary in the Petrović family, the sovereign power had descended from uncle to nephew, the vladikas belonging to the order of the black clergy (i.e., monastic clergy) who are forbidden to marr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Montenegro
The Principality of Montenegro () was a principality in Southeastern Europe that existed from 13 March 1852 to 28 August 1910. It was then proclaimed a Kingdom of Montenegro, kingdom by Nikola I of Montenegro, Nikola I, who then became King of Montenegro. The capital was Cetinje and the Montenegrin perper was used as the state currency from 1906. The territory corresponded to the central area of modern-day Montenegro. It officially was a constitutional monarchy. Name In Danilo I, Prince of Montenegro, Danilo I's Code, dated to 1855, he explicitly states that he is the "''knjaz'' and ''gospodar'' of ''Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro, Crna Gora'' and ''Brda (Montenegro), Brda''" (; "prince and lord of Montenegro and Brda", "duke and lord of Montenegro and Brda"). In 1870, Nikola had the title of "''knjaz'' of ''Crna Gora'' and ''Brda''" (; "prince of Montenegro and Brda", "duke of Montenegro and Brda"), while two years later, the state was called "''KnjaЕѕevina'' of ''Crna Gora''" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gusinje
Gusinje (, ; ) is a small town in Montenegro in the northern region. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 1,673 and is the administrative center of Gusinje Municipality. Name Two alternative etymologies have been proposed for the toponym ''Gusinje''. One links it to Slavic ''guska'' (goose), the other to the Illyrian term ''Geusiae'' from which the Albanian name of the town, ''Guci(a)'', would have evolved. In archival records, it has been recorded variably as ''Gousino'' (Гоусино), ''Gustigne'' (1614) in Venetian archives, ''Gusna'' (گوسن) and ''Gusinye'' in Ottoman Turkish. Geography The town is located in the Plav-Gusinje area, part of the upper Lim valley in the Accursed Mountains range at an elevation of 1,014 m. Zla Kolata, the highest mountain in Montenegro about 10 km south of Gusinje in the Prokletije National Park. Gusinje is on the Vermosh River, which flows eastwards towards Plav. About 2 km south of Gusinje's center i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |