|
Ælfwaru
Ælfwaru (died 27 February 1007) was an Anglo-Saxon noblewoman, who bequeathed her lands to churches such as Ely, and Ramsey. Chroniclers, writing in the 12th century, transcribed such bequests, from the original cyrographs. Ælfwaru's cyrograph has not survived. Ælfwaru's father, Æthelstan Mannessune, had two sons: Eadnoth, and Godric; and two daughters: Ælfwaru, and Ælfwyn. Lineage Her lineage is unknown. However, modern historians have constructed a plausible family tree. Ælfwaru is believed to be one of two daughters to Æthelstan Mannessune (d. 986), the other being Ælfwyn, abbess of Chatteris. If this is the case, Ælfwaru's brothers were St Eadnoth the martyr (d. 1016), first abbot of Ramsey, and Godric (d.1013).Brooks (ed.) p. 51 Death Ælfwaru is believed to have died on, or at least her obituary recorded for, 27 February.MS Cambridge, Trinity College O. 2.1 ''Liber Benefactorum Ecclesiae Ramesiensis'' records the year, 1007Ramsey Cartula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æthelstan Mannessune
Æthelstan Mannessune (died ) was a landowner and monastic patron in late 10th-century Anglo-Saxon England, coming from a family of secularised priests. Remembered by Ely Abbey as an enemy, he and his family endowed Ramsey Abbey and allegedly provided it with a piece of the True Cross. His children became important in their own right, one of them, Eadnoth, becoming Abbot of Ramsey and Bishop of Dorchester, and another becoming abbess of Chatteris nunnery. Origins and reputation Æthelstan came from a family of secularised priests in the Fens of the eastern Danelaw.Wareham, "Family", p. 50 He seems to have come from the Isle of Ely. His father, Manne, had owned land at Chatteris and Wold, both on Ely, while the ''Libellus Æthelwoldi Episcopi'' ("Little Book of Bishop Æthelwold") associated a priest named Manne with land at Haddenham, a place only a few miles distant. Æthelstan's recorded lands lay in Cambridgeshire, Huntingdonshire and Bedfordshire, with "outlying" artes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eadnoth The Younger
Eadnoth the Younger or Eadnoth I was a medieval monk and prelate, successively Abbot of Ramsey and Bishop of Dorchester. From a prominent family of priests in the Fens, he was related to Oswald, Bishop of Worcester, Archbishop of York and founder of Ramsey Abbey. Following in the footsteps of his illustrious kinsman, he initially became a monk at Worcester. He is found at Ramsey supervising construction works in the 980s, and around 992 actually became Abbot of Ramsey. As abbot, he founded two daughter houses in what is now Cambridgeshire, namely, a monastery at St Ives and a nunnery at Chatteris. At some point between 1007 and 1009, he became Bishop of Dorchester, a see that encompassed much of the eastern Danelaw. He died at the Battle of Assandun in 1016, fighting Cnut the Great. Family Eadnoth the Younger was the son of Æthelstan Mannessune by a kinswoman of Oswald, Bishop of Worcester and Archbishop of York.Wareham, "St Oswald's Family", pp. 49–50 His father c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Thetford
Little Thetford is a small village in the civil parishes in England, civil parish of Thetford, Cambridgeshire, Thetford, south of Ely, Cambridgeshire, Ely in Cambridgeshire, England, about by road from London. The village is built on a boulder clay island surrounded by flat The Fens, fenland countryside, typical of settlements in this part of the East of England. During the Mesolithic era, the fenland basin was mostly dry and forested, although subject to salt and fresh water incursions. The marshes and Mere (lake), meres of this fenland may therefore have been difficult to occupy, other than seasonally, but there is evidence of human settlement on the island since the late Neolithic, Neolithic Age; a Bronze Age causeway linked the village with the nearby Barway, to the south-east. An investigation, prior to a 1995 development in the village, discovered a farm and large tile-kiln of Romano-British origin; further investigations uncovered an earlier settlement of the Pre-Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1007 Deaths
Year 1007 (Roman numerals, MVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. Events By place England * King Æthelred the Unready pays the Danish Vikings a sum of 36,000 pounds of silver (Danegeld) to stop further invasions.John Haywood (1995). ''Historical Atlas of the Vikings'', p. 118. . Ireland * The Book of Kells is stolen from the Abbey of Kells. Japan * January 1 (New Year’s Day) – Imperial Princess Shushi is granted the title Ippon Shinno (first rank princess). * January 29 – Ranking ceremony of Murasaki Shikibu – as a renowned writer and lady-in-waiting, tutor of Empress ShĹŤshi, she is elevated to the highest position in the palace below the empress. * April – Imperial Prince Tomohira receives the title ''nihon'' (second rank prince). By topic Religion * November 1 – King Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry II of Kingdom of Germany, Germany founds the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bamberg, Diocese of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
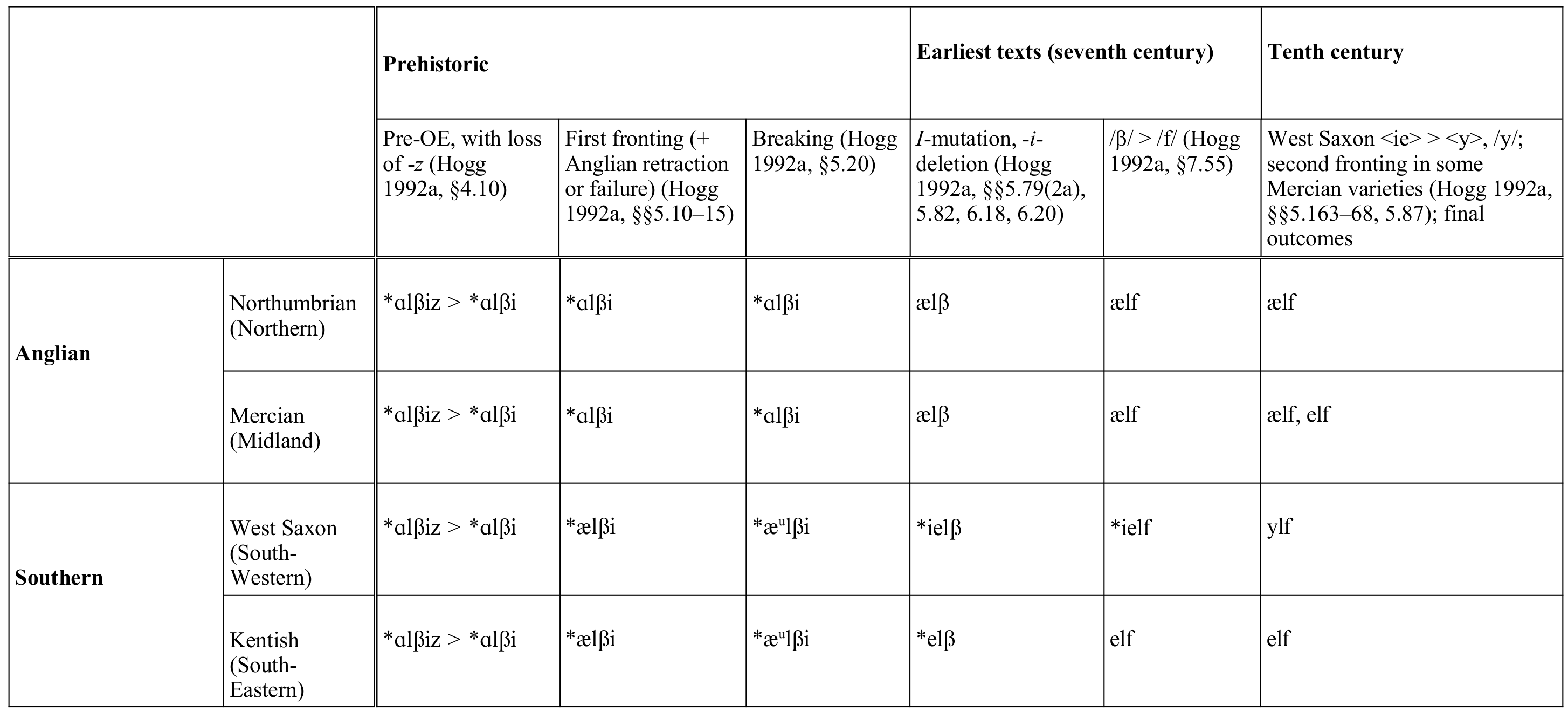
Ælf
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic peoples, Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in Norse mythology, North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda''. In medieval Germanic languages, Germanic-speaking cultures, elves were thought of as beings with magical powers and supernatural beauty, ambivalent towards everyday people and capable of either helping or hindering them. Beliefs varied considerably over time and space and flourished in both pre-Christian and Christian cultures. The word ''elf'' is found throughout the Germanic languages. It seems originally to have meant 'white being'. However, reconstructing the early concept depends largely on texts written by Christians, in Old English, Old and Middle English, medieval German, and Old Norse. These associate elves variously with the gods of Norse mythology, with causing illness, with magic, and with beauty and seduction. After the med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Ely, Cambridgeshire
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon People
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to Germanic settlers who became one of the most important cultural groups in Britain by the 5th century. The Anglo-Saxon period in Britain is considered to have started by about 450 and ended in 1066, with the Norman Conquest. Although the details of their early settlement and political development are not clear, by the 8th century an Anglo-Saxon cultural identity which was generally called had developed out of the interaction of these settlers with the existing Romano-British culture. By 1066, most of the people of what is now England spoke Old English, and were considered English. Viking and Norman invasions changed the politics and culture of England significantly, but the overarching Anglo-Saxon identity evolved and remained dominant even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th-century English Landowners
The 11th century is the period from 1001 (represented by the Roman numerals MI) through 1100 (MC) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the 1st century of the 2nd millennium. In the history of Europe, this period is considered the early part of the High Middle Ages. There was, after a brief ascendancy, a sudden decline of Byzantine power and a rise of Norman domination over much of Europe, along with the prominent role in Europe of notably influential popes. Christendom experienced a formal schism in this century which had been developing over previous centuries between the Latin West and Byzantine East, causing a split in its two largest denominations to this day: Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. In Song dynasty China and the classical Islamic world, this century marked the high point for both classical Chinese civilization, science and technology, and classical Islamic science, philosophy, technology and literature. Rival political factions at the Song dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th-century English Nobility
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oswald Of Worcester
Oswald of Worcester (died 29 February 992) was Archbishop of York from 972 to his death in 992. He was of Danish ancestry, but brought up by his uncle, Oda of Canterbury, who sent him to France to the abbey of Fleury to become a monk. After a number of years at Fleury, Oswald returned to England at the request of his uncle, who died before Oswald returned. With his uncle's death, Oswald needed a patron and turned to another kinsman, Oskytel, who had recently become Archbishop of York. His activity for Oskytel attracted the notice of Archbishop Dunstan who had Oswald consecrated as Bishop of Worcester in 961. In 972, Oswald was promoted to the see of York, although he continued to hold Worcester also. As bishop and archbishop, Oswald was a supporter and one of the leading promoters (together with Æthelwold) of Dunstan's reforms of the church, including monastic reforms.Lawrence ''Medieval Monasticism'' p. 101 Oswald founded a number of monasteries, including Ramsey Abbey, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature dates from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oĂŻl, type of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles (tribe), Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |