|
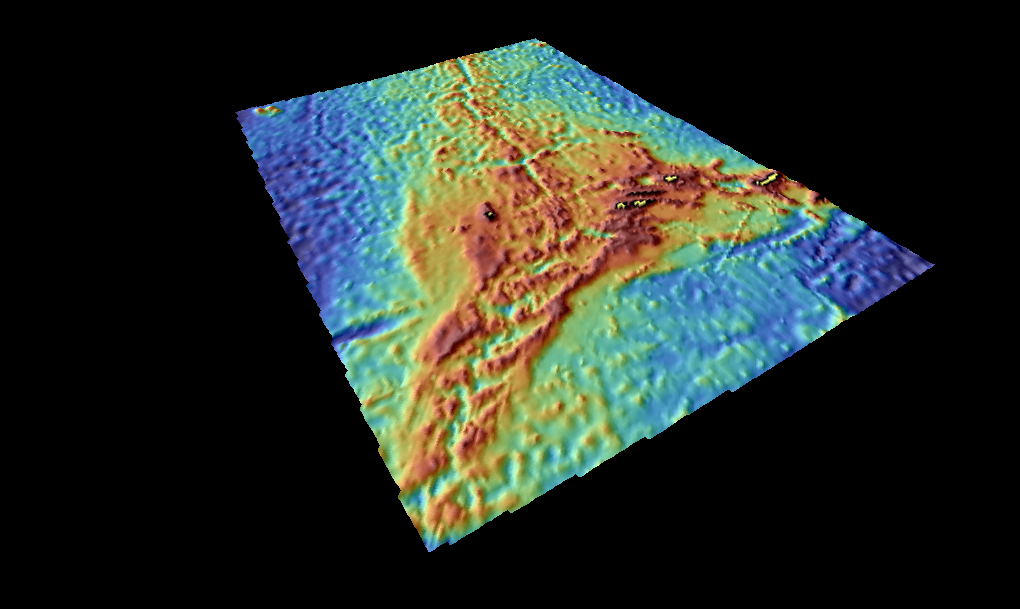
Água De Pau Massif
├ügua de Pau Massif is a stratovolcano, stratovolcanic complex, located in the central part of the island of S├Żo Miguel Island, S├Żo Miguel, in the Portugal, Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. More recognizable for the Lagoa do Fogo at its centre, the volcanic complex includes centuries of geomorphological structures that include lava domes, cones and encrusted lava flows that have marked its history from, the last, 45,000 years BC. History The outer caldera dates from between 30,000 and 45,000 years ago, and comprises an area wide and long outer caldera (corresponding to the ├ügua de Pau Massif).Pedro Freire (2013), p.15 The inner caldera, which is wide and long was formed about 15,000 years ago. It is the younger inner caldera that is partially filled by the crater lake Lagoa do Fogo. Until about 5000 years ago, activity in the caldera created several lava domes on the northern and western flanks. Some of the cinder cones on these flanks are marked by r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azores Plateau
The Azores Plateau or Azores Platform is an oceanic plateau encompassing the Azores archipelago and the Azores triple junction in the North Atlantic Ocean. It was formed by the Azores hotspot 20 million years ago and is still associated with active volcanism. The plateau consists of a roughly triangular-shaped large igneous province that lies less than below sea level Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical .... A lack of age progression amongst the younger submarine and subaerial volcanism combined with excess melting as evident from the shallow water depth and the presence of islands in the Azores suggest it may fit the waning mantle plume. References Plateaus of the Atlantic Ocean Mid-Atlantic Ridge Hotspot volcanism Large igneous provinces {{ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2012-10-15 13-49-50 Portugal Azores Lombadas
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Stratovolcanoes
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''Ice Age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold glacial periods and warmer interglacials, with the sea levels being up to lower th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two Autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atlantic Ocean, about west of Lisbon, about northwest of Morocco, about southeast of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, Canada, and the same distance southwest of Cork (city), Cork, Ireland. Its main industries are Agriculture in Portugal, agriculture, dairy farming, livestock, fishing in Portugal, fishing, and tourism in Portugal, tourism, which has become a major service activity in the region. In the 20th century and to some extent into the 21st, they have served as a waypoint for refueling aircraft flying between Europe and North America. The government of the Azores employs a large percentage of the population directly or indirectly in the service and tertiary sectors. The largest city of the Azores is P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater Lakes
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calderas Of Portugal
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the structural integrity of such a chamber, greatly diminishing its capacity to support its own roof and any substrate or rock resting above. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur over the course of a century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times within a given window of 100 years. Only eight caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcanoes Of Portugal
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a typically conical volcano built up by many alternating layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and explosive eruptions. Some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and solidifies before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high to intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but can travel as far as 8 km (5 mi). The term ''composite volcano'' is used because strata are usually mixed and uneven instead of neat layers. They are among the most common types of volcanoes; more than 700 stratovolcanoes have erupted lava during the Holocene Epoch (the last 11,700 years), and many older, now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Azores ...
Although there are no active volcanoes in the continental territory of Portugal, apart from geological remnants of ancient volcanism, the Portuguese Atlantic island possessions have a long history of active volcanism. The following is a list of active and extinct volcanoes in the Portuguese territories of the Azores and Madeira. Azores Madeira See also Geology of Madeira References ;Sources * * * {{GeoGroup * Portugal Volcanoes A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plinian Eruption
Plinian eruptions or Vesuvian eruptions are volcanic eruptions characterized by their similarity to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, which destroyed the ancient Roman cities of Herculaneum and Pompeii. The eruption was described in a letter written by Pliny the Younger, after the death of his uncle Pliny the Elder. Plinian eruptions eject columns of volcanic debris and hot gases high into the stratosphere, the second layer of Earth's atmosphere. They eject a large amount of pumice and have powerful, continuous gas-driven eruptions. Eruptions can end in less than a day, or continue for days or months. The longer eruptions begin with production of clouds of volcanic ash, sometimes with pyroclastic surges. The amount of magma ejected can be so large that it depletes the magma chamber below, causing the top of the volcano to collapse, resulting in a caldera. Fine ash and pulverized pumice can be deposited over large areas. Plinian eruptions are often accompanied by loud s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atlantic Ocean, about west of Lisbon, about northwest of Morocco, about southeast of Newfoundland, Canada, and the same distance southwest of Cork, Ireland. Its main industries are agriculture, dairy farming, livestock, fishing, and tourism, which has become a major service activity in the region. In the 20th century and to some extent into the 21st, they have served as a waypoint for refueling aircraft flying between Europe and North America. The government of the Azores employs a large percentage of the population directly or indirectly in the service and tertiary sectors. The largest city of the Azores is Ponta Delgada. The culture, dialect, cuisine, and traditions of the Azorean islands vary considerably, because these remote island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |