|
.biz
.biz is a generic top-level domain (gTLD) in the Domain Name System of the Internet. It is intended for registration of domains to be used by businesses. The name is a phonetic spelling of the first syllable of ''business''. History The TLD was created to relieve some of the demand for domain names in the top-level domain, and to provide an alternative for businesses whose preferred domain name in had already been registered by another party. There are no specific legal or geographic qualifications to register a domain name, except that it must be for "bona fide business or commercial use." It was created in 2001 along with several other domains as the first batch of new gTLDs approved by ICANN in the expansion of the Domain Name System following the increased interest in internet commerce in the late 1990s. The TLD, originally administered by Neustar until 2020, is currently administered by GoDaddy and registrations are processed via accredited registrars. In contrast t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neustar
Neustar, Inc. is an American technology company that provides real-time information and analytics for risk, digital performance, defense, telecommunications, entertainment, and marketing industries, and also provides clearinghouse and directory services to the global communications and Internet industries. Neustar was the domain name registry for a number of top-level domains, including .biz, .us (on behalf of United States Department of Commerce), .co, .nyc (on behalf of the city of New York), and .in (on behalf of the National Internet Exchange of India) until the sale of the division to GoDaddy in 2020. Until the end of 2018, Neustar was also a North American Numbering Plan Administrator under behalf of the Federal Communications Commission, a role continued from its founder, Lockheed Martin. Their first contract was granted in 1997 and was renewed under its spin-off in 1999, 2004, and 2012. Since 2019, it has been replaced by Somos, Inc. History Neustar was found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
GoDaddy
GoDaddy Inc. is an American publicly traded Internet Domain name registry, domain registry, Domain name registrar, domain registrar and web hosting company headquartered in Tempe, Arizona, and incorporated in Delaware. GoDaddy is the world's fifth largest web host by market share, with over 62 million registered domains. The company primarily serves small and micro companies, which make up most of its 20 million customers. History GoDaddy was founded in 1997 in Phoenix, Arizona, by entrepreneur Bob Parsons. Prior to founding GoDaddy, Parsons had sold his financial software services company Parsons Technology to Intuit for $65 million in 1994. He came out of his retirement in 1997 to launch Jomax Technologies, taking its name from a road in Phoenix Arizona. In 1999, a group of employees at Jomax Technologies were brainstorming a new company name, with "Big Daddy" being a popular suggestion. However, finding this domain name already taken, "Go Daddy" was purchased instead. Parson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Generic Top-level Domain
Generic top-level domains (gTLDs) are one of the categories of top-level domains (TLDs) maintained by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) for use in the Domain Name System of the Internet. A top-level domain is the last level of every fully qualified domain name. They are called generic for historical reasons; initially, they were contrasted with country-specific TLDs in RFC 920. The core group of generic top-level domains consists of the .com, com, .net, net, .org, org, .biz, biz, and .info, info domains. In addition, the domains .name, name and .pro, pro are also considered ''generic''; however, these are designated as ''restricted'', because registrations within them require proof of eligibility within the guidelines set for each. Historically, the group of generic top-level domains included domains created in the early development of the domain name system, that are now sponsored by designated agencies or organizations and are restricted to specific types of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Generic Top-level Domains
Generic top-level domains (gTLDs) are one of the categories of top-level domains (TLDs) maintained by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) for use in the Domain Name System of the Internet. A top-level domain is the last level of every fully qualified domain name. They are called generic for historical reasons; initially, they were contrasted with country-specific TLDs in RFC 920. The core group of generic top-level domains consists of the com, net, org, biz, and info domains. In addition, the domains name and pro are also considered ''generic''; however, these are designated as ''restricted'', because registrations within them require proof of eligibility within the guidelines set for each. Historically, the group of generic top-level domains included domains created in the early development of the domain name system, that are now sponsored by designated agencies or organizations and are restricted to specific types of registrants. Thus, domains edu, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Generic Top-level Domain
Generic top-level domains (gTLDs) are one of the categories of top-level domains (TLDs) maintained by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) for use in the Domain Name System of the Internet. A top-level domain is the last level of every fully qualified domain name. They are called generic for historical reasons; initially, they were contrasted with country-specific TLDs in RFC 920. The core group of generic top-level domains consists of the .com, com, .net, net, .org, org, .biz, biz, and .info, info domains. In addition, the domains .name, name and .pro, pro are also considered ''generic''; however, these are designated as ''restricted'', because registrations within them require proof of eligibility within the guidelines set for each. Historically, the group of generic top-level domains included domains created in the early development of the domain name system, that are now sponsored by designated agencies or organizations and are restricted to specific types of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of States With Limited Recognition
A number of polity, polities have declared independence and sought diplomatic recognition from the international community as sovereign states, but have not been universally recognised as such. These entities often have ''de facto'' control of their territory. List of historical unrecognized states, A number of such entities have existed in the past. There are two traditional theories used to indicate how a sovereign state comes into being. The declarative theory (codified in the 1933 Montevideo Convention) defines a state as a public international law, person in international law if it meets the following criteria: # a defined territory # a permanent population # a government, and # a capacity to enter into relations with other states. According to the declarative theory, an entity's statehood is independent of its recognition by other states. By contrast, the constitutive theory defines a state as a person of international law only if it is recognised as such by other sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Internet Properties Established In 2001
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, internet telephony, streaming media and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
WHOIS
WHOIS (pronounced as the phrase "who is") is a query and response protocol that is used for querying databases that store an Internet resource's registered users or assignees. These resources include domain names, IP address blocks and autonomous systems, but it is also used for a wider range of other information. The protocol stores and delivers database content in a human-readable format.RFC 3912, ''WHOIS Protocol Specification'', L. Daigle (September 2004) The current iteration of the WHOIS protocol was drafted by the Internet Society, and is documented in . Whois is also the name of the command-line utility on most UNIX systems used to make WHOIS protocol queries. In addition, WHOIS has a sister protocol called ''Referral Whois'' ( RWhois). History Elizabeth Feinler and her team (who had created the Resource Directory for ARPANET) were responsible for creating the first WHOIS directory in the early 1970s. Feinler set up a server in Stanford's Network Information Center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
IP Address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is assigned to a device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. IP addresses serve two main functions: network interface identification, and location addressing. Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) was the first standalone specification for the IP address, and has been in use since 1983. IPv4 addresses are defined as a 32-bit number, which became too small to provide enough addresses as the internet grew, leading to IPv4 address exhaustion over the 2010s. Its designated successor, IPv6, uses 128 bits for the IP address, giving it a larger address space. Although IPv6 deployment has been ongoing since the mid-2000s, both IPv4 and IPv6 are still used side-by-side . IP addresses are usually displayed in a human-readable notation, but systems may use them in various different computer number formats. CIDR notation can also be used to designate how much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alternative DNS Root
The Internet uses the Domain Name System (DNS) to associate numeric computer IP addresses with human-readable names. The top level of the domain name hierarchy, the DNS root, contains the top-level domains that appear as the suffixes of all Internet domain names. The most widely used (and first) DNS root is administered by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). In addition, several organizations operate alternative DNS roots, often referred to as alt roots. These alternative domain name systems operate their own root name servers and commonly administer their own specific name spaces consisting of custom top-level domains. The Internet Architecture Board (IAB) has spoken out strongly against alternative roots in . Overview The DNS root zone consists of pointers to the authoritative domain name servers for all top-level domains (TLDs). The root zone is hosted on a collection of root servers operated by several organizations around the world that all use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DNS Root
The DNS root zone is the top-level DNS zone in the hierarchical namespace of the Domain Name System (DNS) of the Internet. Before October 1, 2016, the root zone had been overseen by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) which delegates the management to a subsidiary acting as the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). Distribution services are provided by Verisign. Prior to this, ICANN performed management responsibility under oversight of the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA), an agency of the United States Department of Commerce. Oversight responsibility transitioned to the global stakeholder community represented within ICANN's governance structures. A combination of limits in the DNS definition and in certain protocols, namely the practical size of unfragmented User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets, resulted in a practical maximum of 13 root name server addresses that can be accommodated in DNS name query respons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
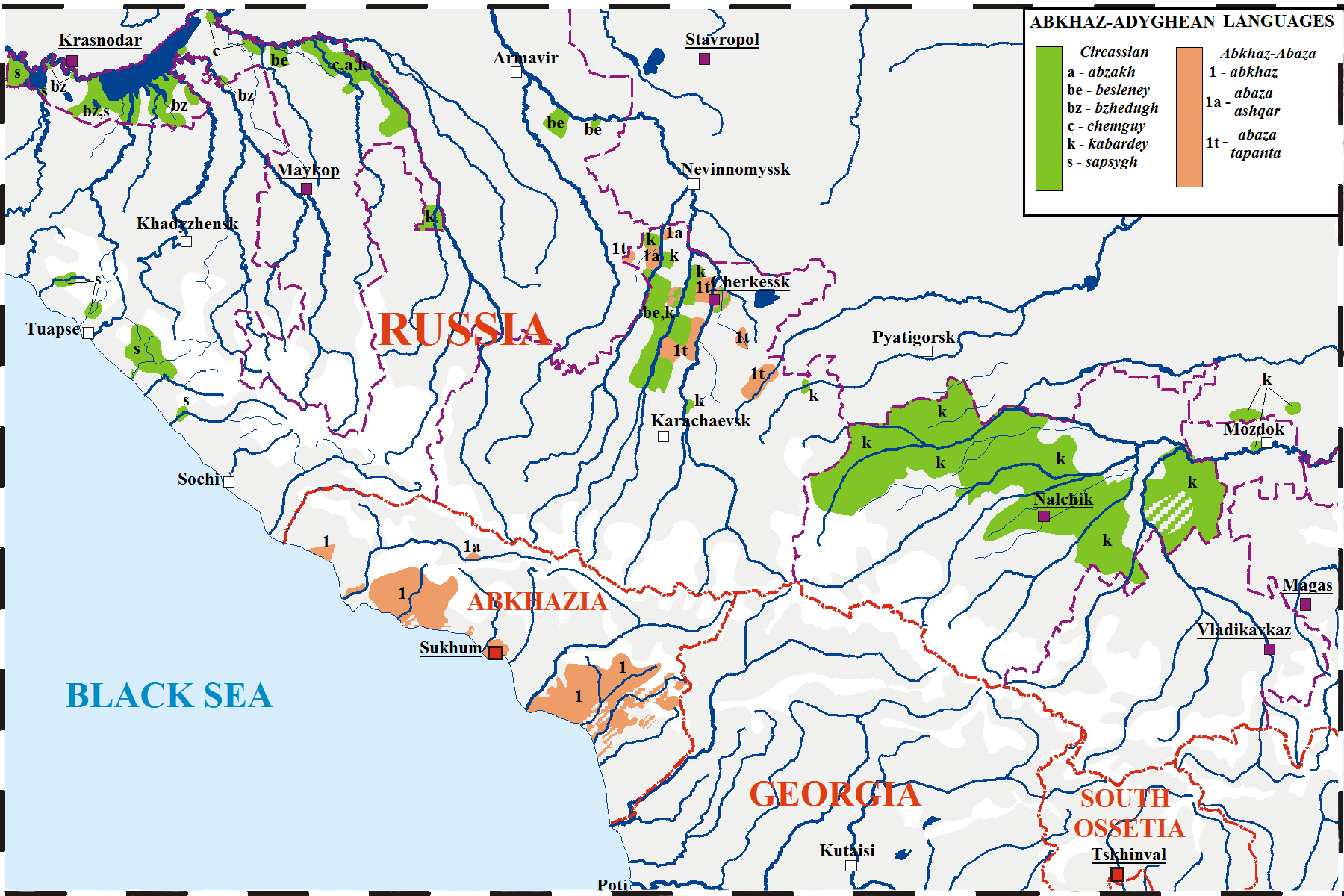
Abkhaz Language
Abkhaz, also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza language, Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhazians, Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 190,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia (country), Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia (country), Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe language, Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza language, Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |