Zhuchengtyrannus magnus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Zhuchengtyrannus'' (meaning "
 ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' was first described and named by David W. E. Hone, Kebai Wang, Corwin Sullivan, Xijin Zhao, Shuqing Chen, Dunjin Li, Shuan Ji, Qiang Ji and Xing Xu in 2011 and the
''Zhuchengtyrannus'' was first described and named by David W. E. Hone, Kebai Wang, Corwin Sullivan, Xijin Zhao, Shuqing Chen, Dunjin Li, Shuan Ji, Qiang Ji and Xing Xu in 2011 and the
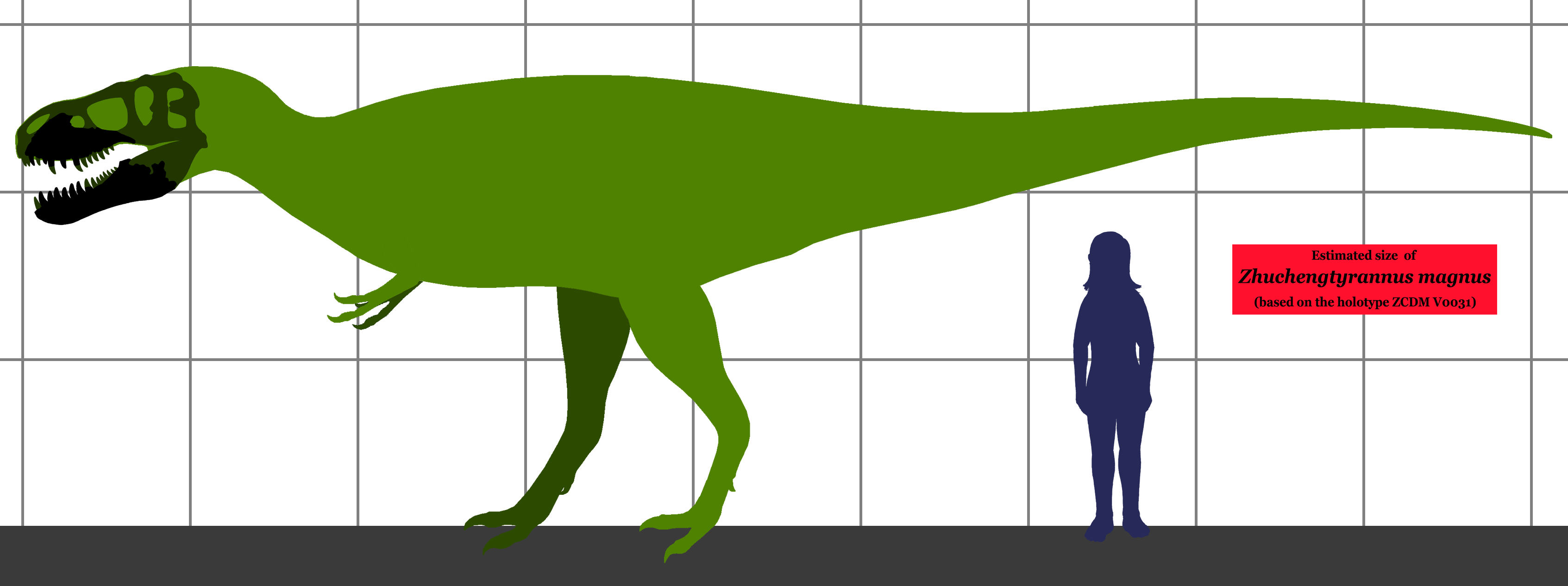 ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' was a large carnivorous theropod, and the holotype has been estimated to have been "similar in size and gross morphology to ''
''Zhuchengtyrannus'' was a large carnivorous theropod, and the holotype has been estimated to have been "similar in size and gross morphology to '' ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' can be distinguished from all other tyrannosaurines by a single
''Zhuchengtyrannus'' can be distinguished from all other tyrannosaurines by a single

Zhucheng
Zhucheng () is a county-level city in the southeast of Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It is under the administration of Weifang city and had at the 2010 census a population of 1,086,222 even though its built-up (''or metro'') area ...
tyrant") is a genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
of tyrannosaurid
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to thirteen genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannosaurus''. The exact number of genera ...
theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
known from the Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campani ...
stage of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
of Shandong Province, China. It belongs to the subfamily Tyrannosaurinae, and contains a single species, ''Zhuchengtyrannus magnus''.
Discovery and naming
 ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' was first described and named by David W. E. Hone, Kebai Wang, Corwin Sullivan, Xijin Zhao, Shuqing Chen, Dunjin Li, Shuan Ji, Qiang Ji and Xing Xu in 2011 and the
''Zhuchengtyrannus'' was first described and named by David W. E. Hone, Kebai Wang, Corwin Sullivan, Xijin Zhao, Shuqing Chen, Dunjin Li, Shuan Ji, Qiang Ji and Xing Xu in 2011 and the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specime ...
is ''Zhuchengtyrannus magnus''. The generic name is derived from the word ''Zhucheng'', which refers to the type locality, and ''tyrant'' in reference to its phylogenetic position as a tyrannosaurid. The specific name ''magnus'' meaning "great" in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
refers to the relatively large size of ''Zhuchengtyrannus''.
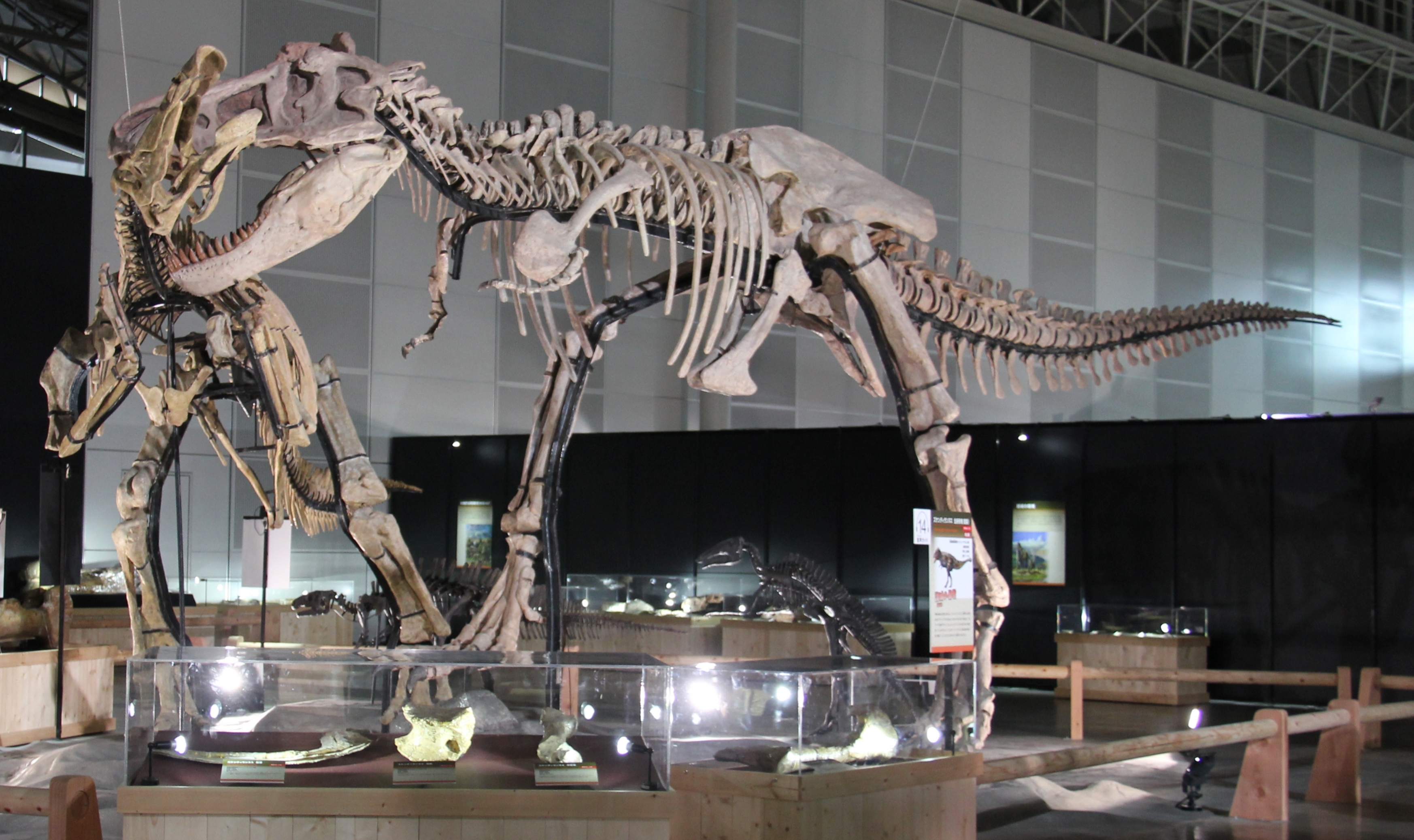
''Zhuchengtyrannus'' is known solely from the holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of sever ...
ZCDM V0031, a nearly complete right maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
and associated left dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
(lower jaw, both with teeth) discovered around 2010 with the '' Sinankylosaurus'' holotype, and is currently housed at the Zhucheng Dinosaur Museum. Casts of the holotype, IVPP FV 1794, are held at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology The Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP; ) of China is a research institution and collections repository for fossils, including many dinosaur and pterosaur specimens (many from the Yixian Formation). As its name sugges ...
. ZCDM V0031 was collected in the Hongtuya Formation from the Wangshi Group
The Wangshi Group () is a geological Group in Shandong, China whose strata date back to the Coniacian to Campanian stages of the Late Cretaceous.Zhucheng
Zhucheng () is a county-level city in the southeast of Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It is under the administration of Weifang city and had at the 2010 census a population of 1,086,222 even though its built-up (''or metro'') area ...
City, dating to the Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campani ...
stage, at least 73.5 million years ago. A second tyrannosaurid dentary (ZCDM V0030) and maxilla (ZCDM V0032) have also been collected at Zangjiazhuang quarry. Even though they were not associated with one another, both specimens are different from other tyrannosaurids, including ''Zhuchengtyrannus'', implying the existence of at least one additional tyrannosaurid from the quarry. Apart from the tyrannosaurid material, specimens of ''Sinoceratops
''Sinoceratops'' is an extinct genus of ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 73 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Shandong province in China. It was named in 2010 by Xu Xing ''et al.'' f ...
'', hadrosaurids (probably '' Shantungosaurus'') and ankylosaurs such as '' Sinankylosaurus'' were recovered from it. ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' was found in an area that was a floodplain in the Cretaceous period and contains one of the highest concentrations of dinosaur bones in the world.
Description
 ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' was a large carnivorous theropod, and the holotype has been estimated to have been "similar in size and gross morphology to ''
''Zhuchengtyrannus'' was a large carnivorous theropod, and the holotype has been estimated to have been "similar in size and gross morphology to ''Tarbosaurus
''Tarbosaurus'' ( ; meaning "alarming lizard") is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur that flourished in Asia about 70 million years ago, at the end of the Late Cretaceous Period, considered to contain a single known species, ''Tarbosaurus ba ...
''", which would result in a body length of and a body mass of based on the largest ''Tarbosaurus'' specimen. The holotype dentary was significantly smaller than the corresponding bones of one of the largest ''Tyrannosaurus
''Tyrannosaurus'' is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' (''rex'' meaning "king" in Latin), often called ''T. rex'' or colloquially ''T-Rex'', is one of the best represented theropods. ''Tyrannosaurus'' live ...
'' specimens ( "Sue"). In 2016 Molina-Pérez and Larramendi estimated the (ZCDM V0030) specimen at 9.6 meters (31.5 feet) long, 2.9 meters (9.5 feet) tall at the hips and 4 tonnes (4.4 short tons) in body mass.
 ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' can be distinguished from all other tyrannosaurines by a single
''Zhuchengtyrannus'' can be distinguished from all other tyrannosaurines by a single autapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to ...
, the presence of a horizontal shelf on the lateral surface of the base of the ascending process of the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
, and a rounded notch in the anterior margin of the maxillary fenestra
A fenestra (fenestration; plural fenestrae or fenestrations) is any small opening or pore, commonly used as a term in the biological sciences. It is the Latin word for "window", and is used in various fields to describe a pore in an anatomical st ...
. ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' also possesses a ventral margin of the antorbital fenestra that lies well above that of the ventral rim of the antorbital fossa. Additionally, the total length of the maxillary fenestra is more than half the distance between the anterior margins of the antorbital fossa and fenestra. Unlike the contemporaneous ''Tarbosaurus
''Tarbosaurus'' ( ; meaning "alarming lizard") is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur that flourished in Asia about 70 million years ago, at the end of the Late Cretaceous Period, considered to contain a single known species, ''Tarbosaurus ba ...
'', ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' lacks a subcutaneous flange on the posterodorsal part of the jugal
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.
Anatomy ...
ramus of the maxilla, and a ventrally convex palatal shelf that covers the bulges of the roots of the rear teeth in medial view.
Classification
It is possible that several isolated teeth from one of the Zhucheng dinosaur quarries, previously given the name ''Tyrannosaurus zhuchengensis'', belong to this or a related species. The ''T. zhuchengensis'' teeth are characterized by serrations that extend all the way to the base of the tooth crown, a feature not seen in any other tyrannosaurine species. All known teeth of ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' are too poorly preserved in this area to compare with ''T. zhuchengensis'', but further finds may clarify their relationship. Aphylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
analysis published with the description of the tyrannosaurine '' Lythronax'' in the journal '' PLOS One'' by Loewen et al. 2013, recovered ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' as the sister taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
of ''Tarbosaurus
''Tarbosaurus'' ( ; meaning "alarming lizard") is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur that flourished in Asia about 70 million years ago, at the end of the Late Cretaceous Period, considered to contain a single known species, ''Tarbosaurus ba ...
''. It also suggests that ''Zhuchengtyrannus'' and other currently known Asian tyrannosaurids were part of an evolutionary radiation descending from the same North American stem that later gave rise to ''Tyrannosaurus
''Tyrannosaurus'' is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' (''rex'' meaning "king" in Latin), often called ''T. rex'' or colloquially ''T-Rex'', is one of the best represented theropods. ''Tyrannosaurus'' live ...
'', recovered as their closest known relative. Below are the results obtained in their phylogenetic analysis:
See also
*Timeline of tyrannosaur research
This timeline of tyrannosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the tyrannosaurs, a group of predatory theropod dinosaurs that began as small, long-armed bird-like creatures with elaborate cr ...
* List of Asian dinosaurs
This is a list of dinosaurs whose remains have been recovered from Asia, excluding India, which was part of a separate landmass for much of the Mesozoic. This list does not include dinosaurs that live or lived after the Mesozoic era such as birds ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q1705935 Tyrannosaurids Monotypic dinosaur genera Campanian life Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Asia Cretaceous China Fossils of China Paleontology in Shandong Fossil taxa described in 2011