Western Interconnection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Western Interconnection is a
The Western Interconnection is a Visualizing The U.S. Electric Grid
/ref> It is not tied to the Alaska Interconnection.
page 10-14 + 18-23. ''WECC'', 2016
Archive
/ref>
Current projects
{{North American Electric Reliability Corporation Electric power transmission systems in the United States Wide area synchronous grids Electric grid interconnections in North America
 The Western Interconnection is a
The Western Interconnection is a wide area synchronous grid
A wide area synchronous grid (also called an "interconnection" in North America) is a three-phase electric power grid that has regional scale or greater that operates at a synchronized utility frequency and is electrically tied together during no ...
and one of the two major alternating current (AC) power grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
s in the North American power transmission grid
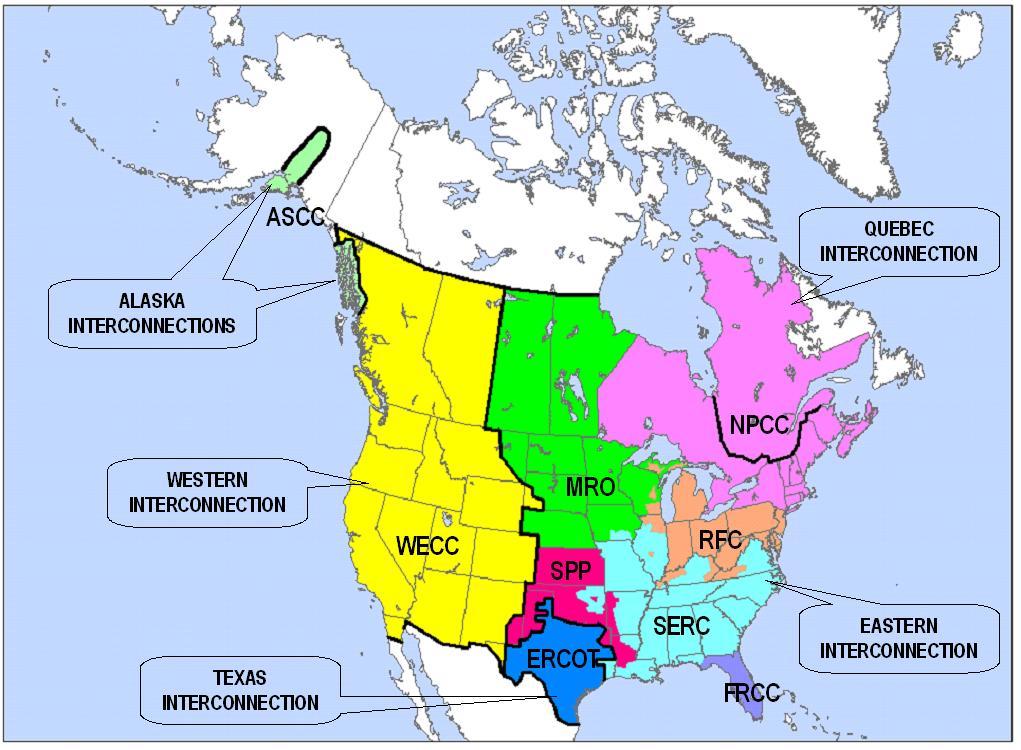
The electrical grid, electrical power grid that powers Northern America is not a single grid, but is instead divided into multiple wide area synchronous grids. The Eastern Interconnection and the Western Interconnection are the largest. Three ot ...
. The other major wide area synchronous grid is the Eastern Interconnection
The Eastern Interconnection is one of the two major alternating-current (AC) electrical grids in the North American power transmission grid. The other major interconnection is the Western Interconnection. The three minor interconnections ...
. The minor interconnections are the Québec Interconnection
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, the Texas Interconnection
The Texas Interconnection is an alternating current (AC) power grid – a wide area synchronous grid – that covers most of the state of Texas. The grid is managed by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT).
The Texas Inter ...
, and the Alaska Interconnection
The Alaska Interconnection (ASCC) is an AC power transmission grid in North America that serves Central and Southeast Alaska. While the Alaska Interconnection is often referred to as one interconnected grid, its two parts are not connected to ea ...
s.
All of the electric utilities in the Western Interconnection are electrically tied together during normal system conditions and operate at a synchronized frequency of 60 Hz. The Western Interconnection stretches from Western Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
south to Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
in Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
, reaching eastward over the Rockies
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
to the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
.
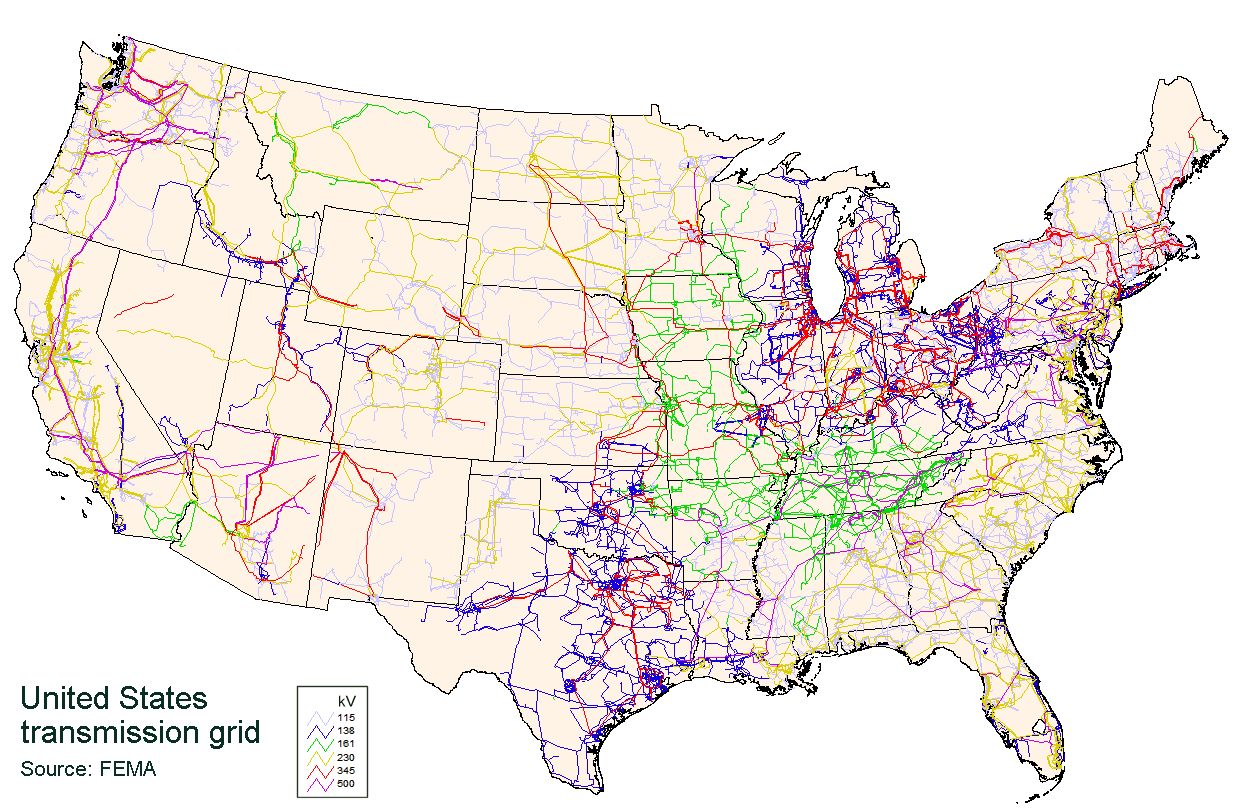
Interconnections can be tied to each other via high-voltage direct current
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system (also called a power superhighway or an electrical superhighway) uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating curre ...
power transmission line
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a ''transmission network''. This is d ...
s (DC tie
An interconnector (also known as a DC tie in the USA) is a structure which enables high voltage DC electricity to flow between electrical grids. An electrical interconnector allows electricity to flow between separate AC networks, or to link sy ...
s) such as the north-south Pacific DC Intertie
The Pacific DC Intertie (also called Path 65) is an electric power transmission line that transmits electricity from the Pacific Northwest to the Los Angeles area using HVDC, high voltage direct current (HVDC). The line capacity is 3.1 gigawatt ...
, or with variable-frequency transformer
A variable-frequency transformer (VFT) is used to transmit electricity between two ( asynchronous or synchronous) alternating current frequency domains. The VFT is a relatively recent development. Most asynchronous grid inter-ties use high-voltage ...
s (VFTs), which permit a controlled flow of energy while also functionally isolating the independent AC frequencies of each side. There are six DC ties to the Eastern Interconnection in the US and one in Canada, and there are proposals to add four additional ties./ref> It is not tied to the Alaska Interconnection.
Consumption
In 2015, WECC had an energy consumption of 883 TWh, roughly equally distributed between industrial, commercial and residential consumption. There was a summerpeak demand
Peak demand on an electrical grid is simply the highest electrical power demand that has occurred over a specified time period (Gönen 2008). Peak demand is typically characterized as annual, daily or seasonal and has the unit of power.
Peak dem ...
of 150,700 MW and a winter peak demand (2014–15) of 126,200 MW.2016 State of the Interconnectionpage 10-14 + 18-23. ''WECC'', 2016
Archive
/ref>
Production
The region had aNameplate capacity
Nameplate capacity, also known as the rated capacity, nominal capacity, installed capacity, or maximum effect, is the intended full-load sustained output of a facility such as a power station,
of 276 GW in 2019. Together, wind, solar, and hydro resources account for 46% of installed capacity. Installed coal capacity was 34 GW, compared to roughly 29 GW of wind and 23 GW of solar. While the resource mix is changing, with wind and solar eclipsing coal in installed capacity, coal still generates almost twice as much power as wind and solar combined.
See also
*Western Electricity Coordinating Council
The Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) promotes Bulk Electric System (BES) reliability for the entire Western Interconnection system. WECC is the Regional Entity responsible for compliance monitoring and enforcement. In addition, WE ...
**WECC Intertie Paths
The Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) coordinates a number of high voltage power links in western North America.https://www.wecc.biz/Reliability/TAS_PathReports_Combined_FINAL.pdf These links, known as WECC Intertie Paths, are not ...
References
Further reading
Current projects
{{North American Electric Reliability Corporation Electric power transmission systems in the United States Wide area synchronous grids Electric grid interconnections in North America