W Virginis variable on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
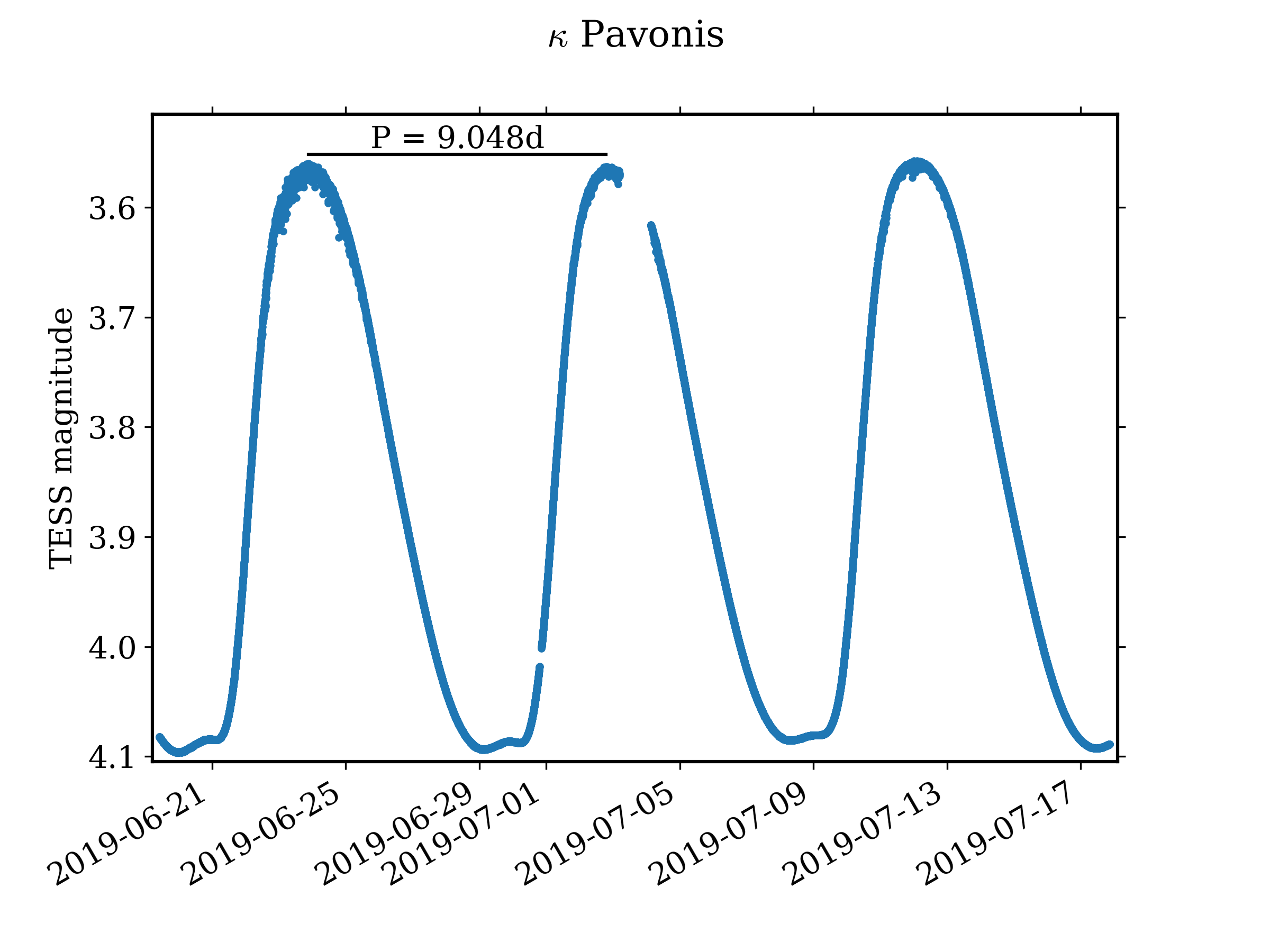 W Virginis variables are a subclass of
W Virginis variables are a subclass of
"The Cepheids of Population II and Related Stars"
''Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific'', 114 p.689–699 (2002) and are of
"The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. The OGLE-III Catalog of Variable Stars. II.Type II Cepheids and Anomalous Cepheids in the Large Magellanic Cloud"
''Acta A.'', vol 58 (2008) They were first recognized as being distinct from classical Cepheids by
PDF
HTML
{{var-star-stub
 W Virginis variables are a subclass of
W Virginis variables are a subclass of Type II Cepheid
Type II Cepheids are variable stars which pulsate with periods typically between 1 and 50 days. They are population II stars: old, typically metal-poor, low mass objects.
Like all Cepheid variables, Type IIs exhibit a relationship between the st ...
s which exhibit pulsation periods between 10–20 days,Wallerstein, G."The Cepheids of Population II and Related Stars"
''Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific'', 114 p.689–699 (2002) and are of
spectral class
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the ...
F6 – K2.W. Strohmeier, ''Variable Stars'', Pergamon (1972)Soszyński, I.; Udalski, A.; Szymański, M. K.; Kubiak, M.; Pietrzyński, G.; Wyrzykowski, Ł.; Szewczyk, O.; Ulaczyk, K.; Poleski, R"The Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. The OGLE-III Catalog of Variable Stars. II.Type II Cepheids and Anomalous Cepheids in the Large Magellanic Cloud"
''Acta A.'', vol 58 (2008) They were first recognized as being distinct from classical Cepheids by
Walter Baade
Wilhelm Heinrich Walter Baade (March 24, 1893 – June 25, 1960) was a German astronomer who worked in the United States from 1931 to 1959.
Biography
The son of a teacher, Baade finished school in 1912. He then studied maths, physics and astro ...
in 1942, in a study of Cepheids in the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The gala ...
that proposed that stars in that galaxy were of two populations.Webb, Stephen, ''Measuring the Universe: The Cosmological Distance Ladder'', Springer, (1999)
See also
*Low-dimensional chaos in stellar pulsations
Stellar pulsations are caused by expansions and contractions in the outer layers as a star seeks to maintain equilibrium. These fluctuations in stellar radius cause corresponding changes in the luminosity of the star. Astronomers are able to ded ...
References
External links
* AAVSO Variable Star of the Month. W Virginis: Spring 200HTML
{{var-star-stub