|
W Virginis Variables
W Virginis variables are a subclass of Type II Cepheids which exhibit pulsation periods between 10–20 days, and are of spectral class F6 – K2. They were first recognized as being distinct from classical Cepheids by Walter Baade in 1942, in a study of Cepheids in the Andromeda Galaxy that proposed that stars in that galaxy were of two populations. See also *Low-dimensional chaos in stellar pulsations Stellar pulsations are caused by expansions and contractions in the outer layers as a star seeks to maintain stellar equilibrium, equilibrium. These fluctuations in stellar radius cause corresponding changes in the stellar luminosity, luminosity o ... References External links * AAVSO Variable Star of the Month. W Virginis: Spring 200PDFHTML {{var-star-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
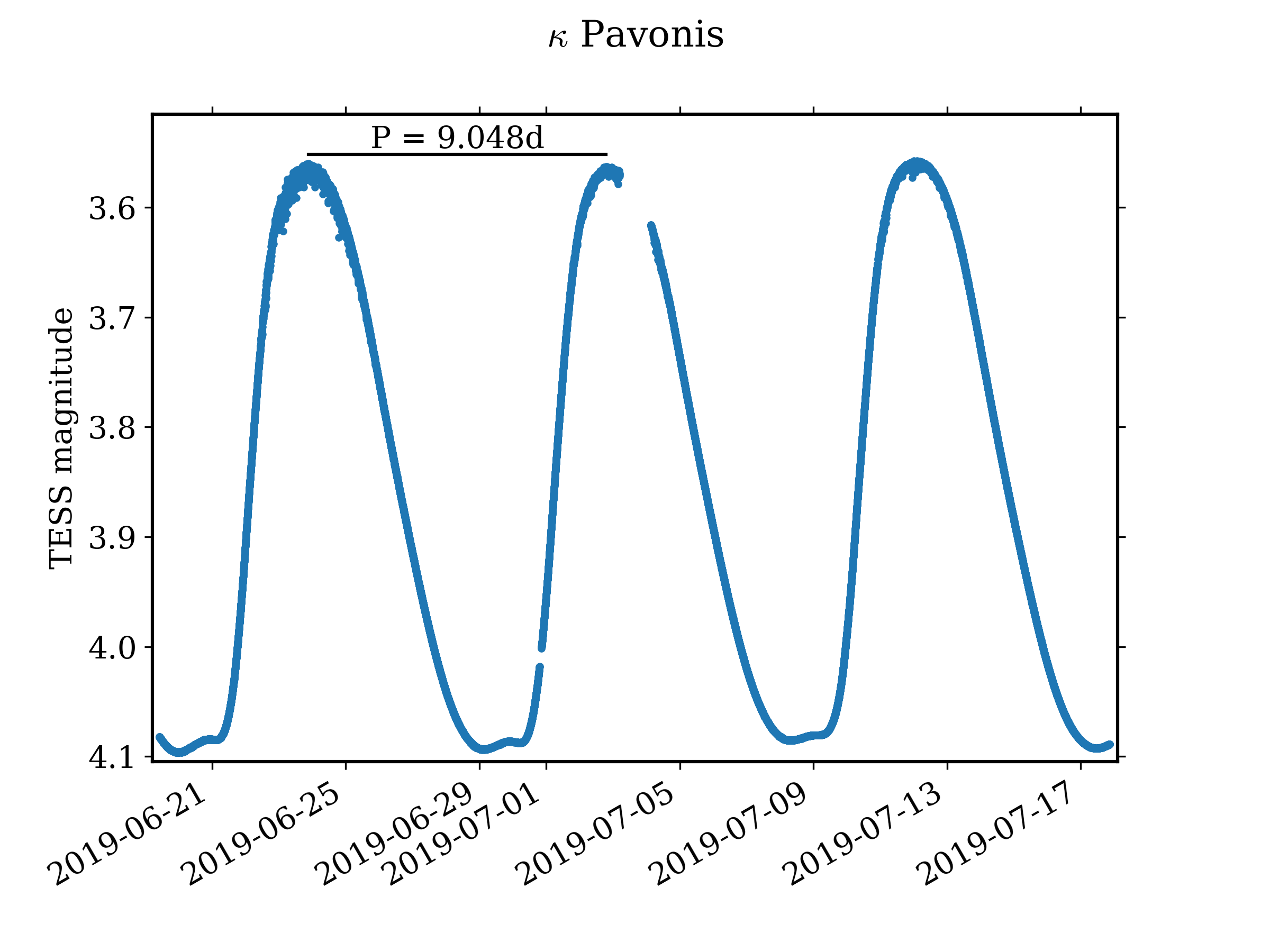
Kappa Pavonis TESS Lightcurve
Kappa (; uppercase Κ, lowercase κ or cursive ; , ''káppa'') is the tenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiceless velar plosive sound in Ancient and Modern Greek. In the system of Greek numerals, has a value of 20. It was derived from the Phoenician letter kaph . Letters that arose from kappa include the Roman K and Cyrillic К. The uppercase form is identical to the Latin K. Greek proper names and placenames containing kappa are often written in English with "c" due to the Romans' transliterations into the Latin alphabet: Constantinople, Corinth, Crete. All formal modern romanizations of Greek now use the letter "k", however. The cursive form is generally a simple font variant of lower-case kappa, but it is encoded separately in Unicode for occasions where it is used as a separate symbol in math and science. In mathematics, the kappa curve is named after this letter; the tangents of this curve were first calculated by Isaac Barrow in the 17th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type II Cepheid
Type II Cepheids are variable stars which pulsate with periods typically between 1 and 50 days. They are population II stars: old, typically metal-poor, low mass objects. Like all Cepheid variables, Type IIs exhibit a period-luminosity relationship, relationship between the star's luminosity and periodic function, pulsation period, making them useful as standard candles for establishing distances where little other data is available Longer period Type II Cepheids, which are more luminous, have been detected beyond the Local Group in the galaxies NGC 5128 and NGC 4258. Classification Historically Type II Cepheids were called W Virginis variables but are now divided into three subclasses based on the length of their period. Stars with periods between 1 and 4 days are of the BL Herculis variable, BL Herculis subclass and 10–20 days belong to the W Virginis variable, W Virginis subclass. Stars with periods greater than 20 days, and usually alternating deep and shallow minima, belon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Classification
''Spectral'' is a 2016 Hungarian-American military science fiction action film co-written and directed by Nic Mathieu. Written with Ian Fried & George Nolfi, the film stars James Badge Dale as DARPA research scientist Mark Clyne, with Max Martini, Emily Mortimer, Clayne Crawford, and Bruce Greenwood in supporting roles. The film is set in a civil war-ridden Moldova as invisible entities slaughter any living being caught in their path. The film was released worldwide on December 9, 2016 on Netflix. On February 1, 2017, Netflix released a prequel graphic novel of the film called ''Spectral: Ghosts of War'' which was made available digitally through the website ComiXology. Plot DARPA researcher Mark Clyne is sent to a US military airbase on the outskirts of Chișinău, to consult his created line of hyperspectral imaging goggles issued to US Army Special Forces led by Army General James Orland, who is covertly supporting the Moldovan government in an ongoing civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Heinrich Walter Baade
Wilhelm Heinrich Walter Baade (March 24, 1893 – June 25, 1960) was a German astronomer who worked in the United States from 1931 to 1959. Early life and education Baade was born the son of a teacher in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. He finished school in 1912. He then studied maths, physics and astronomy at the universities of Münster and Göttingen. He received his PhD in 1919. Career Baade worked at Hamburg Observatory at Bergedorf from 1919 to 1931. In 1920 he discovered 944 Hidalgo, the first of a class of minor planets now called Centaurs which cross the orbits of giant planets. From 1931 to 1958, he worked at Mount Wilson Observatory In 1937, the University of Hamburg wanted Baade as successor of Richard Schorr for the Hamburg Observatory, but he refused. At Mount Wilson Observatory, during World War II, he took advantage of wartime blackout conditions (which reduced light pollution), to resolve stars in the center of the Andromeda Galaxy for the first time. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy and is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way. It was originally named the Andromeda Nebula and is cataloged as Messier 31, M31, and NGC 224. Andromeda has a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter of about and is approximately from Earth. The galaxy's name stems from the area of Earth's sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which itself is named after Andromeda (mythology), the princess who was the wife of Perseus in Greek mythology. The virial mass of the Andromeda Galaxy is of the same order of magnitude as that of the Milky Way, at . The mass of either galaxy is difficult to estimate with any accuracy, but it was long thought that the Andromeda Galaxy was more massive than the Milky Way by a margin of some 25% to 50%. However, this has been called into question by early-21st-century studies indicating a possibly lower mass for the Andromeda Galaxy and a higher mass for the Milky Way. The Androm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-dimensional Chaos In Stellar Pulsations
Stellar pulsations are caused by expansions and contractions in the outer layers as a star seeks to maintain stellar equilibrium, equilibrium. These fluctuations in stellar radius cause corresponding changes in the stellar luminosity, luminosity of the star. Astronomers are able to deduce this mechanism by measuring the stellar spectrum, spectrum and observing the Doppler effect. Many intrinsic variable stars that pulsate with large amplitudes, such as the classical Cepheids, RR Lyrae variable, RR Lyrae stars and large-amplitude Delta Scuti stars show regular light curves. This regular behavior is in contrast with the variability of stars that lie parallel to and to the high-luminosity/low-temperature side of the classical variable stars in the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. These giant stars are observed to undergo pulsations ranging from weak irregularity, when one can still define an average cycling time or Periodic function, period, (as in most RV Tauri variable, RV Tauri and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |