VIA Nano on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The VIA Nano (formerly code-named VIA Isaiah) is a
 * Out-of-order and
* Out-of-order and
VIA Nano Processor
VIA Nano X2 Dual-Core Processor
VIA QuadCore Processor
64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit CPUs and ALUs are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A ...
CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, a ...
for personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or te ...
s. The VIA Nano was released by VIA Technologies
VIA Technologies Inc. (), is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory. It was the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets. As a fabless semiconductor company, VIA ...
in 2008 after five years of development by its CPU division, Centaur Technology
Centaur Technology is an x86 CPU design company started in 1995 and subsequently a wholly owned subsidiary of VIA Technologies. In 2015, the documentary ''Rise of the Centaur'' covered the early history of the company.
History
Centaur Technologi ...
. This new Isaiah 64-bit architecture was designed from scratch, unveiled on 24 January 2008, and launched on 29 May, including low-voltage variants and the Nano brand name. The processor supports a number of VIA-specific x86 extensions designed to boost efficiency in low-power appliances.
History
UnlikeIntel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 ser ...
and AMD, VIA uses two distinct development code names for each of its CPU cores. In this case, the codename 'CN' was used in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
by Centaur Technology. Biblical names are used as codes by VIA in Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
, and Isaiah was the choice for this particular processor and architecture. It is expected that the VIA Isaiah will be twice as fast in integer performance and four times as fast in floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can ...
performance as the previous-generation VIA Esther
The VIA C7 is an x86 central processing unit designed by Centaur Technology and sold by VIA Technologies.
Product history
The C7 delivers a number of improvements to the older VIA C3 cores but is nearly identical to the latest VIA C3 Nehemiah c ...
at an equivalent clock speed. Power consumption is also expected to be on par with the previous-generation VIA CPUs, with thermal design power ranging from 5 W to 25 W. Being a completely new design, the Isaiah architecture was built with support for features like the x86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit version of the x86 instruction set, first released in 1999. It introduced two new modes of operation, 64-bit mode and compatibility mode, along with a new 4-level paging ...
instruction set and x86 virtualization
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware-a ...
which were unavailable on its predecessors, the VIA C7
The VIA C7 is an x86 central processing unit designed by Centaur Technology and sold by VIA Technologies.
Product history
The C7 delivers a number of improvements to the older VIA C3 cores but is nearly identical to the latest VIA C3 Nehemiah ...
line, while retaining their encryption extensions. Several independent tests showed that the VIA Nano performs better than the single-core Intel Atom
Intel Atom is the brand name for a line of IA-32 and x86-64 instruction set ultra-low-voltage processors by Intel Corporation designed to reduce electric consumption and power dissipation in comparison with ordinary processors of the Intel Co ...
across a variety of workloads. In a 2008 Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, sc ...
test, a VIA Nano gained significant performance in memory subsystem after its CPUID changed to Intel, hinting at the possibility that the benchmark software only checks the CPUID instead of the actual features supported by the CPU to choose a code path. The benchmark software used had been released before the release of VIA Nano.
On November 3, 2009, VIA launched the Nano 3000 series. VIA claims that these models can offer a 20% performance boost and 20% more energy efficiency than the Nano 1000 and 2000 series. Benchmarks run by VIA claim that a 1.6 GHz 3000-series Nano can outperform the ageing Intel Atom N270 by about 40–54%. The 3000 series adds the SSE4
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; m ...
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA), but it shoul ...
instruction set extensions, which were first introduced with 45 nm revisions of the Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 ser ...
Core 2
Intel Core 2 is the processor family encompassing a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single-die, whereas the quad-co ...
architecture.
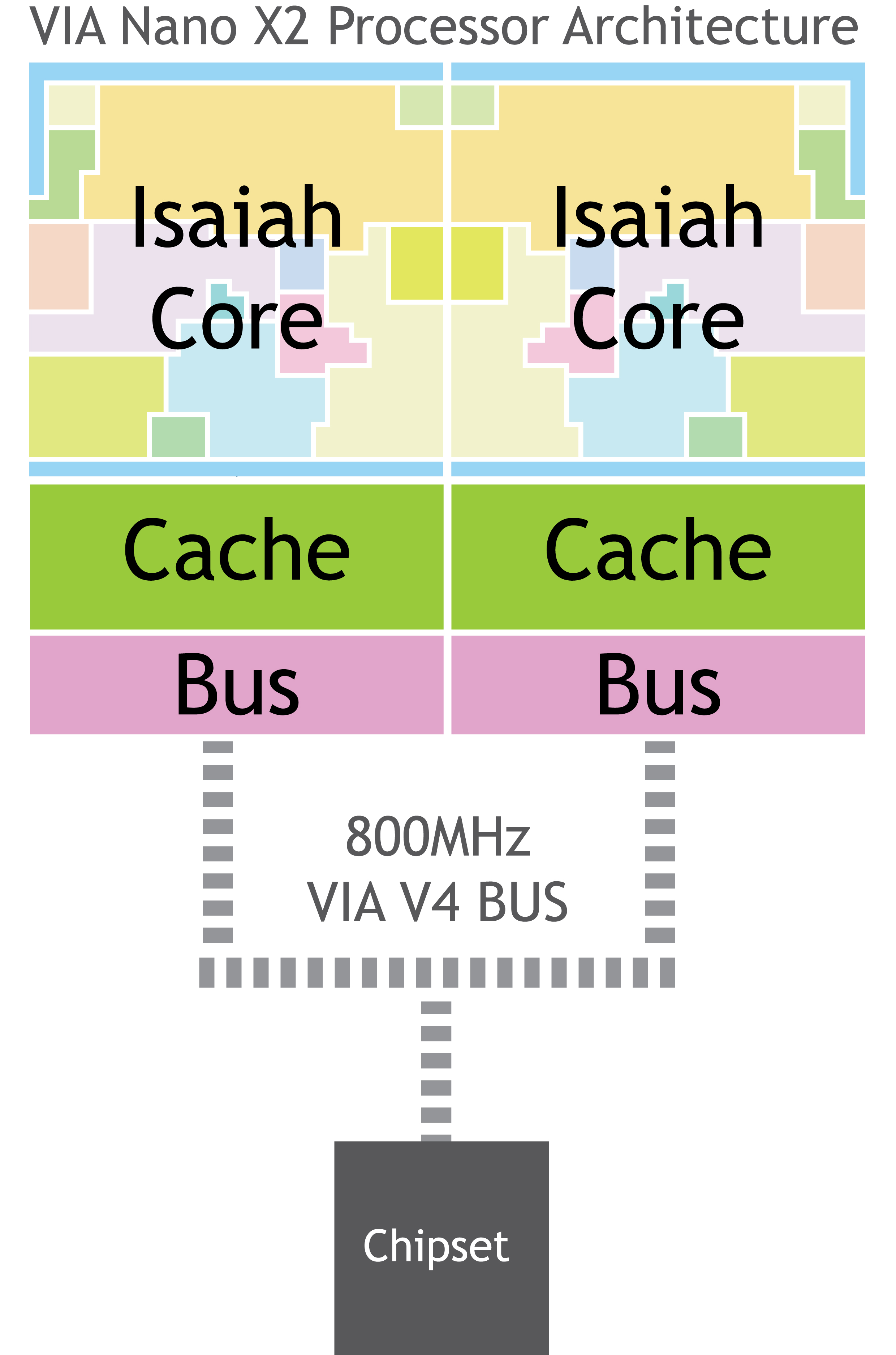
On November 11, 2011, VIA released the VIA Nano X2 Dual-Core Processor with their first ever dual core pico-itx mainboard. The VIA Nano X2 is built on a 40 nm process and supports the SSE4
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; m ...
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA), but it shoul ...
instruction set extensions, critical to modern floating point dependent applications. Via claims 30% higher performance in comparison to Intel's Atom with a 50% higher clock.
The Zhaoxin joint venture processors, released from 2014, are based on the VIA Nano series.
Features
*x86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit version of the x86 instruction set, first released in 1999. It introduced two new modes of operation, 64-bit mode and compatibility mode, along with a new 4-level paging ...
instruction set
* Clock speed from 1 GHz to 2 GHz
* Bus speed of 533 MHz or 800 MHz (1066 MHz for Nano x2)
* 64 KB data and 64 KB instructions L1 cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, whic ...
and 1 MB L2 cache per core.
* 65 nm manufacturing process (40 nm for Nano x2)
* Superscalar
A superscalar processor is a CPU that implements a form of parallelism called instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. In contrast to a scalar processor, which can execute at most one single instruction per clock cycle, a sup ...
out-of-order instruction execution
* Support for MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, and SSE4 instruction set
* Support for x86 virtualization
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware-a ...
with Intel-compatible implementation (disabled before stepping 3)
* Support for ECC memory
* Pin-compatible with VIA C7
The VIA C7 is an x86 central processing unit designed by Centaur Technology and sold by VIA Technologies.
Product history
The C7 delivers a number of improvements to the older VIA C3 cores but is nearly identical to the latest VIA C3 Nehemiah ...
and VIA Eden
VIA Eden is a name of a variant of VIA's C3/ C7 x86 processors, designed to be used in embedded devices. They have smaller package sizes, lower power consumption, and somewhat lower computing performance than their C equivalents, due to reduced c ...
Architecture overview
 * Out-of-order and
* Out-of-order and superscalar
A superscalar processor is a CPU that implements a form of parallelism called instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. In contrast to a scalar processor, which can execute at most one single instruction per clock cycle, a sup ...
design: Providing much better performance than its predecessor, the VIA C7 processor, which was in-order. This puts the Isaiah architecture in line with same year offerings from AMD and Intel.
* Instructions fusion: Allows the processor to combine some instructions as a single instruction, reducing power requirements and giving higher performance (the Atom uses a similar strategy in processing x86 instructions in a more 'whole' manner, rather than breaking them into RISC-like micro-ops).
* Improved branch prediction
In computer architecture, a branch predictor is a digital circuit that tries to guess which way a branch (e.g., an if–then–else structure) will go before this is known definitively. The purpose of the branch predictor is to improve the flow ...
: Uses eight predictors in two pipeline stages.
* CPU cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, whi ...
design: An exclusive cache design means that contents of the L1 cache is not duplicated in the L2 cache, providing a larger total cache.
* Data prefetch: Incorporating new mechanisms for data-prefetch, including both the loading of a special 64-line cache before loading the L2 cache and a direct load to the L1 cache.
** Fetches four x86 instructions per cycle as opposed to Intel's three to five cycles.
** Issues three micro-operations/clock to execution units
* Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remember ...
access: Merges smaller stores into larger load data.
* Execution units
In computer engineering, an execution unit (E-unit or EU) is a part of the central processing unit (CPU) that performs the operations and calculations as instructed by the computer program. It may have its own internal control sequence unit (not ...
: Seven execution units are available, that allows up to seven micro-ops being executed per clock.
** Two integer units (ALU1 and ALU2)
*** ALU1 is feature complete, while ALU2 lacks some low usage instructions and therefore is more suited for tasks like address calculations.
** Two store units, one for Address Store and one for Data Store according to VIA
Via or VIA may refer to the following:
Science and technology
* MOS Technology 6522, Versatile Interface Adapter
* ''Via'' (moth), a genus of moths in the family Noctuidae
* Via (electronics), a through-connection
* VIA Technologies, a Taiwa ...
.
** One load unit
** Two media units (MEDIA-A and MEDIA-B) with a 128-bit wide datapath, supporting 4 single precision or 2 double-precision operations. Media computation refers to the use of the two media units.
*** MEDIA-A executes floating-point "add" instructions (2-clock latency for single-precision
Single-precision floating-point format (sometimes called FP32 or float32) is a computer number format, usually occupying 32 bits in computer memory; it represents a wide dynamic range of numeric values by using a floating radix point.
A floatin ...
and double-precision
Double-precision floating-point format (sometimes called FP64 or float64) is a floating-point number format, usually occupying 64 bits in computer memory; it represents a wide dynamic range of numeric values by using a floating radix point.
F ...
), integer SIMD, encryption, divide and square root.
*** MEDIA-B executes floating-point "multiply" instructions (2-clock latency for single-precision, 3-clock latency for double-precision).
*** Because of the parallelism introduced with the two media units, media computation can provide four "add" and four "multiply" instructions per clock.
** A new implementation of FP-addition with the lowest clock-latency for a x86 processor so far.
** Almost all integer SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA), but it shoul ...
instructions execute in one clock.
** Implements MMX MMX may refer to:
* 2010, in Roman numerals
Science and technology
* MMX (instruction set), a single-instruction, multiple-data instruction set designed by Intel
* MMX Mineração, a Brazilian mining company
* Martian Moons eXploration, a Japane ...
, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier SSE i ...
, SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
, SSSE3
Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSSE3 or SSE3S) is a SIMD instruction set created by Intel and is the fourth iteration of the SSE technology.
History
SSSE3 was first introduced with Intel processors based on the Core microarchitectu ...
multimedia instruction sets
** Implements SSE4.1 multimedia instruction set (VIA Nano 3000 series)
** Implements SSE4.1 multimedia instruction set (VIA Nano x2 series)
* Power Management
Power management is a feature of some electrical appliances, especially copiers, computers, computer CPUs, computer GPUs and computer peripherals such as monitors and printers, that turns off the power or switches the system to a low-power st ...
: Besides requiring very low power, many new features are included.
** Includes a new C6 power state (Caches are flushed, internal state saved, and core voltage is turned off).
** ''Adaptive P-State Control'': Transition between performance and voltage states without stopping execution.
** ''Adaptive Overclocking'': Automatic overclocking if there is low temperature in the processor core.
** ''Adaptive Thermal Limit'': Adjusting of the processor to maintain a user predefined temperature.
* Encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can d ...
: Includes the VIA PadLock engine
** Hardware support for AES encryption, secure hash algorithm SHA-1
In cryptography, SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1) is a cryptographically broken but still widely used hash function which takes an input and produces a 160- bit (20- byte) hash value known as a message digest – typically rendered as 40 hexa ...
and SHA-256 and Random Number Generation
Random number generation is a process by which, often by means of a random number generator (RNG), a sequence of numbers or symbols that cannot be reasonably predicted better than by random chance is generated. This means that the particular out ...
Around 2014/8/31 rumors appeared about a potential Isaiah II refresh.
See also
* List of VIA Nano microprocessors *List of VIA microprocessors
This article lists x86-compliant microprocessors sold by VIA Technologies, grouped by technical merits: cores within same group have much in common.
Cyrix design ( Cyrix III)
* All models support: '' MMX, 3DNow!''
Centaur Technology desig ...
* Netbook
Netbook was a commonly used term that identified a product class of small and inexpensive laptops which were sold from 2007 to around 2013. These machines were designed primarily as cost-effective tools for consumers to access the Inte ...
References
External links
VIA Nano Processor
VIA Nano X2 Dual-Core Processor
VIA QuadCore Processor
Press
* * * {{VIA Nano