Transition (computer science) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Transition refers to a computer science paradigm in the context of
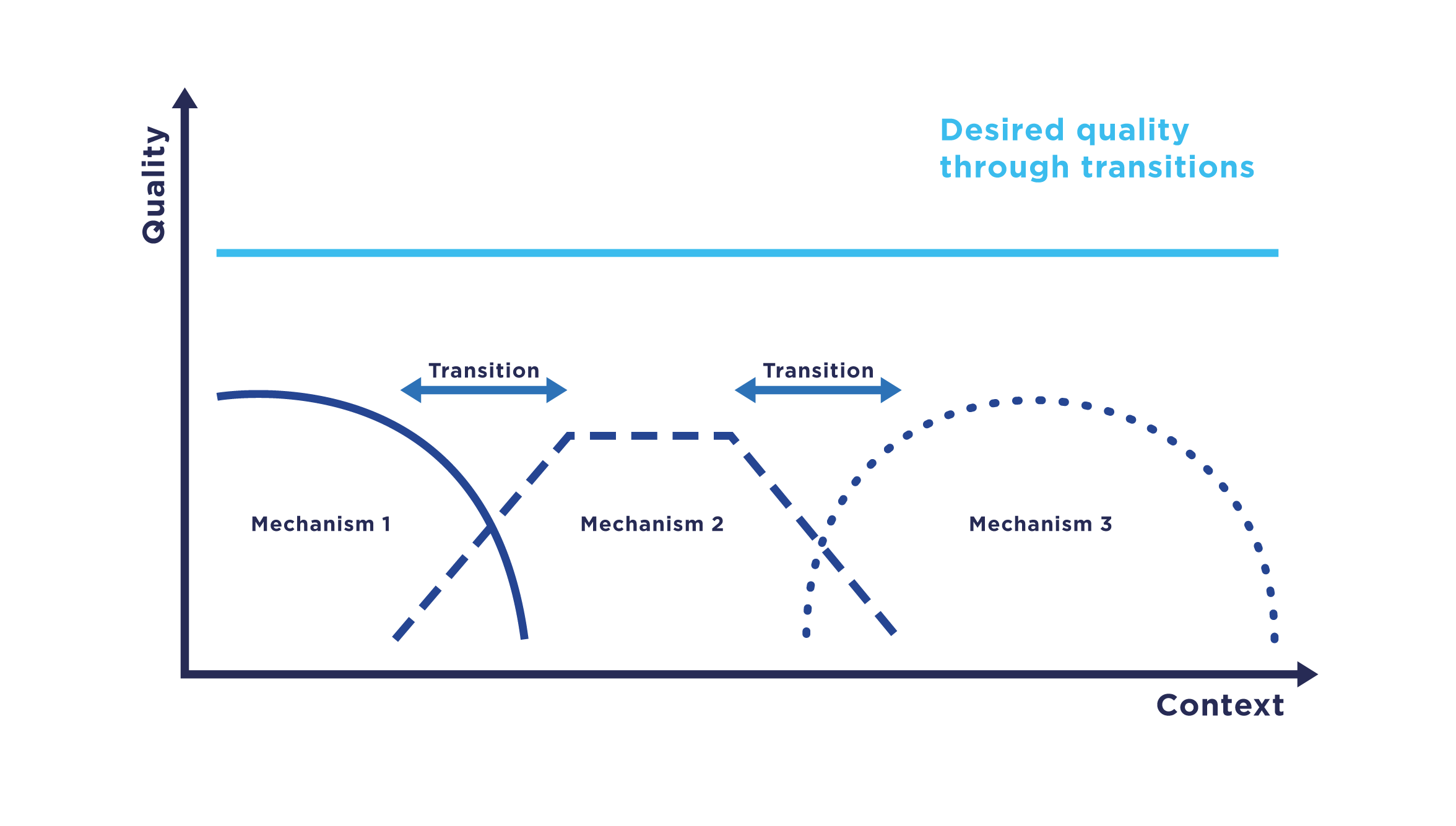
Transition refers to a computer science paradigm in the context of 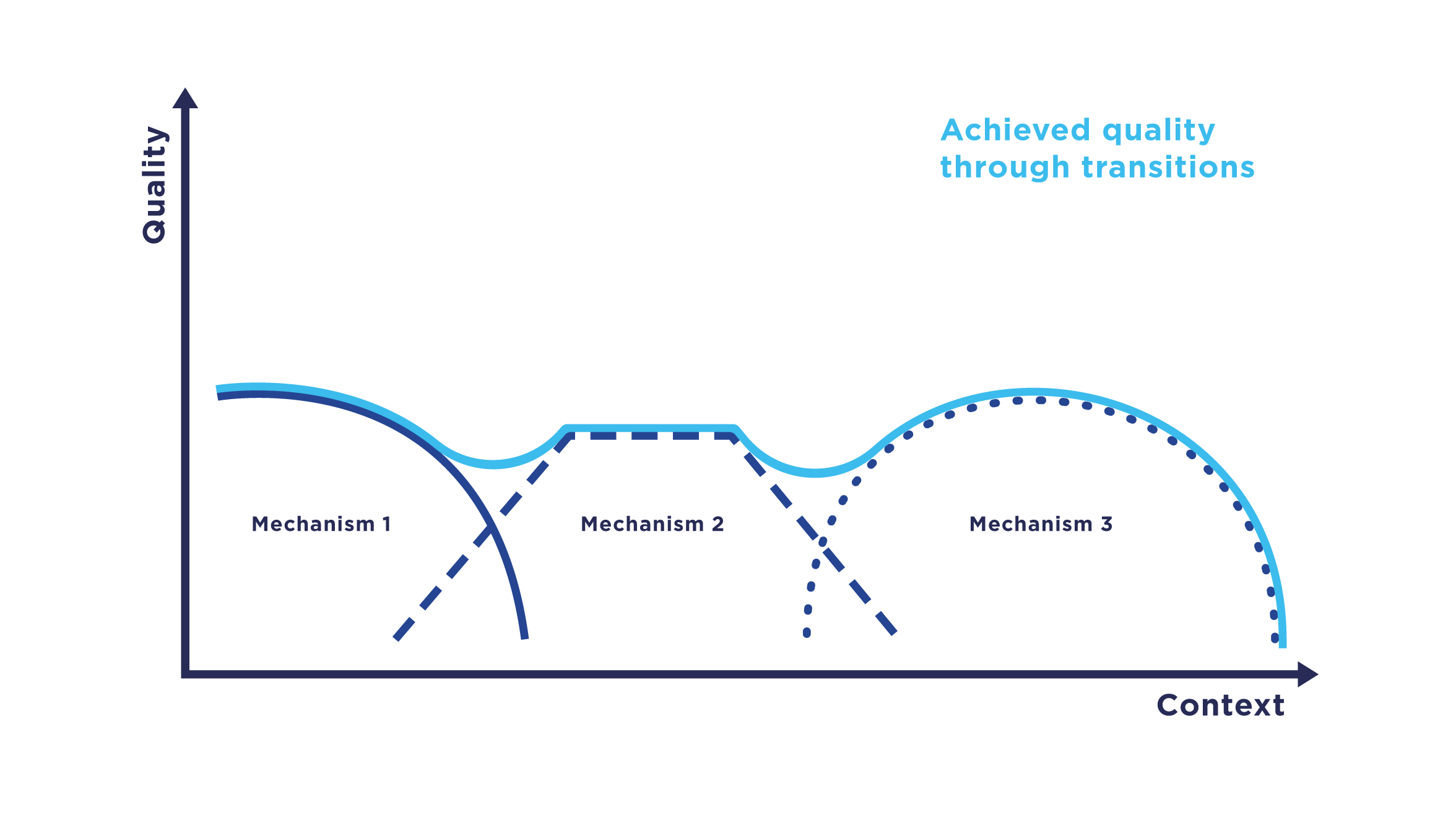 Transitions enable communication systems to adapt to changing conditions during runtime. This change in conditions can, for example, be a rapid increase in the load on a certain service that may be caused, e.g., by large gatherings of people with mobile devices. A transition often impacts multiple mechanisms at different communication layers of a layered architecture.
Mechanisms are given as conceptual elements of a networked communication system and are linked to specific functional units, for example, as a service or protocol component. In some cases, a mechanism can also comprise an entire protocol. For example on the transmission layer, LTE can be regarded as such a mechanism. Following this definition, there exist numerous communication mechanisms that are partly equivalent in their basic functionality, such as
Transitions enable communication systems to adapt to changing conditions during runtime. This change in conditions can, for example, be a rapid increase in the load on a certain service that may be caused, e.g., by large gatherings of people with mobile devices. A transition often impacts multiple mechanisms at different communication layers of a layered architecture.
Mechanisms are given as conceptual elements of a networked communication system and are linked to specific functional units, for example, as a service or protocol component. In some cases, a mechanism can also comprise an entire protocol. For example on the transmission layer, LTE can be regarded as such a mechanism. Following this definition, there exist numerous communication mechanisms that are partly equivalent in their basic functionality, such as
MAKI
Computer science
 Transition refers to a computer science paradigm in the context of
Transition refers to a computer science paradigm in the context of communication systems
A communications system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. Commun ...
which describes the change of communication mechanisms, i.e., functions of a communication system, in particular, service and protocol
Protocol may refer to:
Sociology and politics
* Protocol (politics)
Protocol originally (in Late Middle English, c. 15th century) meant the minutes or logbook taken at a meeting, upon which an agreement was based. The term now commonly refers to ...
components. In a transition, communication mechanisms within a system are replaced by functionally comparable mechanisms with the aim to ensure the highest possible quality, e.g., as captured by the quality of service
Quality of service (QoS) is the description or measurement of the overall performance of a service, such as a telephony or computer network, or a cloud computing service, particularly the performance seen by the users of the network. To quantitat ...
.
 Transitions enable communication systems to adapt to changing conditions during runtime. This change in conditions can, for example, be a rapid increase in the load on a certain service that may be caused, e.g., by large gatherings of people with mobile devices. A transition often impacts multiple mechanisms at different communication layers of a layered architecture.
Mechanisms are given as conceptual elements of a networked communication system and are linked to specific functional units, for example, as a service or protocol component. In some cases, a mechanism can also comprise an entire protocol. For example on the transmission layer, LTE can be regarded as such a mechanism. Following this definition, there exist numerous communication mechanisms that are partly equivalent in their basic functionality, such as
Transitions enable communication systems to adapt to changing conditions during runtime. This change in conditions can, for example, be a rapid increase in the load on a certain service that may be caused, e.g., by large gatherings of people with mobile devices. A transition often impacts multiple mechanisms at different communication layers of a layered architecture.
Mechanisms are given as conceptual elements of a networked communication system and are linked to specific functional units, for example, as a service or protocol component. In some cases, a mechanism can also comprise an entire protocol. For example on the transmission layer, LTE can be regarded as such a mechanism. Following this definition, there exist numerous communication mechanisms that are partly equivalent in their basic functionality, such as Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for Wireless LAN, local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by ...
, Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is li ...
and Zigbee
Zigbee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks with small, low-power digital radios, such as for home automation, medical device data collection, and oth ...
for local wireless networks and UMTS and LTE
LTE may refer to:
Science and technology
* LTE (telecommunication) (Long-Term Evolution), a mobile telephony standard
** LTE Advanced, an enhancement
** LTE Advanced Pro, a further enhancement
* Compaq LTE, a line of laptop computers
* Leukotrie ...
for broadband wireless connections. For example, LTE and Wi-Fi have equivalent basic functionality, but they are technologically significantly different in their design and operation. Mechanisms affected by transitions are often components of a protocol or service. For example, in case of video streaming/transmission, the use of different video data encoding can be carried out depending on the available data transmission rate. These changes are controlled and implemented by transitions; A research example is a context-aware video adaptation service to support mobile video applications. Through analyzing the current processes in a communication system, it is possible to determine which transitions need to be executed at which communication layer in order to meet the quality requirements. In order for communication systems to adapt to the respective framework conditions, architectural approaches of self-organizing, adaptive systems can be used, such as the MAPE cycle (Monitor-Analyze-Plan-Execute). This central concept of Autonomic Computing
Autonomic computing (AC) is distributed computing resources with self-management (computer science), self-managing characteristics, adapting to unpredictable changes while hiding intrinsic complexity to operators and users. Initiated by IBM in 2001 ...
can be used to determine the state of the communication system, to analyze the monitoring data and to plan and execute the necessary transition(s). A central goal is that users do not consciously perceive a transition while running applications and that the functionality of the used services is perceived as smooth and fluid.
Recent research
The study of new and fundamental design methods, models and techniques that enable automated, coordinated and cross-layer transitions between functionally similar mechanisms within a communication system is the main goal of a collaborative research center funded by the German research foundation (DFG). The DFG collaborative research center 1053 MAKI - Multi-mechanism Adaptation for the future Internet - focuses on research questions in the following areas: (i) Fundamental research on transition methods, (ii) Techniques for adapting transition-capable communication systems on the basis of achieved and targeted quality, and (iii) specific and exemplary transitions in communication systems as regarded from different technical perspectives. A formalization of the concept of transitions that captures the features and relations within a communication system to express and optimize the decision making process that is associated with such a system is given in. The associated building blocks comprise (i) DynamicSoftware Product Lines
Software product lines (SPLs), or software product line development, refers to software engineering methods, tools and techniques for creating a collection of similar software systems from a shared set of software assets using a common means of pro ...
, (ii) Markov Decision Processes and (iii) Utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings.
* In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish ...
Design. While Dynamic Software Product Lines provide a method to concisely capture a large configuration space and to specify run time variability of adaptive systems, Markov Decision Processes provide a mathematical tool to define and plan transitions between available communication mechanisms. Finally, utility functions quantify the performance of individual configurations of the transition-based communication system and provide the means to optimize the performance in such a system.
Applications of the idea of transitions have found their way to wireless sensor network
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) refer to networks of spatially dispersed and dedicated sensors that monitor and record the physical conditions of the environment and forward the collected data to a central location. WSNs can measure environmental ...
s and mobile networks, distributed reactive programming, WiFi firmware modification, planning of autonomic computing systems, analysis of CDNs, flexible extensions of the ISO OSI stack, 5G mmWave
Extremely high frequency (EHF) is the International Telecommunication Union designation for the band of radio frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum from 30 to 300 gigahertz (GHz). It is in the microwave part of the radio spectrum, between t ...
vehicular communications, the analysis of MapReduce
MapReduce is a programming model and an associated implementation for processing and generating big data sets with a parallel and distributed algorithm on a cluster.
A MapReduce program is composed of a ''map'' procedure, which performs filte ...
-like parallel systems, scheduling of Multipath TCP
Multipath TCP (MPTCP) is an ongoing effort of the Internet Engineering Task Force's (IETF) Multipath TCP working group, that aims at allowing a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection to use multiple paths to maximize throughput and increa ...
, adaptivity for beam training in 802.11ad, operator placement in dynamic user environments, DASH
The dash is a punctuation mark consisting of a long horizontal line. It is similar in appearance to the hyphen but is longer and sometimes higher from the baseline. The most common versions are the endash , generally longer than the hyphen ...
video player analysis, adaptive bitrate streaming
Adaptive bitrate streaming is a technique used in streaming multimedia over computer networks.
While in the past most video or audio streaming technologies utilized streaming protocols such as RTP with RTSP, today's adaptive streaming techn ...
and complex event processing Event processing is a method of tracking and analyzing (processing) streams of information (data) about things that happen (events), and deriving a conclusion from them. Complex event processing (CEP) consists of a set of concepts and techniques de ...
on mobile devices.
References
{{ReflistExternal links
MAKI
Computer science