Thracian warfare on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The history of Thracian warfare spans from the 10th century BC up to the 1st century AD in the region defined by Ancient
The history of Thracian warfare spans from the 10th century BC up to the 1st century AD in the region defined by Ancient
 The ''Odrysian kingdom'' (
The ''Odrysian kingdom'' (
"Celtic Settlement in North-Western Thrace during the Late Fourth and Third Centuries BC"
 In the 4th century BC, both infantry and cavalry troops started wearing helmetsThe Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 20 (some of leather)The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald, 1998, , page 199 and some
In the 4th century BC, both infantry and cavalry troops started wearing helmetsThe Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 20 (some of leather)The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald, 1998, , page 199 and some
Thracians
{{DEFAULTSORT:Thracian Warfare Thracian culture Indo-European warfare Ancient warfare Wars involving the Balkans

 The history of Thracian warfare spans from the 10th century BC up to the 1st century AD in the region defined by Ancient
The history of Thracian warfare spans from the 10th century BC up to the 1st century AD in the region defined by Ancient Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Latin historians as Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
. It concerns the armed conflicts of the Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
tribes and their kingdoms in the Balkans. Apart from conflicts between Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
and neighboring nations and tribes, numerous wars were recorded among Thracian tribes.
Mythological
Instances of Thracian people engaging in armed conflict occur in theIliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
of Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
and in Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
. The Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
Temenids
In Greek mythology, Temenus ( el, Τήμενος, ''Tḗmenos'') was a son of Aristomachus (Heracleidae), Aristomachus and brother of Cresphontes and Aristodemus.
Temenus was a great-great-grandson of Heracles and helped lead the fifth and final ...
ousted the Thracians from Pieria (later central Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
ia).The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 4 The Thracians, prominent warriors who became allies of Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in prese ...
, came from the Aegean coast. In the Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek Epic poetry, epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by moder ...
, there is only one instance of Thracians, that of Cicones
The Cicones (; ) or Ciconians were a Homeric ThracianHerodotus, ''The Histories'' (Penguin Classics), edd. John M. Marincola and Aubery de Selincourt, 2003, p. 452 (I10): "The Thracian tribes lying along his route were the Paeti, Cicones, Biston ...
again on the coast, but they are weak.
The Thracians were a particularly fierce culture in terms of violence and conflict and so they appeared in Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
as mostly associated with its stories of strife. The god of war Ares
Ares (; grc, Ἄρης, ''Árēs'' ) is the Greek god of war and courage. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. The Greeks were ambivalent towards him. He embodies the physical valor necessary for success in war b ...
was said to have been born in Thrace and was also heavily worshiped there; in contrast to the revulsion of his worship by many other Balkan city states. Homer recounts in the book of Odyssey that an embarrassed Ares retreated among his Thracian followers when his love affair with the goddess Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols include ...
was caught and the two were promptly ensnared by Hephaestus
Hephaestus (; eight spellings; grc-gre, Ἥφαιστος, Hḗphaistos) is the Greek god of blacksmiths, metalworking, carpenters, craftsmen, artisans, sculptors, metallurgy, fire (compare, however, with Hestia), and volcanoes.Walter Burk ...
.
Tribal wars
Thracian tribes fought amongst each other and they allied themselves with theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
s against other Thracian tribes. Those allied with the Greeks were more civilized and they were usually established in settlements along the Thracian coast. The interior tribes were known as savages, retaining their barbarous habits even until the Roman period. The tribal wars also kept Thrace from becoming a major regional power due to the lack of a central government.
At the onset of the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
, the Thracian tribes were united under the rule of Sitalces, king of the Odrysae. It was allied with Athens during the conflict. However, the kingdom was again split into different parts after the death of king Seuthes. It was during this time when Philip of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king (''basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the a ...
conquered a large swath of Thrace, absorbing the territory and its tribes into Macedon.
Kingdoms
 The ''Odrysian kingdom'' (
The ''Odrysian kingdom'' (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
, "Βασιλεία Όδρυσων") was a union of Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
tribes that endured between the 5th century BC and the 3rd century BC. The Odrysian state was the first Thracian kingdom that acquired power in the region, by the unification of many Thracian tribes
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) including possibly or partly Thracian or Dacian tribes, and non-Thracian or non-Dacian tribes that inhabited the lands known as Thrace and Dacia. A great number o ...
under a single ruler, King Teres
Teres may refer to:
Anatomy:
*Teres major muscle, a muscle of the upper limb; one of seven scapulohumeral muscles
*Teres minor muscle, a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff
*Pronator teres muscle, a muscle located mainly in the human fore ...
5th century BC. It became involved in wars and military conflicts against the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
colonies, the kingdom of Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
and the Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
, the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
, Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
, Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
,Nikola Theodossiev"Celtic Settlement in North-Western Thrace during the Late Fourth and Third Centuries BC"
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved f ...
and Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
tribes. Sometimes it was allied with various Ancient Greek tribes
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
or Greek city states
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
. During the Peloponnesian
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
war, Thracians were the allies of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
.The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 5 The Thracians fought alongside Athenians
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
and Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
ians against the forces of the Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
ns. Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
generals like Iphicrates
Iphicrates ( grc-gre, Ιφικράτης; c. 418 BC – c. 353 BC) was an Athenian general, who flourished in the earlier half of the 4th century BC. He is credited with important infantry reforms that revolutionized ancient Greek warfare by ...
The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 9 and Charidemos fought for the Odrysae as well. The Thracians served under Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
kings in 310 BC.The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 12 Odrysian military strength was based on intra-tribal eliteThe Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald,1998, , page 149 making the kingdom prone to fragmentation. Although the kingdom was wealthy, a large proportion of its income was in kind and suitable portions had to be paid to the tribal chiefs. The army was mostly fed and paid by plunder. Sitalces was able to raise an army supposedly 150,000 strong for his invasion of Macedonia in 429 BC but these economic and political factors (plus the onset of winter) meant that this army only held together for about six weeks and any Thracian conquests were ephemeral.
The Sapaeans
Sapaeans, Sapaei or Sapaioi (Ancient Greek, "Σαπαίοι") were a Thracian tribe close to the Greek city of Abdera. One of their kings was named Abrupolis
and had allied himself with the Romans. They ruled Thrace after the Odrysians until its ...
ruled Thrace after the Odrysians until its incorporation to the Roman Empire as a province. Thrace became a Client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
of Rome at 11 BC and was annexed at 46 AD.
Thracian troop types and organization
Infantry and Cavalry
Thrace had the potential to muster a huge number of troopsThe Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 3 though this rarely occurred. By tradition, Thracians honored warriors and, according toHerodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
, despised all other occupations.
The Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
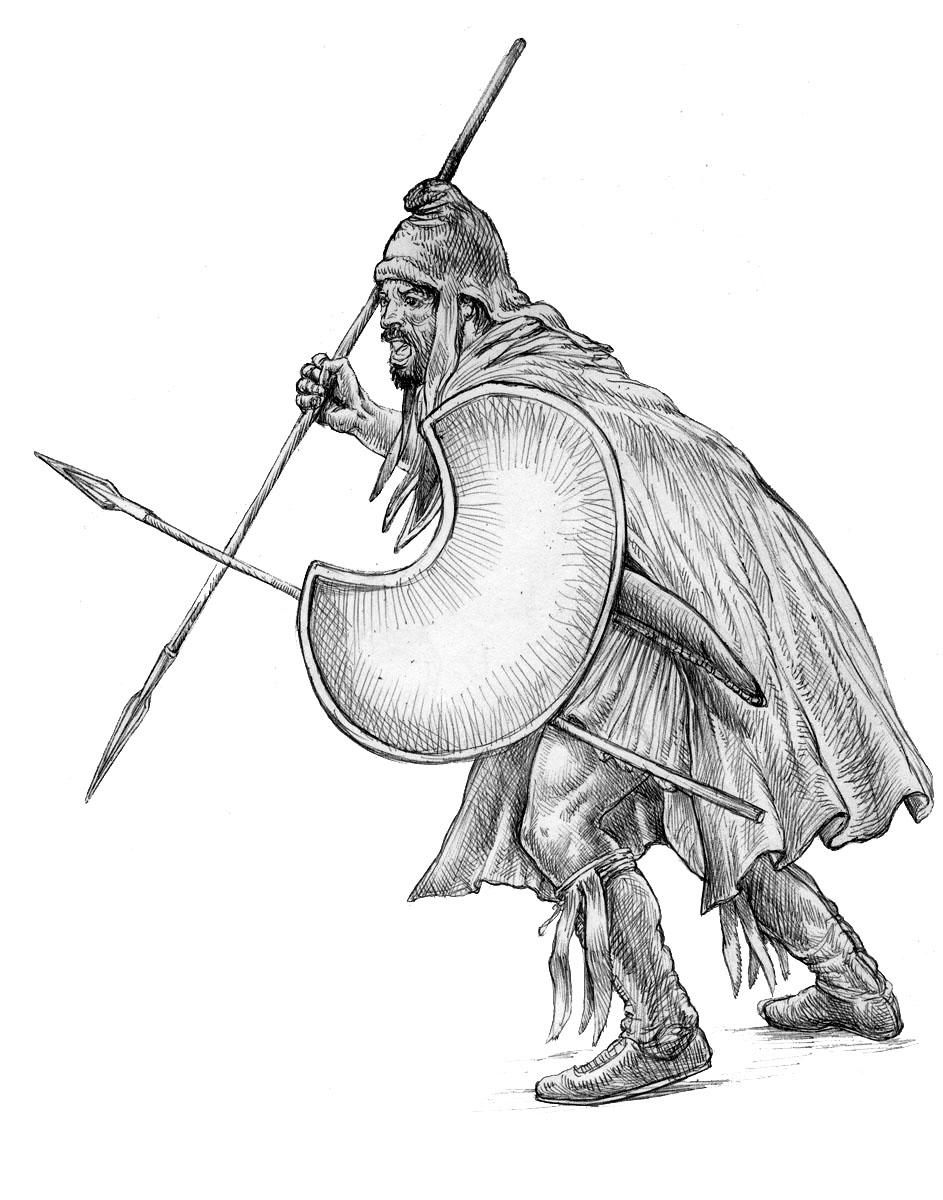
fought as peltast
A ''peltast'' ( grc-gre, πελταστής ) was a type of light infantryman, originating in Thrace and Paeonia, and named after the kind of shield he carried. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis disting ...
s using javelins
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with th ...
and crescent or round wicker shields called ''peltes''. Missile weapons were favored but close combat weaponry was carried by the Thracians as well. These close combat weapons varied from the dreaded rhomphaia
The rhomphaia ( grc, ῥομφαία) was a close-combat bladed weapon used by the Thracians as early as 350-400 BC. Rhomphaias were weapons with a straight or slightly curved single-edged blade attached to a pole, which in most cases was consider ...
to clubs
Club may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Club'' (magazine)
* Club, a ''Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' character
* Clubs (suit), a suit of playing cards
* Club music
* "Club", by Kelsea Ballerini from the album ''kelsea''
Brands and enterprises
...
(used to knock the heads off the spears in Xenophon's Anabasis
Anabasis (from Greek ''ana'' = "upward", ''bainein'' = "to step or march") is an expedition from a coastline into the interior of a country. Anabase and Anabasis may also refer to:
History
* ''Anabasis Alexandri'' (''Anabasis of Alexander''), a ...
by Thynians), one- and two-sided axes, bows, knives, spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fasten ...
s, akinakes
The acinaces, also spelled akinakes (Greek ) or akinaka (unattested Old Persian ''*akīnakah'', Sogdian ''kynʼk'') is a type of dagger or xiphos (short sword) used mainly in the first millennium BCE in the eastern Mediterranean Basin, especially ...
and long swords. Thracians shunned armor and greaves and fought as light as possible, favoring mobility above all other traits and had excellent horsemen. The sica
The sica was a short sword or large dagger of ancient Illyrians, Thracians and Dacians, used in Ancient Rome too, originating in the Halstatt culture. It was originally depicted as a curved sword (see the Zliten mosaic as well as numerous oil la ...
was considered their nationalCompletely parsed Cicero: the first oration of Cicero against Catiline by Marcus Tullius Cicero, LeaAnn A. Osburn, Archibald A. Maclardy, , 2004, page 122, "and was the national weapon of Thracians" weapon.
The Bithyni
The Bithyni (; el, Βιθυνοί) were a Thracian tribe who, along with the Thyni, migrated to Anatolia. Herodotus, Xenophon and Strabo all assert that the Bithyni and Thyni settled together in what would be known as Bithynia and Thynia. Accordin ...
an Thracians had contributed a number of 6,000 men (60,000 according to Herodotus) in Xerxes I of Persia
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of ...
campaign of 480 BC but in general resisted Persian occupation and turned against Mardonius's army as he retreated. The Triballi
The Triballi ( grc, Τριβαλλοί, Triballoí, lat, Triballi) were an ancient people who lived in northern Bulgaria in the region of Roman Oescus up to southeastern Serbia, possibly near the territory of the Morava Valley in the late Iron A ...
frequently used Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
and Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
ic equipment.The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 6 Thracians decorated their bodies with tattoos like the Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
and the Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
.
Thucidides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scientif ...
writes of their infantry tactics when attacked by Theban cavalry:The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 7
"''dashing out and closing their ranks according to the tactics of their country''"
Arrian
Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; la, Lucius Flavius Arrianus; )
was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander and philosopher of the Roman period.
''The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best ...
writes of a tactic using wagons
A wagon or waggon is a heavy four-wheeled vehicle pulled by draught animals or on occasion by humans, used for transporting goods, commodities, agricultural materials, supplies and sometimes people.
Wagons are immediately distinguished from ...
.
Archaic
A Thracian javelinman would wield a crescent wicker shield and a couple of javelins. This troop type was to persist into the classic and Hellenistic era. Organized groups of spearmen or javelin throwers were not used.Classical
 In the 4th century BC, both infantry and cavalry troops started wearing helmetsThe Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 20 (some of leather)The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald, 1998, , page 199 and some
In the 4th century BC, both infantry and cavalry troops started wearing helmetsThe Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 20 (some of leather)The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald, 1998, , page 199 and some peltast
A ''peltast'' ( grc-gre, πελταστής ) was a type of light infantryman, originating in Thrace and Paeonia, and named after the kind of shield he carried. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis disting ...
s are seen with greaves.
Principal weapons in the 4th century BC (as well as earlier) were the spear and short knife.
Armor, when it was available (for the nobility), was at first leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ...
or bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
but iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
armour started appearing in the 4th century BC.The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 21
Thracian cavalry would wear leather armor or no armor and would be armed with javelins, a bow, or a spear. Only royal cavalry would wear armor.The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 22 Oval
An oval () is a closed curve in a plane which resembles the outline of an egg. The term is not very specific, but in some areas (projective geometry, technical drawing, etc.) it is given a more precise definition, which may include either one or ...
shields and peltes (even by heavy cavalry) were later used. Thracian cavalry was numerous. It was also legendary for its combat power so that Philip of Macedon adopted its wedge-shaped formation for the Macedonian cavalry maneuvers.
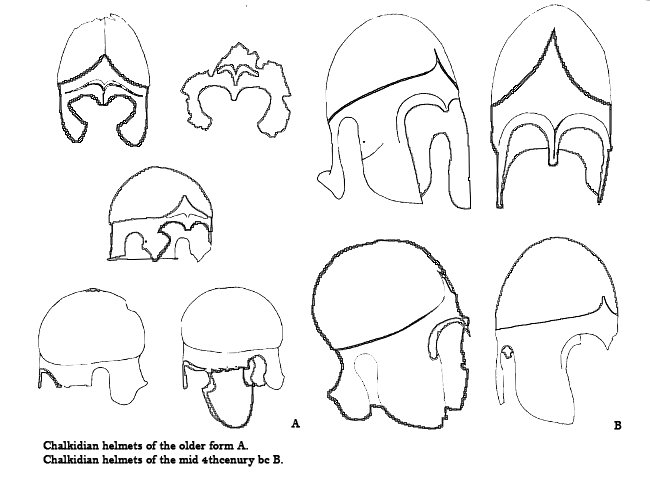
The helmet type used mostly was the Chalcidian type helmetThe Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald, 1998, , page 201 (over 60 have been found) and, to a much lesser extent, the Corinthian type helmet (one has been found), Phrygian type helmet
The Phrygian helmet, also known as the Thracian helmet, was a type of helmet that originated in ancient Greece and was widely used in Thrace, Dacia, Magna Graecia and the Hellenistic world until well into the Roman Empire.
Characteristics
The ...
, Attic type helmet and Scythian type helmet (an open face helmet) with many hybrid types occurring. No Illyrian type helmet
The Illyrian type helmet (or Greco-Illyrian type helmet) is a style of bronze helmet, which in its later variations covered the entire head and neck, and was open-faced in all of its forms.. It originated in Peloponnese, ancient Greece, and was ...
has been found in the east Balkans.
Hellenistic
A Thracian footman (3rd century BC - 1st century BC) could wield a knife or sword,Rhomphaia
The rhomphaia ( grc, ῥομφαία) was a close-combat bladed weapon used by the Thracians as early as 350-400 BC. Rhomphaias were weapons with a straight or slightly curved single-edged blade attached to a pole, which in most cases was consider ...
, a helmet, two javelins and a light oval
An oval () is a closed curve in a plane which resembles the outline of an egg. The term is not very specific, but in some areas (projective geometry, technical drawing, etc.) it is given a more precise definition, which may include either one or ...
wooden shield (or a heavier iron-rimmed and spined thureos). No Thracian infantry wore greaves until the 4th century BC. Later native and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
types started being used, the Greek type being rarer. Thracians used mixed Thracian and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
equipment and armors from different time periods, to the point of wearing armors that ceased to be used elsewhere; this is something they did even in the classic era. Later they adopted Roman armaments.
Thracian mercenaries
Thracians were highly sought as mercenaries due to their ferocity in battle, but they were infamous for their love of plunder. Thracian mercenaries played an important role in the affairs betweenAthenians
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
and Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
ns. The Odomantii were described as expensive mercenaries. In one instance in 413 BC, Dii
:''Dii'' ''is also the plural of Latin Deus.''
The Dii (; grc, Δίοι, Díoi) were an independent Thracian tribe, swordsmen, who lived among the foothills of Mount Rhodope in Thrace, and particularly in the east bank of Nestos, from the ...
mercenaries were so expensive to pay that after they missed the boat to Sicily the Athenians
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
sent them home. They were hired occasionally by Persians.The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 8 Croesus
Croesus ( ; Lydian: ; Phrygian: ; grc, Κροισος, Kroisos; Latin: ; reigned: c. 585 – c. 546 BC) was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC.
Croesus was ...
had hired many Thracian swordsmen for the Lydia
Lydia (Lydian language, Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the mod ...
n army. They also served in the Republican Roman and Mithridatic armies, as well as the armies of the Diadocii. They provided up to one third of the cavalry in Macedonian armies and up to a fifth of their infantry (usually as levies or allies rather than mercenaries). They later formed one of the most important nationalities in the Roman army, contributing up to 20,000 troops at any one time to auxiliary units during the early empire.
Nobility
A Thracian chieftain could have access to armor and helmets. One could be equipped with a Chalcidian type helmet, a breastplate (this sort of armor is rarely found outsideCrete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
and only one has been found in Thrace, a bell-type cuirass) with a mitrai (a plate attached to the bottom of the cuirass to protect the abdomen), a wicker
Wicker is the oldest furniture making method known to history, dating as far back as 5,000 years ago. It was first documented in ancient Egypt using pliable plant material, but in modern times it is made from any pliable, easily woven material. ...
pelte
A ''peltast'' ( grc-gre, πελταστής ) was a type of light infantryman, originating in Thrace and Paeonia, and named after the kind of shield he carried. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis distin ...
, two javelins and a sword. Body armor was restricted to nobles and army commanders. Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
armor was in use in Thrace before the classical age
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
. Nobles would sometimes wear pectorals on their chests as a sign of rank.
Navy
There was no Thracian navy but there were instances of Thracians turning to piracy. The Greek cities of the coast that paid tribute to the Thracian kings did sometimes provide the Thracian kings with ships.Fortifications
Even though Thracians attempted to build only onepolis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
, they had forts in hills built as places of refuge. Thracian villages had basic fortifications as Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, wikt:Ξενοφῶν, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Anci ...
witnesses in Anabasis
Anabasis (from Greek ''ana'' = "upward", ''bainein'' = "to step or march") is an expedition from a coastline into the interior of a country. Anabase and Anabasis may also refer to:
History
* ''Anabasis Alexandri'' (''Anabasis of Alexander''), a ...
. Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historiography, Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his t ...
in his Annals describes a Roman attack against a hill fort. There were many Thracian hill forts and some were inhabited. Other fortified Thracian towns existed at places like Hellis and Kabyle.
External influences
Scythian
Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
s akinakes
The acinaces, also spelled akinakes (Greek ) or akinaka (unattested Old Persian ''*akīnakah'', Sogdian ''kynʼk'') is a type of dagger or xiphos (short sword) used mainly in the first millennium BCE in the eastern Mediterranean Basin, especially ...
, Scythian saddles and horse archer
A horse archer is a cavalryman armed with a bow and able to shoot while riding from horseback. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, it was a highly successful technique for hunting, f ...
equipment to the Scythian type helmet also called Kuban type. It was an open-face bronze helmet that stopped halfway (like a skullcap) and had leather flaps with sewn bronze plates that protected the back part of the head including the nape and the sides of the face. The Scythian cavalry wedge had been adopted by the Thracian cavalry. Despite the power of the Odrysians except during the reigns of Teres and Sitalkes they were still weaker than the Scythians militarily. Scale armor was adopted as well as a composite metal cuirass. The most northern Thracian tribe, the Getai, were so similar to the Scythians that they were often confused with them. Odrysian Thracian kings made treaties and royal marriages as equals with the Scythians. The royal name Spartokos (Spartacus) is shared between some Thracian royalty and some Crimean Skythian kings.
Celtic
Thracian warfare was affected byCelts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
in a variety of ways like the adoption of certain long swords though this must not have been universal among them. The Triballi
The Triballi ( grc, Τριβαλλοί, Triballoí, lat, Triballi) were an ancient people who lived in northern Bulgaria in the region of Roman Oescus up to southeastern Serbia, possibly near the territory of the Morava Valley in the late Iron A ...
had adopted Celtic equipment. Another weapon, the sica
The sica was a short sword or large dagger of ancient Illyrians, Thracians and Dacians, used in Ancient Rome too, originating in the Halstatt culture. It was originally depicted as a curved sword (see the Zliten mosaic as well as numerous oil la ...
was called ''Thracian sword'' (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
,"Θρακικον ξίφος") though it did not originate from there, despite its popular usage (it was considered their national weapon). The sword's utmost origin was the Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European Archaeological culture, culture of Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe ...
and the Thracians may have adopted or inherited it.
Hellenic and Hellenistic

Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
affected Thracian warfare early on with the xiphos
The ''xiphos'' ( grc, ξίφος ; plural ''xiphe'', grc, ξίφη ) is a double-edged, one-handed Iron Age straight shortsword used by the ancient Greeks. It was a secondary battlefield weapon for the Greek armies after the dory or javelin. ...
and other swords, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
type greave
A greave (from the Old French ''greve'' "shin, shin armour") or jambeau is a piece of armour that protects the leg.
Description
The primary purpose of greaves is to protect the tibia from attack. The tibia, or shinbone, is very close to the skin ...
s, breastplates, a variety of helmets and other equipment. During the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
more Greek armaments were adopted. Seuthes had adopted a Greek tactic for a night march (though night marches and attacks were a favourite Thracian tactic). Thracian kings
This article lists rulers of Thrace and Dacia, and includes Thracian, Paeonian, Celtic, Dacian, Scythian, Persian or Ancient Greek up to the point of its fall to the Roman Empire, with a few figures from Greek mythology.
Mythological
*Haemus, bec ...
were the first to be Hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in the ...
.
Roman
Thracians of the Roman client states usedRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
equipment. From 11 BC onwards Thracians would start resembling Roman legionaries
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of ...
. Thracians in Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
, Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus r ...
and the North were Romanized
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and ...
.
Barbarians
Thracians were regarded as warlike, ferocious, and savagely bloodthirsty. Thracians were seen as "''Barbarians''" by other peoples, namely theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
s and the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
. Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
in his ''Republic'' considers them, along with the Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved f ...
, extravagant and high-spirited; and in his ''Laws'' considers them a war-like nation, grouping them with Celts, Persians, Scythians, Iberians and Carthaginians. Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
wrote of Cotys' sober and gentle character being unlike that of most Thracians. Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historiography, Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his t ...
in his ''Annals'' writes of them being wild, savage and impatient, disobedient even to their own kings. Polyaenus
Polyaenus or Polyenus ( ; see ae (æ) vs. e; grc-gre, Πoλύαινoς, Polyainos, "much-praised") was a 2nd-century CE Greek author, known best for his ''Stratagems in War'' ( grc-gre, Στρατηγήματα, Strategemata), which has been pr ...
and Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
write how the Thracians broke their pacts of truce
A ceasefire (also known as a truce or armistice), also spelled cease fire (the antonym of 'open fire'), is a temporary stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions. Ceasefires may be between state act ...
with trickery. The Thracians struck their weapons against each other before battle and engaged in night attacks. Diegylis
Diegylis (Ancient Greek: Διήγυλις) was a chieftain of the Thracian Caeni tribe and father of Ziselmius. He is described by ancient sources (such as Diodorus Siculus) as extremely bloodthirsty.Diodorus Siculus, ''Bibliotheca historica'', ...
was considered one of the most bloothirsty chieftains by Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
. An Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
club for lawless youths was named after the Triballi
The Triballi ( grc, Τριβαλλοί, Triballoí, lat, Triballi) were an ancient people who lived in northern Bulgaria in the region of Roman Oescus up to southeastern Serbia, possibly near the territory of the Morava Valley in the late Iron A ...
. The Dii
:''Dii'' ''is also the plural of Latin Deus.''
The Dii (; grc, Δίοι, Díoi) were an independent Thracian tribe, swordsmen, who lived among the foothills of Mount Rhodope in Thrace, and particularly in the east bank of Nestos, from the ...
The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald, 1998, , page 100 were responsible for the worst atrocities of the Peloponnesian war
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
killing every living thing, including children and dogs, in Tanagra
Tanagra ( el, Τανάγρα) is a town and a municipality north of Athens in Boeotia, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Schimatari. It is not far from Thebes, and it was noted in antiquity for the figurines named after it. The Ta ...
and Mycalessos
Mycale (). also Mykale and Mykali ( grc, Μυκάλη, ''Mykálē''), called Samsun Dağı and Dilek Dağı (Dilek Peninsula) in modern Turkey, is a mountain on the west coast of central Anatolia in Turkey, north of the mouth of the Maeander an ...
. Thracians would impale Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
heads on their spears and Rhomphaias such as in the Kallinikos Callinicus or Kallinikos ( el, Καλλίνικος) is a surname or male given name; the feminine form is Kalliniki, Callinice or Callinica ( el, Καλλινίκη). It is of Greek origin, meaning "beautiful victor".
People named Callinicus Seleu ...
skirmish in 171 BC. Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
writes that "they sell their children and let their daughters commerce with whatever men they please".
List of Thracian battles
This is a list of battles or conflicts that Thracians had a leading or crucial role in, usually as mercenaries. *6th century BCPersian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
against Thracian tribes, Thracian defeat
*401 BC Clearchus The name Clearchus or Clearch may refer to:
* Clearchus of Athens, Greek comic poet
* Clearchus of Heraclea (c. 401 BCE – 353 BCE), Greek tyrant of Heraclea Pontica
* Clearchus of Rhegium, Greek sculptor, pupil of Eucheirus, teacher of Pythagoras ...
against Thracians, Thracian Victory
*376 BC Chabrias
Chabrias ( el, Χαβρίας; bef. 420–357 BC) was an Athenian general active in the first half of the 4th century BC. During his career he was involved in several battles, both on land and sea. The orator Demosthenes described him as one o ...
against Thracians, Thracian defeat
*331 BC Antipater
Antipater (; grc, , translit=Antipatros, lit=like the father; c. 400 BC319 BC) was a Macedonian general and statesman under the subsequent kingships of Philip II of Macedon and his son, Alexander the Great. In the wake of the collaps ...
against Memnon of Rhodes
Memnon of Rhodes (Greek: Μέμνων ὁ Ῥόδιος; c. 380 – 333 BC) was a prominent Rhodian Greek commander in the service of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. Related to the Persian aristocracy by the marriage of his sister to the satrap ...
and Seuthes III of Thrace, Thracian and Rhodian VictoryThe Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 11
*323 BC Lysimachus
Lysimachus (; Greek: Λυσίμαχος, ''Lysimachos''; c. 360 BC – 281 BC) was a Thessalian officer and successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became King of Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedon.
Early life and career
Lysimachus was b ...
against Seuthes III, Thracian Victory
*279 BC Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They s ...
against Seuthopolis
Seuthopolis (Ancient Greek: Σευθόπολις) was an ancient hellenistic-type city founded by the Thracian king Seuthes III between 325–315 BC and the capital of the Odrysian kingdom.
Its ruins are now located at the bottom of the Koprinka ...
, Thracian defeat
*214 BC Thracians against Tylis
Tylis (Greek: Τύλις) or Tyle was a capital of a short-lived Balkan state mentioned by Polybius that was founded by Celts led by Comontorius in the 3rd century BC. Following their invasion of Thrace and Greece in 279 BC, the Gauls were defeat ...
, Thracian victory
*110 BC Minucius Rufus against Bessi and Scordisci
The Scordisci ( el, Σκορδίσκοι) were a Celtic Iron Age cultural group centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morava) and Danube rivers. They were historically no ...
, Thracian defeatThe Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, 2001, , page 14
*AD 7 Marcus Valerius Messalla Messallinus
Marcus Valerius Messalla Messallinus (also spelled as Messalinus,Gagarin, ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece and Rome: Academy Bible'', p.131 c. 36 BC – after AD 21) was a Roman senator who was elected consul for 3 BC.
Early life
Messa ...
, Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the Patric ...
& Rhoemetalces against Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
ns and Pannonians
This is a list of ancient tribes in the ancient territory of Illyria ( grc-gre, Ἰλλυρία; la, Illyria). The name ''Illyrians'' seems to be the name of a single Illyrian tribe that was the first to come into contact with the ancient Greeks ...
, Marcus Valeurius victory, it is not known how long Rhoemetalces participated
See also
*Dacian warfare
The history of Dacian warfare spans from c. 10th century BC up to the 2nd century AD in the region defined by Ancient Greek and Latin historians as Dacia, populated by a collection of Thracian, Ionian, and Dorian tribes. It concerns the armed con ...
*Illyrian warfare
The history of Illyrian warfare of the Illyrians spans from the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC up to the 1st century AD in the region of Illyria and in southern Italy where the Iapygian civilization flourished.
It concerns the armed conflicts ...
*Celtic warfare
Celtic Warfare was the type of warfare practiced by the various Celtic peoples and tribes, from Classical antiquity through the Migration period.
No Celtic group employed a regular military as we would understand it today. Organization was var ...
*List of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) including possibly or partly Thracian or Dacian tribes, and non-Thracian or non-Dacian tribes that inhabited the lands known as Thrace and Dacia. A great number o ...
*List of rulers of Thrace and Dacia
This article lists rulers of Thrace and Dacia, and includes Thracian, Paeonian, Celtic, Dacian, Scythian, Persian or Ancient Greek up to the point of its fall to the Roman Empire, with a few figures from Greek mythology.
Mythological
*Haemus, bec ...
*Rhomphaia
The rhomphaia ( grc, ῥομφαία) was a close-combat bladed weapon used by the Thracians as early as 350-400 BC. Rhomphaias were weapons with a straight or slightly curved single-edged blade attached to a pole, which in most cases was consider ...
*Sica
The sica was a short sword or large dagger of ancient Illyrians, Thracians and Dacians, used in Ancient Rome too, originating in the Halstatt culture. It was originally depicted as a curved sword (see the Zliten mosaic as well as numerous oil la ...
References
External links
Thracians
{{DEFAULTSORT:Thracian Warfare Thracian culture Indo-European warfare Ancient warfare Wars involving the Balkans