Third Anglo–Dutch War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Third Anglo-Dutch War ( nl, Derde Engels-Nederlandse Oorlog), 27 March 1672 to 19 February 1674, was a naval conflict between the Dutch Republic and England, in alliance with France. It is considered a subsidiary of the wider 1672 to 1678
 The 1652–1654 First Anglo-Dutch War was the result of commercial rivalry and Orangist support for the exiled Charles II, uncle of William of Orange. Peace terms agreed in 1654 with the
The 1652–1654 First Anglo-Dutch War was the result of commercial rivalry and Orangist support for the exiled Charles II, uncle of William of Orange. Peace terms agreed in 1654 with the  Terms included an Anglo-French military alliance against the Republic, creation of a Dutch rump state for his nephew William and a British brigade for the French army. The treaty was signed in December 1670, but omitted secret clauses not revealed until 1677; Louis agreed to pay Charles £230,000 per year for the brigade, £1 million for the navy and £200,000 for his public conversion to Catholicism, the timing of which was left up to him. Aware Louis was negotiating with De Witt over dividing the Spanish Netherlands, Charles demanded
Terms included an Anglo-French military alliance against the Republic, creation of a Dutch rump state for his nephew William and a British brigade for the French army. The treaty was signed in December 1670, but omitted secret clauses not revealed until 1677; Louis agreed to pay Charles £230,000 per year for the brigade, £1 million for the navy and £200,000 for his public conversion to Catholicism, the timing of which was left up to him. Aware Louis was negotiating with De Witt over dividing the Spanish Netherlands, Charles demanded
 Louis instructed de Pomponne, his ambassador in The Hague, to continue negotiations with De Witt as a delaying tactic while he finalised invasion plans. The English envoy,
Louis instructed de Pomponne, his ambassador in The Hague, to continue negotiations with De Witt as a delaying tactic while he finalised invasion plans. The English envoy,  England provided two-thirds of an Anglo-French fleet of 98 "great ships and frigates", whose role was to gain control of Dutch waters, land an expeditionary force and attack its shipping. Parliament generally approved naval expenditure, seen as protecting English trade, but refused to fund land forces. The British brigade was largely composed of Dumbarton's, a mercenary unit in French service since 1631, and very few members saw service before the war ended.
The refusal of Parliament to approve taxes for a war against the Protestant Dutch in alliance with Catholic France forced Charles to seek other sources of finance. In January 1672, he suspended repayment of Crown debts in the
England provided two-thirds of an Anglo-French fleet of 98 "great ships and frigates", whose role was to gain control of Dutch waters, land an expeditionary force and attack its shipping. Parliament generally approved naval expenditure, seen as protecting English trade, but refused to fund land forces. The British brigade was largely composed of Dumbarton's, a mercenary unit in French service since 1631, and very few members saw service before the war ended.
The refusal of Parliament to approve taxes for a war against the Protestant Dutch in alliance with Catholic France forced Charles to seek other sources of finance. In January 1672, he suspended repayment of Crown debts in the
 The speed with which the Republic was over-run in 1672 means it is still referred to as the '' Rampjaar'' or 'Year of disaster'. On 7 May, a French army of around 80,000 entered Liège; accompanied by Louis, they bypassed the Dutch stronghold of Maastricht, crossed the Meuse and besieged the Dutch-held Rhine fortress towns of Rheinberg, Orsoy, Buderich and Wesel. The last of these surrendered on 9 June, while troops from Münster and Cologne simultaneously entered the provinces of
The speed with which the Republic was over-run in 1672 means it is still referred to as the '' Rampjaar'' or 'Year of disaster'. On 7 May, a French army of around 80,000 entered Liège; accompanied by Louis, they bypassed the Dutch stronghold of Maastricht, crossed the Meuse and besieged the Dutch-held Rhine fortress towns of Rheinberg, Orsoy, Buderich and Wesel. The last of these surrendered on 9 June, while troops from Münster and Cologne simultaneously entered the provinces of
 William rejected the offer, since it gave the Dutch nothing they did not already hold. Arlington and Buckingham then met with Louis and agreed the Heeswijk Accord on 16 July. This set out a list of shared demands and undertook not to conclude a separate peace, but neither side placed any reliance on it. Leopold's envoy in the Hague, Francois-Paul de Lisola, gave the States-General assurances of Imperial support and arranged for Spanish troops to hold the Dutch fortress cities of
William rejected the offer, since it gave the Dutch nothing they did not already hold. Arlington and Buckingham then met with Louis and agreed the Heeswijk Accord on 16 July. This set out a list of shared demands and undertook not to conclude a separate peace, but neither side placed any reliance on it. Leopold's envoy in the Hague, Francois-Paul de Lisola, gave the States-General assurances of Imperial support and arranged for Spanish troops to hold the Dutch fortress cities of
 In the first two wars, both navies, particularly the Dutch, employed aggressive tactics that often resulted in heavy ship losses for the defeated side. In the Third Anglo-Dutch War, the priority was to minimise losses, and it was common for fleets to engage using the ' line-ahead' formation, an essentially defensive approach; despite inflicting considerable damage, neither side lost any ships at the Texel.
When the Water Line froze during the winter of 1673, the French were unable to break it, thwarted by thin ice and companies of Dutch sailors equipped with ice skates, under Johan de Liefde. Attempts in the spring to drain the northern part of the line or cross on rafts also proved unsuccessful. With an eastern approach impractical, the Royal Navy was ordered to blockade the coast in co-operation with a French squadron; if possible, they were to land an invasion force, although how this would be accomplished was unclear. Lacking experience of amphibious operations, this meant capturing a Dutch port, despite limited knowledge of the dangerous
In the first two wars, both navies, particularly the Dutch, employed aggressive tactics that often resulted in heavy ship losses for the defeated side. In the Third Anglo-Dutch War, the priority was to minimise losses, and it was common for fleets to engage using the ' line-ahead' formation, an essentially defensive approach; despite inflicting considerable damage, neither side lost any ships at the Texel.
When the Water Line froze during the winter of 1673, the French were unable to break it, thwarted by thin ice and companies of Dutch sailors equipped with ice skates, under Johan de Liefde. Attempts in the spring to drain the northern part of the line or cross on rafts also proved unsuccessful. With an eastern approach impractical, the Royal Navy was ordered to blockade the coast in co-operation with a French squadron; if possible, they were to land an invasion force, although how this would be accomplished was unclear. Lacking experience of amphibious operations, this meant capturing a Dutch port, despite limited knowledge of the dangerous  Hoping to unnerve the Dutch, Prince Rupert leaked information claiming his fleet was accompanied by ships carrying an invasion force; in reality, it remained in
Hoping to unnerve the Dutch, Prince Rupert leaked information claiming his fleet was accompanied by ships carrying an invasion force; in reality, it remained in  The Allies continued to hold their position off the Dutch coast; on 14 June, De Ruyter took advantage of favourable winds and launched the Second Battle of the Schooneveld. Once again, this caused chaos in the unprepared Allied fleet, which suffered severe damage and returned to the Thames for repairs. In late July, Rupert put to sea again, hoping to draw the Dutch north by feinting against The Hague or
The Allies continued to hold their position off the Dutch coast; on 14 June, De Ruyter took advantage of favourable winds and launched the Second Battle of the Schooneveld. Once again, this caused chaos in the unprepared Allied fleet, which suffered severe damage and returned to the Thames for repairs. In late July, Rupert put to sea again, hoping to draw the Dutch north by feinting against The Hague or
 In previous conflicts, investing in privateers had been very profitable for the English, but from 1672 to 1673 Dutch raiders captured over 2,800 French and English ships, far more than their counterparts, The province of Zealand alone operated 120 privateers. Having failed to blockade the Dutch coast, English merchants were excluded from the vital Baltic trade in shipbuilding materials, while the loss of
In previous conflicts, investing in privateers had been very profitable for the English, but from 1672 to 1673 Dutch raiders captured over 2,800 French and English ships, far more than their counterparts, The province of Zealand alone operated 120 privateers. Having failed to blockade the Dutch coast, English merchants were excluded from the vital Baltic trade in shipbuilding materials, while the loss of  In early 1673, Arlington's former secretary Peter du Moulin fled to the Republic, where he started a propaganda campaign backed by the world's largest per capita printing capacity. England was soon flooded with tens of thousands of pamphlets accusing Charles of conspiring with Louis to make the country Catholic again. Many were convinced of its truth, particularly when Charles gave permission for his brother and heir James to marry
In early 1673, Arlington's former secretary Peter du Moulin fled to the Republic, where he started a propaganda campaign backed by the world's largest per capita printing capacity. England was soon flooded with tens of thousands of pamphlets accusing Charles of conspiring with Louis to make the country Catholic again. Many were convinced of its truth, particularly when Charles gave permission for his brother and heir James to marry
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
.
In the 1670 Secret Treaty of Dover, Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of England, Scotland and Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest surviving child of ...
agreed to support an attack by Louis XIV of France on the Dutch Republic. By doing so, Louis hoped to gain control of the Spanish Netherlands, while Charles sought to restore the damage to his prestige caused by the 1667 Raid on the Medway. Under the treaty, Charles also received secret payments which he hoped would make him financially independent of the English Parliament.
The French offensive in May and June 1672 quickly over-ran most of the Republic, with the exception of the core province of Holland, where they were halted by water defences. In early June, the Anglo-French fleet was badly damaged by the Dutch under Michiel de Ruyter at the Battle of Solebay
The naval Battle of Solebay took place on 28 May Old Style, 7 June New Style 1672 and was the first naval battle of the Third Anglo-Dutch War.
The battle began as an attempted raid on Solebay port where an English fleet was anchored and large ...
, ensuring they retained control of vital trade routes. In late June, Johan de Witt resigned as Grand Pensionary, and Charles' nephew William III of Orange was appointed Stadtholder
In the Low Countries, ''stadtholder'' ( nl, stadhouder ) was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and H ...
. Charles tried to persuade him to make peace, but William refused; he knew the alliance with France was unpopular in England, while fear of French success brought support from Emperor Leopold
Leopold I (Leopold Ignaz Joseph Balthasar Franz Felician; hu, I. Lipót; 9 June 1640 – 5 May 1705) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia. The second son of Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor, by his first wife, Maria An ...
and Spain.
By the end of 1672, the Dutch had regained much of the territory lost in May, and with hopes of a quick victory gone, Parliament refused to provide Charles with further funding for a war which the majority opposed. From June to July 1673, the Dutch and Anglo-French fleets fought three separate battles; although largely inconclusive, they ended any prospect of the Republic being conquered. Instead, Louis focused on taking the Spanish Netherlands, an objective as harmful to English interests as it was to Dutch; domestic opposition forced Charles to agree to the Second Peace of Westminster
The Treaty of Westminster of 1674 was the peace treaty that ended the Third Anglo-Dutch War. Signed by the Dutch Republic and the Kingdom of England, the treaty provided for the return of the colony of New Netherland (now New York) to England an ...
in February 1674.
Background
 The 1652–1654 First Anglo-Dutch War was the result of commercial rivalry and Orangist support for the exiled Charles II, uncle of William of Orange. Peace terms agreed in 1654 with the
The 1652–1654 First Anglo-Dutch War was the result of commercial rivalry and Orangist support for the exiled Charles II, uncle of William of Orange. Peace terms agreed in 1654 with the English Protectorate
The Protectorate, officially the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland, refers to the period from 16 December 1653 to 25 May 1659 during which England, Wales, Scotland, Ireland and associated territories were joined together in the Com ...
included the permanent exclusion of the House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (Dutch: ''Huis van Oranje-Nassau'', ) is the current reigning house of the Netherlands. A branch of the European House of Nassau, the house has played a central role in the politics and government of the Netherlands ...
from public office, ensuring Republican political control. When Charles regained the English throne in 1660, his Orangist links meant Grand Pensionary Johan de Witt opposed negotiations for an Anglo-Dutch alliance; after these broke down, he agreed a treaty of assistance with Louis XIV in 1662.
Despite their long-standing support in the Dutch Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Refo ...
against Spain, French objectives in the Low Countries threatened Dutch commercial interests. The 1648 Peace of Münster
The Peace of Münster was a treaty between the Lords States General of the Seven United Netherlands and the Spanish Crown, the terms of which were agreed on 30 January 1648. The treaty, parallelly negotiated to but not part of the Peace of We ...
permanently closed the Scheldt estuary, benefiting De Witt's power base of Amsterdam by eliminating their closest rival, Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, and keeping it shut was a vital objective. Changes in this region also concerned England, since control of ports on the North Flemish coast allowed a hostile power to blockade the Channel
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
.
In 1665, an attack by the Duke of York
Duke of York is a title of nobility in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of English (later British) monarchs. The equivalent title in the Scottish peerage was D ...
on the West-Indische Compagnie
The Dutch West India Company ( nl, Geoctrooieerde Westindische Compagnie, ''WIC'' or ''GWC''; ; en, Chartered West India Company) was a chartered company of Dutch merchants as well as foreign investors. Among its founders was Willem Usselincx ( ...
led to the Second Anglo-Dutch War; in the first 18 months, the Dutch suffered a serious naval defeat at Lowestoft
Lowestoft ( ) is a coastal town and civil parish in the East Suffolk district of Suffolk, England.OS Explorer Map OL40: The Broads: (1:25 000) : . As the most easterly UK settlement, it is north-east of London, north-east of Ipswich and sou ...
, an invasion by Münster and an attempted Orangist coup, both financed by England. The prospect of an English victory led Louis to activate the 1662 treaty, although the Dutch considered the support provided inadequate. When the States of Holland blocked his requests for territorial compensation, Louis launched the War of Devolution in May 1667 and rapidly occupied much of the Spanish Netherlands and Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté (, ; ; Frainc-Comtou: ''Fraintche-Comtè''; frp, Franche-Comtât; also german: Freigrafschaft; es, Franco Condado; all ) is a cultural and historical region of eastern France. It is composed of the modern departments of Doubs, ...
.
His refusal to recall Parliament forced Charles to pay off his fleet in early 1667, leading to the humiliating Raid on the Medway. Despite this triumph, the Dutch were more worried by French gains; they quickly negotiated an end to the war in July 1667, then started talks in London on a shared approach for reversing them. Sensing an opportunity, Charles proposed an alliance to Louis, who was unwilling to pay the subsidies demanded; however, De Witt welcomed English envoys to The Hague, seeing it as a way to put pressure on France.
French tariffs on imports imposed in early 1667 increased opposition in the States General, who preferred a weak Spain as a neighbour to a strong France. On 23 January 1668, the Republic, England and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
signed the Triple Alliance Triple Alliance may refer to:
* Aztec Triple Alliance (1428–1521), Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan and in central Mexico
* Triple Alliance (1596), England, France, and the Dutch Republic to counter Spain
* Triple Alliance (1668), England, the ...
, committing to mutual support in the event of an attack on one by France or Spain. A secret clause agreed to provide Spain military assistance if France continued the war. Charles disclosed the secret clause to Louis, who felt betrayed by the Dutch. Louis returned most of his acquisitions in the 1668 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, although he retained Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
and Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Euromet ...
.
Concluding the Dutch would never voluntarily accept French aims in the Spanish Netherlands, Louis decided the best way to achieve them was to eliminate the Republic. This meant breaking up the Triple Alliance; since the subsidies promised by the Dutch remained unpaid, it was easy to detach Sweden by offering money, making England his next target. The French and English kings negotiated the 1670 Secret Treaty of Dover, using Henrietta of England as a mediator, Charles' sister and Louis' sister in law. Very few English statesmen were aware of its provisions.
 Terms included an Anglo-French military alliance against the Republic, creation of a Dutch rump state for his nephew William and a British brigade for the French army. The treaty was signed in December 1670, but omitted secret clauses not revealed until 1677; Louis agreed to pay Charles £230,000 per year for the brigade, £1 million for the navy and £200,000 for his public conversion to Catholicism, the timing of which was left up to him. Aware Louis was negotiating with De Witt over dividing the Spanish Netherlands, Charles demanded
Terms included an Anglo-French military alliance against the Republic, creation of a Dutch rump state for his nephew William and a British brigade for the French army. The treaty was signed in December 1670, but omitted secret clauses not revealed until 1677; Louis agreed to pay Charles £230,000 per year for the brigade, £1 million for the navy and £200,000 for his public conversion to Catholicism, the timing of which was left up to him. Aware Louis was negotiating with De Witt over dividing the Spanish Netherlands, Charles demanded Walcheren
Walcheren () is a region and former island in the Dutch province of Zeeland at the mouth of the Scheldt estuary. It lies between the Eastern Scheldt in the north and the Western Scheldt in the south and is roughly the shape of a rhombus. The two ...
, Cadzand and Sluys
Sluis (; zea, label=Zeelandic, Sluus ; french: Écluse) is a town and municipality located in the west of Zeelandic Flanders, in the south-western Dutch province of Zeeland.
The current incarnation of the municipality has existed since 1 January ...
, whose possession would give him control of Dutch sea routes.
National tensions between England and the Republic significantly diminished after 1667, and there was minimal support for an anti-Dutch alliance with France. Exchanging the Dutch colony of New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
for the spice island of Run
Run(s) or RUN may refer to:
Places
* Run (island), one of the Banda Islands in Indonesia
* Run (stream), a stream in the Dutch province of North Brabant
People
* Run (rapper), Joseph Simmons, now known as "Reverend Run", from the hip-hop group ...
resolved a major area of dispute, while both were concerned by French aims in the Low Countries, and English merchants were also affected by French tariffs. Most Dutch and English politicians considered the Triple Alliance an essential protection against French expansion; in early 1671, Parliament allocated money to ensure the Royal Navy could fulfil its obligations under the treaty.
Preparations
 Louis instructed de Pomponne, his ambassador in The Hague, to continue negotiations with De Witt as a delaying tactic while he finalised invasion plans. The English envoy,
Louis instructed de Pomponne, his ambassador in The Hague, to continue negotiations with De Witt as a delaying tactic while he finalised invasion plans. The English envoy, Sir William Temple
Sir William Temple, 1st Baronet (25 April 162827 January 1699) was an English diplomat, statesman and essayist. An important diplomat, he was recalled in 1679, and for a brief period was a leading advisor to Charles II, with whom he then fell ...
, was entrusted by Charles with the same mission. Since Dutch defences were concentrated along their southern border with the Spanish Netherlands, Louis agreed an alliance with Electoral Cologne
The Electorate of Cologne (german: Kurfürstentum Köln), sometimes referred to as Electoral Cologne (german: Kurköln, links=no), was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the 10th to the early 19th century. ...
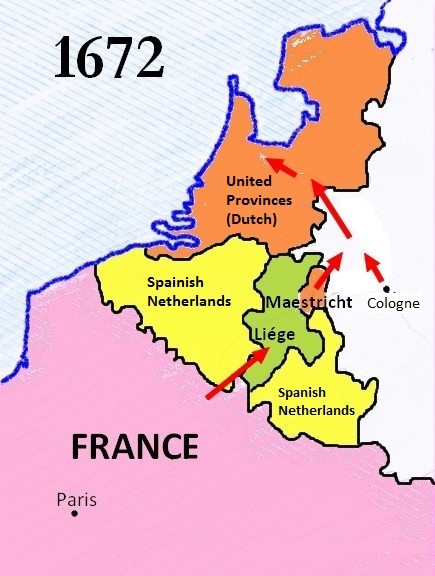
, allowing his army to advance through the Principality of Liège for an attack from the east (see Map). It also complied with an undertaking to Emperor Leopold I not to use the Spanish Netherlands as an invasion route.
In April 1672, France agreed to pay Sweden subsidies in return for its neutrality, while also promising military assistance if 'threatened' by Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia (german: Brandenburg-Preußen; ) is the historiographic denomination for the early modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohenz ...
; this offset an agreement of 6 May between the Dutch and Frederick William, whose territories included the Duchy of Cleves on their eastern border. Hoping to gain English backing, on 25 February 1672 the States General appointed Charles' 22-year-old nephew William as captain-general of the federal army, which had an authorised total of 83,000 men. Uncertainty over French strategy meant most of these were based in the wrong place, while many garrisons were below strength; on 12 June, one commander reported he had only four companies available from an official total of eighteen.
The Republic was better prepared for a naval war, although to avoid provoking the English, on 4 February the States General reduced the naval budget from 7.9 million to 4.8 million guilders. At the end of the Second Anglo-Dutch War in 1667, the Dutch Navy was the largest in Europe but by 1672 the combined Anglo-French fleet outnumbered them by over a third. However, the French were inexperienced, their ships badly designed and their relationship with the Royal Navy was damaged by mutual suspicion.
In the battles of 1666, the Dutch had been hampered by lack of familiarity with their new, much heavier, warships, the complex federal command system and conflict between Michiel de Ruyter and Cornelis Tromp. By 1672, these had been corrected, and De Ruyter's intensive training of his fleet in line-of-battle
The line of battle is a tactic in naval warfare in which a fleet of ships forms a line end to end. The first example of its use as a tactic is disputed—it has been variously claimed for dates ranging from 1502 to 1652. Line-of-battle tacti ...
manoeuvres installed a new sense of coherence and discipline. Dutch ships were generally better gun platforms, whose shallow draft suited operations close to shore but were slow and less effective in open seas. Although Dutch numbers were further reduced by Friesland retaining ships for defence against Münster, better training and design gave them operational equality.
 England provided two-thirds of an Anglo-French fleet of 98 "great ships and frigates", whose role was to gain control of Dutch waters, land an expeditionary force and attack its shipping. Parliament generally approved naval expenditure, seen as protecting English trade, but refused to fund land forces. The British brigade was largely composed of Dumbarton's, a mercenary unit in French service since 1631, and very few members saw service before the war ended.
The refusal of Parliament to approve taxes for a war against the Protestant Dutch in alliance with Catholic France forced Charles to seek other sources of finance. In January 1672, he suspended repayment of Crown debts in the
England provided two-thirds of an Anglo-French fleet of 98 "great ships and frigates", whose role was to gain control of Dutch waters, land an expeditionary force and attack its shipping. Parliament generally approved naval expenditure, seen as protecting English trade, but refused to fund land forces. The British brigade was largely composed of Dumbarton's, a mercenary unit in French service since 1631, and very few members saw service before the war ended.
The refusal of Parliament to approve taxes for a war against the Protestant Dutch in alliance with Catholic France forced Charles to seek other sources of finance. In January 1672, he suspended repayment of Crown debts in the Stop of the Exchequer
The Great Stop of the Exchequer or Stop of the Exchequer was a repudiation of state debt that occurred in England in 1672 under the reign of Charles II of England.
The stop and its causes
Under Charles II the state finances were in such a grievou ...
, which produced £1.3 million but had disastrous economic effects; many City of London merchants were ruined and it shut off the short-term financing essential to international trade. In late March, two weeks before a formal declaration of war, he ordered an attack on a Dutch Levant Company convoy in the Channel, which was beaten off by its escort under Cornelis Evertsen the Youngest.
The unpopularity of the French alliance and lack of funding forced Charles to gamble on a quick war. In an attempt to gain support from Nonconformists, he issued a Royal Declaration of Indulgence on 15 March, but by also removing restrictions on Catholics, it did little to reduce opposition. Hostility increased when Charles appointed his Catholic brother James
James is a common English language surname and given name:
*James (name), the typically masculine first name James
* James (surname), various people with the last name James
James or James City may also refer to:
People
* King James (disambiguat ...
as Lord High Admiral rather than his Protestant uncle, Prince Rupert
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, (17 December 1619 (O.S.) / 27 December (N.S.) – 29 November 1682 (O.S.)) was an English army officer, admiral, scientist and colonial governor. He first came to prominence as a Royalist cavalr ...
. Even the Royal Navy found it difficult to recruit enough sailors to fully man the fleet.
His chief minister, Lord Arlington, was instructed to "break with (the Dutch), yet to lay the breach at their door". This was done using manufactured incidents, including the ''Merlin'' affair, which took place near Brill
Brill may refer to:
Places
* Brielle (sometimes "Den Briel"), a town in the western Netherlands
* Brill, Buckinghamshire, a village in England
* Brill, Cornwall, a small village to the west of Constantine, Cornwall, UK
* Brill, Wisconsin, an uni ...
in August 1671. The royal yacht was ordered to sail through the Dutch fleet, who duly struck their flag in salute, but failed to fire white smoke, an honour afforded only to warships. A formal complaint to the States General was dismissed and few in England were even aware of the incident; its use as a pretext, combined with the attack on the Dutch convoy, led some English politicians to declare the conflict "unjust". England declared war on 27 March, followed by France on 6 April.
The war in 1672
Overview
When the French invaded the Dutch Republic in May 1672, it initially seemed as if they had won an overwhelming victory. By the end of June, onlythe Dutch Water Line
The Dutch Waterline ( nl, Hollandsche Waterlinie, modern spelling: ''Hollandse Waterlinie'') was a series of water-based defences conceived by Maurice of Nassau in the early 17th century, and realised by his half brother Frederick Henry. Combine ...
stood between them and the core province of Holland; by opening the sluices, the Dutch managed to stop the French advance. Dutch survival depended on control of the sea lanes, which ensured they could bring in vital supplies and keep trade routes open. Although outnumbered, on 7 June De Ruyter attacked the combined Anglo-French fleet at the Battle of Solebay
The naval Battle of Solebay took place on 28 May Old Style, 7 June New Style 1672 and was the first naval battle of the Third Anglo-Dutch War.
The battle began as an attempted raid on Solebay port where an English fleet was anchored and large ...
; both sides lost one ship each, but it ended significant naval operations for the year.
His unexpected success proved a mixed blessing for Louis, since it distracted from the main objectives of capturing the Spanish Netherlands. The possibility of France controlling the Republic, the largest commercial power in Europe, brought the Dutch support from Emperor Leopold
Leopold I (Leopold Ignaz Joseph Balthasar Franz Felician; hu, I. Lipót; 9 June 1640 – 5 May 1705) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia. The second son of Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor, by his first wife, Maria An ...
and Spain among others. It also increased opposition in England, where many had opposed an alliance with Catholic France from the start. Peace negotiations made little progress; an over-confident Louis made demands unacceptable even to his English allies, while the Dutch used the opportunity to acquire allies and rebuild their army. By the end of 1672, they had regained much of the territory lost in May; Charles had run out of money and Parliament was unwilling to provide further financing.
French success: May to June
 The speed with which the Republic was over-run in 1672 means it is still referred to as the '' Rampjaar'' or 'Year of disaster'. On 7 May, a French army of around 80,000 entered Liège; accompanied by Louis, they bypassed the Dutch stronghold of Maastricht, crossed the Meuse and besieged the Dutch-held Rhine fortress towns of Rheinberg, Orsoy, Buderich and Wesel. The last of these surrendered on 9 June, while troops from Münster and Cologne simultaneously entered the provinces of
The speed with which the Republic was over-run in 1672 means it is still referred to as the '' Rampjaar'' or 'Year of disaster'. On 7 May, a French army of around 80,000 entered Liège; accompanied by Louis, they bypassed the Dutch stronghold of Maastricht, crossed the Meuse and besieged the Dutch-held Rhine fortress towns of Rheinberg, Orsoy, Buderich and Wesel. The last of these surrendered on 9 June, while troops from Münster and Cologne simultaneously entered the provinces of Overijssel
Overijssel (, ; nds, Oaveriessel ; german: Oberyssel) is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the eastern part of the country. The province's name translates to "across the IJssel", from the perspective of the ...
and Gelderland.
On 12 June, the French crossed the Lower Rhine into the Betuwe
Batavia (; , ) is a historical and geographical region in the Netherlands, forming large fertile islands in the river delta formed by the waters of the Rhine (Dutch: ''Rijn'') and Meuse (Dutch: ''Maas'') rivers. During the Roman empire, it was an ...
near Schenkenschans
Schenkenschanz is a small community in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany that was incorporated into the town of Kleve (Cleves) in 1969. Schenkenschanz is site of the former Schenkenschans fortress that was of significance in the Dutch Revolt.
Today ...
and, recrossing the Lower Rhine to outflank the IJssel Line, occupied Arnhem on 16 June and Zutphen on 25 June. Now in danger of being cut off from the core province of Holland, William and his troops retreated through Utrecht behind the Holland Water Line; the inundations were released on 22 June, stopping the French advance in this area. On 5 July, Overijssel
Overijssel (, ; nds, Oaveriessel ; german: Oberyssel) is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the eastern part of the country. The province's name translates to "across the IJssel", from the perspective of the ...
surrendered to Bernhard von Galen
Christoph Bernhard Freiherr von Galen (12 October 1606, Drensteinfurt – 19 September 1678) was Prince-bishop of Münster. He was born into a noble Westphalian family.
Background, education and conversion to Roman Catholicism
Christoph Bernha ...
, Prince-Bishop of Münster, who occupied Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Nov ...
; he reached Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
, but flooding prevented a proper siege and his troops were soon starving.
The States General had responded to the March attack on the Smyrna convoy by expanding the active fleet from forty-eight to sixty vessels, and ordering the construction of thirty-six new vessels. This still left them outnumbered by the combined Anglo-French fleet, and De Ruyter withdrew into shoal
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. It ...
waters near the Dutch coast, awaiting an opportunity. Disasters on land meant De Witt needed a victory; he ordered De Ruyter to attack, accompanied by Cornelis de Witt to ensure these instructions were carried out.
When the Allied fleet withdrew to Solebay near Southwold, Norfolk to resupply, on 7 June De Ruyter surprised it at the Battle of Solebay
The naval Battle of Solebay took place on 28 May Old Style, 7 June New Style 1672 and was the first naval battle of the Third Anglo-Dutch War.
The battle began as an attempted raid on Solebay port where an English fleet was anchored and large ...
. The Duke of York led his squadrons against the main Dutch fleet, but his French colleague d'Estrées either misunderstood his intentions or deliberately ignored them, sailing in the opposite direction. The thirty French ships fought a separate encounter at long-range with fifteen ships from the Admiralty of Zeeland, under Adriaen Banckert
Adriaen van Trappen Banckert (c.1615 – 22 April 1684) was a Dutch admiral. In English literature he is sometimes known as ''Banckers''. His first name is often rendered in the modern spelling ''Adriaan''. ''Van Trappen'' was the original family ...
. D'Estrées was later condemned by some of his own officers for failing to engage them more closely.
The Earl of Sandwich was killed when the '' Royal James'' was sunk by fireships, with other ships suffering heavy damage. Although ship losses were roughly equal, Solebay ensured the Dutch retained control of their coastal waters, secured their trade routes and ended hopes of an Anglo-French landing in Zeeland. Anger at the alleged lack of support from D'Estrées increased opposition to the war, and Parliament was reluctant to approve funds for essential repairs. For the rest of the year, this restricted English naval operations to a failed attack on the Dutch East India Company Return Fleet.
However, this did not offset the damage caused by Dutch defeats on land, and it was impossible to hide the gravity of the crisis. A stream of venomous Orangist pamphlets accused the De Witt brothers in particular and the Regent regime in general of betraying the country to the French. There was widespread rioting, with Orangists seizing control of city councils and demanding William take over government. On 22 June, Johan de Witt was badly wounded in an assassination attempt; one of the attackers, Jacob van der Graaf, was quickly arrested, tried and executed, increasing popular anger with the De Witts.
Negotiations
The Dutch were helped by the incompatibility of French and English objectives, while initial success meant Louis over-estimated the strength of his position. French expansion in the Spanish Netherlands was primarily intended to grow their economy at the expense of the Dutch, but undermined English trade and security as well. If Louis also gained control of Holland, the financial and commercial centre of Europe, the potential increase in French influence threatened every other European state. On 14 June, the States of Holland opened negotiations, offering Louis the right to occupy key fortresses in the south, plus an indemnity of ten million guilders. He responded with additional demands including religious freedom for Catholics, or French sovereignty over Utrecht andGuelders
The Duchy of Guelders ( nl, Gelre, french: Gueldre, german: Geldern) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in pr ...
. Both sides were using talks as a delaying tactic, assuming their position would improve; Louis knew the envoys were not authorised to negotiate on religion or the territorial integrity of the provinces and would have to request further instructions. The English were to be ceded Delfzijl, in Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
, already besieged by Münster.
Depicting Charles as the one man who could save them from the French, Orangist pressure led to William's appointment as stadtholder of Holland on 4 July. Hoping for a quick win, Charles sent Arlington and Buckingham
Buckingham ( ) is a market town in north Buckinghamshire, England, close to the borders of Northamptonshire and Oxfordshire, which had a population of 12,890 at the 2011 Census. The town lies approximately west of Central Milton Keynes, sou ...
to Brill, accompanied by Orangist exiles who had fled the Republic after their failed coup in 1666. They arrived at William's headquarters in Nieuwerbrug on 5 July, cheered by crowds who believed they brought promises of English support. The mood quickly changed when their terms were made public. France and Münster were to retain their conquests and William would be appointed Sovereign Prince of Holland, in return for which he would pay England ten million guilders, £10,000 per annum for North Sea herring rights, and allow English garrisons to occupy Brill, Sluys
Sluis (; zea, label=Zeelandic, Sluus ; french: Écluse) is a town and municipality located in the west of Zeelandic Flanders, in the south-western Dutch province of Zeeland.
The current incarnation of the municipality has existed since 1 January ...
and Vlissingen.
 William rejected the offer, since it gave the Dutch nothing they did not already hold. Arlington and Buckingham then met with Louis and agreed the Heeswijk Accord on 16 July. This set out a list of shared demands and undertook not to conclude a separate peace, but neither side placed any reliance on it. Leopold's envoy in the Hague, Francois-Paul de Lisola, gave the States-General assurances of Imperial support and arranged for Spanish troops to hold the Dutch fortress cities of
William rejected the offer, since it gave the Dutch nothing they did not already hold. Arlington and Buckingham then met with Louis and agreed the Heeswijk Accord on 16 July. This set out a list of shared demands and undertook not to conclude a separate peace, but neither side placed any reliance on it. Leopold's envoy in the Hague, Francois-Paul de Lisola, gave the States-General assurances of Imperial support and arranged for Spanish troops to hold the Dutch fortress cities of 's-Hertogenbosch
s-Hertogenbosch (), colloquially known as Den Bosch (), is a city and municipality in the Netherlands with a population of 157,486. It is the capital of the province of North Brabant and its fourth largest by population. The city is south of th ...
and Breda
Breda () is a city and municipality in the southern part of the Netherlands, located in the province of North Brabant. The name derived from ''brede Aa'' ('wide Aa' or 'broad Aa') and refers to the confluence of the rivers Mark and Aa. Breda has ...
, releasing their garrisons for the field army.
A second letter from Charles on 18 July urged William to accept his terms, claiming the De Witts were the only obstacle to peace. He responded by offering fishing rights, £400,000, Sluys and Surinam Surinam may refer to:
* Surinam (Dutch colony) (1667–1954), Dutch plantation colony in Guiana, South America
* Surinam (English colony) (1650–1667), English short-lived colony in South America
* Surinam, alternative spelling for Suriname
...
, in return for recognition as Prince of Holland and England agreeing a separate peace. Based on the Heeswijk Accord, Louis demanded the Dutch cede their naval base at Hellevoetsluis to England, a demand he knew was unacceptable. After the terms were rejected on 20 July, Arlington and Buckingham returned to London.
Johan de Witt had resigned as Grand Pensionary in June, while Cornelis was arrested for allegedly plotting to murder William. On 15 August, Charles' letter blaming the De Witts was published in Holland; motives are still debated but the effect was to inflame tensions and the two brothers were lynched by an Orangist civil militia on 20th. The Orangist Gaspar Fagel became Grand Pensionary and on 27 August the States of Holland passed legislation that removed their political opponents from local office and thus secured William's political position.
Dutch recovery: July to December
On 7 July, the inundations were fully set; their effectiveness would be reduced when the waters froze in winter but for now, Holland was secure from French advance. This gave the States time to enact the military reforms approved on 16 July, while they were boosted by the return of 20,000 prisoners ransomed from the French. In addition to unofficial Spanish support, on 25 July Leopold promised to invade the Rhineland and Alsace with 16,000 troops, along with the 20,000 promised by Frederick William in May. This forced Louis to divert 40,000 men to meet this threat, with nearly 50,000 tied up in garrisons around the Republic. English hopes of a quick victory vanished after Solebay, while the removal of the De Witts secured William's position and ended his dependence on Charles. The Münster army disintegrated due to lack of supplies and on 27 August, von Galen abandoned the siege of Groningen; the besiegers lost over 11,000 men, including 6,000 deserters, many of whom joined the Dutch. William led attacks on Woerden and Charleroi, which were over-ambitious and unsuccessful but restored Dutch morale, while Coevorden was recaptured on 31 December. Although their position remained precarious, by the end of 1672 the Dutch had regained much of the territory lost in May and Louis found himself involved in a wider European war of attrition. Despite his French subsidies, Charles had run out of money and faced considerable domestic opposition to continuing the war. This increased when the Dutch Cape Colony dispatched an expeditionary force to the English-held island ofSaint Helena
Saint Helena () is a British overseas territory located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote volcanic tropical island west of the coast of south-western Africa, and east of Rio de Janeiro in South America. It is one of three constitu ...
, and took possession on behalf of the Dutch East India Company.
1673
Overview
After the French failed to breach the Holland Water Line, the Anglo-French fleet was tasked with defeating the Dutch navy, allowing them to blockade the Dutch coast and threaten the Republic with starvation, or land an invasion force. However, poor co-ordination meant they failed to exploit their numerical advantage, and De Ruyter was able to prevent his fleet being overwhelmed. Although the Battle of Texel on 21 August was inconclusive, it was a strategic Dutch victory as the damage inflicted on the English fleet forced them to return home for repairs. Never popular to begin with, English support for the war dissolved along with hopes for a quick victory. In late 1673, the French withdrew from the Republic, and focused on conquering the Spanish Netherlands, a frightening prospect for most English politicians. Combined with a Dutch pamphlet campaign claiming Charles had agreed to restore Catholicism, Parliament refused to fund the war, while the level of opposition made Charles fear for his own position. In February 1674, theSecond Peace of Westminster
The Treaty of Westminster of 1674 was the peace treaty that ended the Third Anglo-Dutch War. Signed by the Dutch Republic and the Kingdom of England, the treaty provided for the return of the colony of New Netherland (now New York) to England an ...
ended the war; it was greeted with popular enthusiasm in both countries, not least by commercial interests in Amsterdam and London, and the treaty was ratified with exceptional speed.
Naval battles
 In the first two wars, both navies, particularly the Dutch, employed aggressive tactics that often resulted in heavy ship losses for the defeated side. In the Third Anglo-Dutch War, the priority was to minimise losses, and it was common for fleets to engage using the ' line-ahead' formation, an essentially defensive approach; despite inflicting considerable damage, neither side lost any ships at the Texel.
When the Water Line froze during the winter of 1673, the French were unable to break it, thwarted by thin ice and companies of Dutch sailors equipped with ice skates, under Johan de Liefde. Attempts in the spring to drain the northern part of the line or cross on rafts also proved unsuccessful. With an eastern approach impractical, the Royal Navy was ordered to blockade the coast in co-operation with a French squadron; if possible, they were to land an invasion force, although how this would be accomplished was unclear. Lacking experience of amphibious operations, this meant capturing a Dutch port, despite limited knowledge of the dangerous
In the first two wars, both navies, particularly the Dutch, employed aggressive tactics that often resulted in heavy ship losses for the defeated side. In the Third Anglo-Dutch War, the priority was to minimise losses, and it was common for fleets to engage using the ' line-ahead' formation, an essentially defensive approach; despite inflicting considerable damage, neither side lost any ships at the Texel.
When the Water Line froze during the winter of 1673, the French were unable to break it, thwarted by thin ice and companies of Dutch sailors equipped with ice skates, under Johan de Liefde. Attempts in the spring to drain the northern part of the line or cross on rafts also proved unsuccessful. With an eastern approach impractical, the Royal Navy was ordered to blockade the coast in co-operation with a French squadron; if possible, they were to land an invasion force, although how this would be accomplished was unclear. Lacking experience of amphibious operations, this meant capturing a Dutch port, despite limited knowledge of the dangerous shoals
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. It o ...
protecting their approaches.
 Hoping to unnerve the Dutch, Prince Rupert leaked information claiming his fleet was accompanied by ships carrying an invasion force; in reality, it remained in
Hoping to unnerve the Dutch, Prince Rupert leaked information claiming his fleet was accompanied by ships carrying an invasion force; in reality, it remained in Great Yarmouth
Great Yarmouth (), often called Yarmouth, is a seaside town and unparished area in, and the main administrative centre of, the Borough of Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, England; it straddles the River Yare and is located east of Norwich. A pop ...
, and was in any case insufficient for the task. In May, the English fleet of 81 ships approached the Dutch coast, while De Ruyter's 55 ships took up a defensive position in the Schooneveld
The Schooneveld is a shallow basin at the mouth of the Scheldt river, near the island of Walcheren, off the coast of the Netherlands. It runs parallel to the continental coast, narrowing from the southwest to the northeast, bounded by the irregula ...
. Early on 7 June, Prince Rupert detached a light squadron, hoping to tempt De Ruyter into battle where the Allies could use their superior numbers. The alternative was forcing the Dutch fleet into Hellevoetsluis, where they could be blockaded while transports brought troops over to assault Den Briel or Vlissingen.
However, De Ruyter's speed of response allowed him to attack before the main Allied fleet was ready, launching the First Battle of the Schooneveld. At Solebay the previous year, the French squadron had sailed in the opposite direction to that of the English; to counter accusations this had been deliberate, they now formed the centre squadron. However, their inexperience and poor positioning left gaps which allowed De Ruyter to sail through the Allied centre.
The French commanders had been ordered by Louis not to risk their ships, but focus on learning from the English and Dutch. They therefore disengaged, later writing enthusiastic reports about the tactical genius of the manoeuvre used by De Ruyter. Their defection threatened to cut off the Allied rear under Sir Edward Spragge
Sir Edward Spragge (name also written as Spragg or Sprague) (circa 1620 – 21 August 1673) was an Irish-born English admiral of the Royal Navy. He was a fiery, brilliantly accomplished seaman who fought in many great actions after the restoration ...
; he took his own squadron to attack Tromp, who was also being engaged by Rupert, but fear of running aground meant this was not done with any conviction. Now split into four parts and in considerable confusion, the Allies withdrew after nine hours of fighting; they were not pursued, since De Ruyter decided not to take any unnecessary risks.
 The Allies continued to hold their position off the Dutch coast; on 14 June, De Ruyter took advantage of favourable winds and launched the Second Battle of the Schooneveld. Once again, this caused chaos in the unprepared Allied fleet, which suffered severe damage and returned to the Thames for repairs. In late July, Rupert put to sea again, hoping to draw the Dutch north by feinting against The Hague or
The Allies continued to hold their position off the Dutch coast; on 14 June, De Ruyter took advantage of favourable winds and launched the Second Battle of the Schooneveld. Once again, this caused chaos in the unprepared Allied fleet, which suffered severe damage and returned to the Thames for repairs. In late July, Rupert put to sea again, hoping to draw the Dutch north by feinting against The Hague or Den Helder
Den Helder () is a municipality and a city in the Netherlands, in the province of North Holland. Den Helder occupies the northernmost point of the North Holland peninsula. It is home to the country's main naval base.
From here the Royal TESO fe ...
; although De Ruyter preferred to remain where he was, he was ordered out to escort a valuable incoming Dutch East India Company treasure fleet. While both sides suffered severe damage in the resulting Battle of Texel, Prince Rupert was forced to return home for repairs.
The conduct of the French led to widespread recriminations and accusations they had failed to support their English colleagues. Whether this was fair remains a matter of dispute; in all three battles, De Ruyter took advantage of Allied deficiencies in fighting instructions and signalling. Regardless, it deepened suspicions between the English and French, further undercutting popular support for the war, while ending any hopes of starving the Dutch through a naval blockade. The result was an overwhelming strategic victory for the Dutch. even though four ships of the Spice Fleet had fallen into Allied hands. For De Ruyter, the successful campaign, by repelling attacks by much superior fleets to save his homeland, had been the highlight of his career, as the English readily acknowledged: the Duke of York
Duke of York is a title of nobility in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of English (later British) monarchs. The equivalent title in the Scottish peerage was D ...
concluded that among admirals, "he was the greatest that ever to that time was in the world". The English had to abandon their plans for an invasion from the sea, and the large costs of repair troubled Parliament.
Anti-war sentiment in England
 In previous conflicts, investing in privateers had been very profitable for the English, but from 1672 to 1673 Dutch raiders captured over 2,800 French and English ships, far more than their counterparts, The province of Zealand alone operated 120 privateers. Having failed to blockade the Dutch coast, English merchants were excluded from the vital Baltic trade in shipbuilding materials, while the loss of
In previous conflicts, investing in privateers had been very profitable for the English, but from 1672 to 1673 Dutch raiders captured over 2,800 French and English ships, far more than their counterparts, The province of Zealand alone operated 120 privateers. Having failed to blockade the Dutch coast, English merchants were excluded from the vital Baltic trade in shipbuilding materials, while the loss of New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
and Dutch attacks on English possessions in India caused further damage to their trade. These material losses compounded a moral unease about the justifiability of the war; after Solebay, John Evelyn wrote: "the loss of my Lord Sandwich redoubled the loss to me, as well the folly of hazarding so brave a fleet, and losing so many good men, for no provocation in the world but because the Hollander exceeded us in industry, and all things else but envy."
The effect was to increase English disillusionment with the war, while stabilising their military position restored Dutch credit, allowing the Estates to expand the military budget to a hundred million guilders, three times annual tax revenues. Louis had attacked the Republic hoping for a quick victory; once this failed, he faced a war of attrition on multiple fronts. In July 1673, French troops captured Maastricht; on 30 August, the Dutch agreed the Alliance of the Hague with Leopold and Spain. In October, they were joined by Charles IV, Duke of Lorraine, whose duchy was occupied by France, forming the Quadruple Alliance.
William made sure the peace negotiations held in Cologne with France and England failed. In September, he recaptured Naarden, Münster and Cologne made peace, and French troops withdrew from the Dutch Republic, retaining only Grave and Maastricht. With a French victory over the Dutch now unlikely, the war became one for control of Flanders, an issue that divided England and France. This was an important factor in English opposition to the French alliance, but internal events were even more significant.
 In early 1673, Arlington's former secretary Peter du Moulin fled to the Republic, where he started a propaganda campaign backed by the world's largest per capita printing capacity. England was soon flooded with tens of thousands of pamphlets accusing Charles of conspiring with Louis to make the country Catholic again. Many were convinced of its truth, particularly when Charles gave permission for his brother and heir James to marry
In early 1673, Arlington's former secretary Peter du Moulin fled to the Republic, where he started a propaganda campaign backed by the world's largest per capita printing capacity. England was soon flooded with tens of thousands of pamphlets accusing Charles of conspiring with Louis to make the country Catholic again. Many were convinced of its truth, particularly when Charles gave permission for his brother and heir James to marry Mary of Modena
Mary of Modena ( it, Maria Beatrice Eleonora Anna Margherita Isabella d'Este; ) was Queen of England, Scotland and Ireland as the second wife of James II and VII. A devout Roman Catholic, Mary married the widower James, who was then the young ...
, a devout Catholic. In February 1673, Parliament refused to approve further taxes unless Charles withdrew his proposed Indulgence and accepted a Test Act barring Catholics from public office. In June 1673, James resigned as Lord High Admiral, which was seen as confirmation of rumours he had secretly become a Catholic and could not comply with the Test Act. As Charles had no legitimate offspring, James' marriage now presented the strong prospect of a Catholic dynasty ruling England in the future.
Buckingham, who learned of the secret provisions of the Treaty of Dover the previous year, reacted to the changed public mood by leaking them to other politicians, including Arlington. As a result, the Cabal Ministry joined those advocating peace with the Dutch; shocked by the revelation of Charles' agreement with Louis, Lord Shaftesbury began to consider removing the House of Stuart entirely. With his backing, John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 – 28 October 1704) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers and commonly known as the "father of liberalism ...
developed the legal concepts that appeared in his work the Two Treatises of Government, a general denunciation of absolute monarchy.
Second Peace of Westminster
In this situation Charles felt that continuing the alliance was a grave threat to his personal position and that Parliament would no longer fund a war. He informed the French ambassadorColbert de Croissy
Charles Colbert, marquis de Croissy (1625 – July 28, 1696) was a French statesman and diplomat.
Biography
Colbert was born in Reims. Like his elder brother Jean-Baptiste Colbert, he began his career in the office of the minister of war Le Tel ...
that to his regret, he had to terminate the English war effort. He told the Dutch via the Spanish consul in London, the Marquess del Fresno, that, his main war aim to install his noble nephew as stadtholder having been attained, he no longer objected to concluding a lasting peace between the two Protestant brother nations, if only some minor "indemnities" could be paid. At first the States of Holland were disinclined to grant Charles's demands: as England had accomplished nothing in the war, it was, in their opinion, not entitled to any reward. But William convinced them that there was some chance of bringing Charles into the war ''against'' France eventually. Furthermore, Spain had not yet declared war on France and was willing to do so only if England made peace, because it feared English attacks on its American colonies.
After a short exchange of proposals by means of trumpeters, the Treaty of Westminster was publicly proclaimed in London on 17 February Old Style. It was approved by the States of Holland and West Frisia on 4 March (New Style), and ratified by the States General on 5 March.
The treaty stipulated that New York—formerly New Netherland—would henceforth be an English possession and that Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
, captured by the Dutch in 1667, would remain their colony, confirming the status quo of 1667. An "indemnity" of two million guilders was to be paid by the Dutch. Eventually, William would force Charles to set off these indemnities against the debts he owed to the House of Orange, so the English king actually received very little.
Despite the peace, Monmouth's brigade would not be withdrawn from the French army and it would be allowed to recruit in Britain until the end of the Franco-Dutch War. In April that year, William attempted to convince his uncle to enter the war against Louis but failed. Until the end of the War of Holland in 1678, Charles tried to negotiate between the two parties, at times pretending to consider a conflict with France, when such pretence was beneficial to him. In 1677, he forced his niece Mary to marry William; this would later prove to be a fundamental cause of the fall of his brother in 1688.
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Anglo-Dutch War, 3rd Anglo-Dutch Wars Conflicts in 1672 Conflicts in 1673 Conflicts in 1674 Dutch Republic–England relations Wars involving the Dutch Republic