Philippines administrative divisions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Philippines is divided into four levels of administrative divisions with the lower three being defined in the Local Government Code of 1991 as local government units (LGUs). They are, from the highest to the lowest:
# Regions ( fil, rehiyon), mostly used to organize national services. Of the 17 regions, only one – the

 The Philippines is broadly divided into three traditional island groups: Luzon, the Visayas, and Mindanao. The
The Philippines is broadly divided into three traditional island groups: Luzon, the Visayas, and Mindanao. The
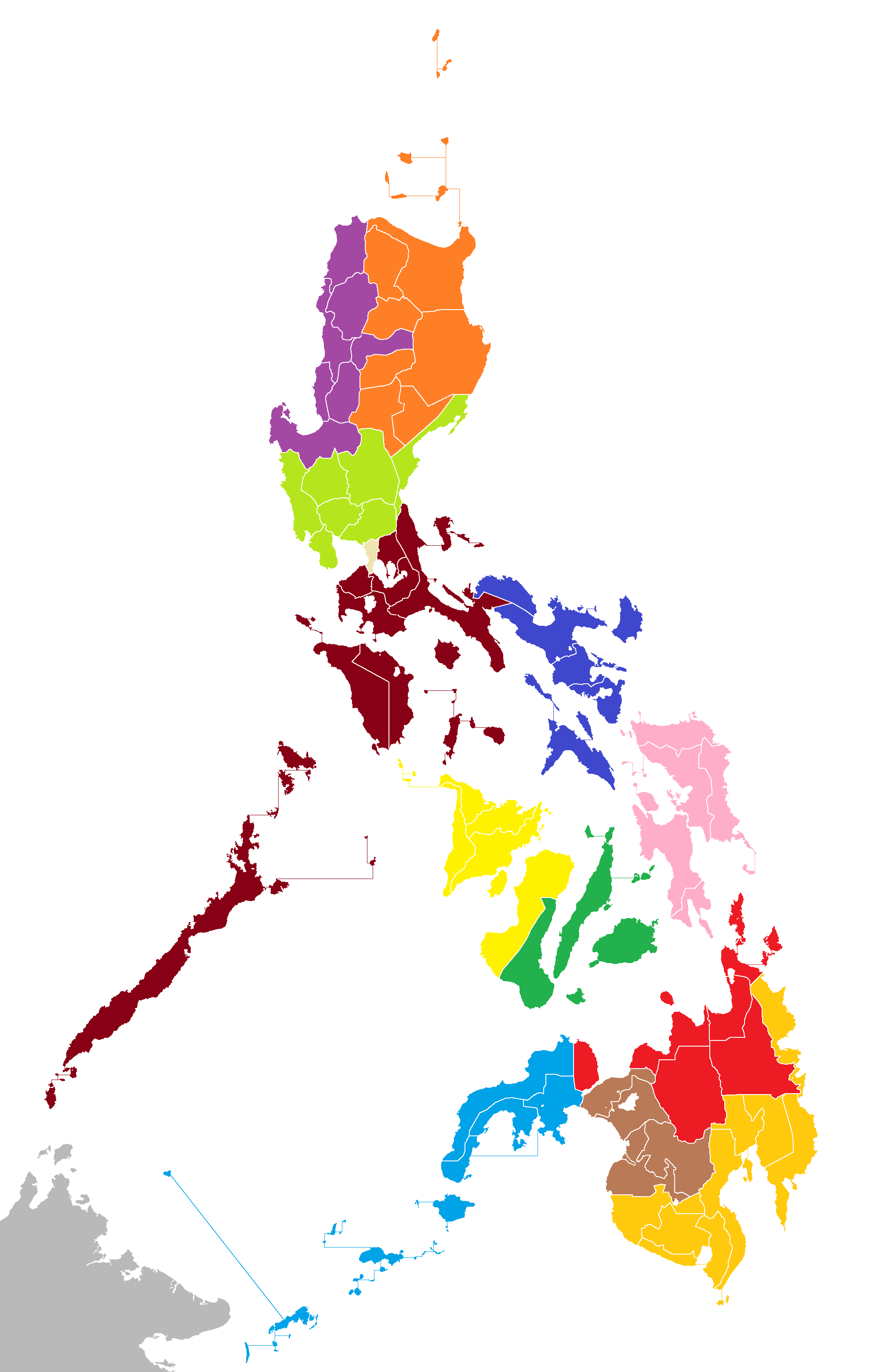 The Philippines is divided into thirteen ''judicial regions'', to organize the judiciary. The judicial regions still reflect the original regional configuration introduced by President
The Philippines is divided into thirteen ''judicial regions'', to organize the judiciary. The judicial regions still reflect the original regional configuration introduced by President
 The electoral constituencies for the election of territory-based members of the House of Representatives of the Philippines are more precisely ''representative'' or ''congressional districts''. Each province is guaranteed at least one seat, and more populous provinces are also provided more. Many cities that have a population of at least 250,000 inhabitants are also granted one or more seats.
If a province or a city is composed of only one legislative district, it said to be the ''lone district'' (e.g., the " Lone District of Guimaras"). Multiple districts within more populous cities and provinces are given numerical designations (e.g., the "2nd District of Cagayan").
The electoral constituencies for the election of territory-based members of the House of Representatives of the Philippines are more precisely ''representative'' or ''congressional districts''. Each province is guaranteed at least one seat, and more populous provinces are also provided more. Many cities that have a population of at least 250,000 inhabitants are also granted one or more seats.
If a province or a city is composed of only one legislative district, it said to be the ''lone district'' (e.g., the " Lone District of Guimaras"). Multiple districts within more populous cities and provinces are given numerical designations (e.g., the "2nd District of Cagayan").
The Local Government Code of the Philippines
{{Asia topic, Administrative divisions of Philippines pt:Divisões administrativas das Filipinas
Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao
ar, منطقة بانجسامورو ذاتية الحكم فى مسلمى مينداناو
, native_name =
, settlement_type = Autonomous regions of the Philippines, Autonomous region
, anthem = Bangsa ...
– has an elected government to which the central government has devolved competencies.
# Provinces ( fil, lalawigan or probinsya), independent cities
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity (such as a province).
Historical precursors
In the Holy Roman Empire, and to a degree in its successor states ...
( fil, lungsod or siyudad), and one independent municipality (Pateros
Pateros, officially the Municipality of Pateros ( tgl, Bayan ng Pateros), is the lone municipality of Metro Manila, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,643 people.
This municipality is famous for its duck-rai ...
).
# Component cities ( fil, lungsod or siyudad) and municipalities ( fil, bayan or munisipalidad) within a province.
# Barangays (formerly known, and sometimes still referred to as, ''barrios'') within a city or municipality.
Other divisions also exist for specific purposes:
* Geographic island groups in popular and widespread use;
* Local administrative districts in use by some local governments;
* Judicial regions for regional trial courts;
* Legislative districts
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other poli ...
for the election of legislators at national, regional, and local levels;
* A special geographic area
The Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) of the Philippines has a special geographic area (SGA) in the province of Cotabato, a province which is part of the Soccsksargen region. This area consists of 63 barangays in six munici ...
used for the organization of Bangsamoro barangays in Cotabato; and
* Special-purpose districts for various government agencies.
Administrative divisions
Regions
Administrative regions
''Administrative regions'' are groupings of geographically adjacent LGUs which are established, disestablished and modified by the President of the Philippines based on the need to more coherently make economic development policies and coordinate the provision of national government services within a larger area beyond the province level. No plebiscites have been conducted so far to democratically confirm the creation, abolition or alteration of the boundaries of regular administrative regions, as the Constitution does not mandate it. An administrative region is not a local government unit (LGU), but rather a group of LGUs to which the president has provided an unelected policy-making and coordinating structure, called the Regional Development Council (RDC). Metro Manila is recognized in law as a "special development and administrative region," and was thus given a metropolitan authority; the Metro Manila Council within the MMDA serves as the National Capital Region's RDC. Administrative regions are composed of provinces and/or independent cities, or, in the case ofPateros
Pateros, officially the Municipality of Pateros ( tgl, Bayan ng Pateros), is the lone municipality of Metro Manila, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,643 people.
This municipality is famous for its duck-rai ...
, an independent municipality. The Philippine Statistics Authority further divides the LGUs of Metro Manila into four numbered geographic districts for statistical purposes.
Autonomous regions
The 1987 Constitution allows for the creation of '' autonomous regions'' in theCordillera Central Central Cordillera refers to the New Guinea Highlands.
Cordillera Central, meaning ''central range'' in Spanish, may refer to the following mountain ranges:
* Cordillera Central, Andes (disambiguation), several mountain ranges in South America
** ...
of Luzon and in the Muslim-majority
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
areas of Mindanao. However, only the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao
ar, منطقة بانجسامورو ذاتية الحكم فى مسلمى مينداناو
, native_name =
, settlement_type = Autonomous regions of the Philippines, Autonomous region
, anthem = Bangsa ...
and its predecessor, the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, have been approved by voters in plebiscites held in 1989, 2001
The September 11 attacks against the United States by Al-Qaeda, which Casualties of the September 11 attacks, killed 2,977 people and instigated the global war on terror, were a defining event of 2001. The United States led a Participants in ...
and 2019
File:2019 collage v1.png, From top left, clockwise: Hong Kong protests turn to widespread riots and civil disobedience; House of Representatives votes to adopt articles of impeachment against Donald Trump; CRISPR gene editing first used to experim ...
. Voters in the Cordilleras rejected autonomy in 1990 and 1998
1998 was designated as the ''International Year of the Ocean''.
Events January
* January 6 – The '' Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon, and later finds evidence for frozen water, in soil in permanently ...
; hence the Cordillera Administrative Region remains as a regular administrative region with no delegated powers or responsibilities.
The sole autonomous region at present, the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao
ar, منطقة بانجسامورو ذاتية الحكم فى مسلمى مينداناو
, native_name =
, settlement_type = Autonomous regions of the Philippines, Autonomous region
, anthem = Bangsa ...
, comprises local government units that have consented by plebiscite to be placed under the authority of the Bangsamoro Regional Government. An autonomous region, while possessing a government, is not a local government unit (LGU) ''per se'', as the autonomous regional government's organization and structure is not defined by the Local Government Code of 1991, unlike provinces, cities, municipalities and barangays. Rather, an autonomous region is a group of LGUs to which Congress has provided via statute a very specific form of regional governance structure, along with certain powers and responsibilities.
Local government units
In the Local Government Code of 1991, a ''local government unit'' (LGU) can take the form of a province, a city, a municipality, or a barangay. All LGUs have local legislatures (''Sanggunian'') and local chief executives (governor, mayor, or barangay captain) that are elected by popular vote. Per the Local Government Code of 1991, section 25, the President of the Philippines exercises direct supervisory authority over provinces and independent cities (i.e., highly urbanized and independent component cities); thus, LGUs that belong to these categories form the primary level of LGUs in the Philippines.Pateros
Pateros, officially the Municipality of Pateros ( tgl, Bayan ng Pateros), is the lone municipality of Metro Manila, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,643 people.
This municipality is famous for its duck-rai ...
, by virtue of not belonging to any province, effectively also constitutes a primary level LGU.
Provinces
A ''province'' is composed of component cities and municipalities, over which it exercises supervisory authority. Each province is headed by a governor. Its legislative body is theSangguniang Panlalawigan
Sangguniang Panlalawigan (abbreviated as SP; ), commonly known as the Provincial Board, are the legislatures in Philippine provinces. They are the legislative branches of the provinces, and their powers and responsibilities are defined by the Loca ...
.
Cities and municipalities
Three different legal classes of cities exist in the Philippines.Independent cities
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity (such as a province).
Historical precursors
In the Holy Roman Empire, and to a degree in its successor states ...
, of which there are currently 38 – classified either as ''highly urbanized'' (33) or ''independent component'' (5) cities – are cities which are not under the jurisdiction of any province. Thus, these cities are autonomously governed, do not share their tax revenues with any province, and in most cases, their residents are not eligible to elect or be elected to provincial offices. Cities that are under the political jurisdiction of a province form the third legal class of cities, called ''component'' cities. The voters in these cities are allowed to vote and run for positions in the provincial government.
''Municipalities'' are always under the jurisdiction of a province, except for Pateros
Pateros, officially the Municipality of Pateros ( tgl, Bayan ng Pateros), is the lone municipality of Metro Manila, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,643 people.
This municipality is famous for its duck-rai ...
, which is self-governing.
A city or municipality is divided into barangays, over which it exercises supervisory authority. A city or municipality is headed by a mayor. The Sangguniang Panlungsod
The Sangguniang Panlungsod (SP) is the local legislative body of a city governments in the Philippines. The name of the legislative body comes from the Tagalog words "''sanggunian''" ("council") – ultimately from the rootword "''sangguni''" ...
is the legislative body for cities and Sangguniang Bayan for municipalities.
Barangays
The ''barangay'' is the smallest local government unit in the Philippines. Although "barangay" is sometimes translated into English as "village," a barangay can be: * an urban neighborhood, such as a city block or a gated community (e.g.,Forbes Park, Makati
Forbes Park is a private subdivision, gated community, and barangay in Makati, Metro Manila, Philippines. Established in 1949, Forbes Park was named after William Cameron Forbes, the fifth American Governor-General of the Philippines during the ...
);
* a sizable urban district (e.g., Payatas, Quezon City);
* a single hamlet or village (e.g., Pag-asa, Kalayaan, Palawan);
* a small town (e.g., Mangagoy, Bislig, Surigao del Sur); or
* a rural district composed of disperse settlements (e.g., Nagacadan, Kiangan, Ifugao).
Each barangay is headed by a Barangay Captain. Its local legislative body is the Sangguniang Barangay.
Other divisions
Island groups
 The Philippines is broadly divided into three traditional island groups: Luzon, the Visayas, and Mindanao. The
The Philippines is broadly divided into three traditional island groups: Luzon, the Visayas, and Mindanao. The Philippine flag
The national flag of the Philippines ( tgl, Pambansang watawat ng Pilipinas; ilo, Nailian a bandera ti Filipinas; ceb, Nasudnong bandila ng Pilipinas; es, Bandera Nacional de Filipinas) is a horizontal List of flags by design#Bicolour, bicol ...
's three stars are often taken to represent each of these geographical groupings. These island groups, however, have no specific administrative bodies, either elected or appointed, although many agencies and institutions, both government and private, use island groupings for certain purposes. For example, the Palarong Pambansa rotates yearly hosting duties among the island groups, while the League of Municipalities of the Philippines
The League of Municipalities of the Philippines - or more simply the League of Municipalities or LMP - is a formal organization of all the municipalities in the Philippines. Presently, sixty eight municipalities are part of this organization.
Stat ...
organizes its members and meetings by Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao "clusters."
Local administrative districts
Some LGUs use geographic divisions that are solely used for administrative purposes.Geographic districts and zones
Certain cities officially organize their constituent barangays into geographic districts: * Baguio: 20 (Districts 1–20) *Calbayog
Calbayog, officially the City of Calbayog ( war, Siyudad han Calbayog; fil, Lungsod ng Calbayog), is a 1st class component city in the province of Samar, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 186,960 people.
It lies ...
: 3 (Calbayog
Calbayog, officially the City of Calbayog ( war, Siyudad han Calbayog; fil, Lungsod ng Calbayog), is a 1st class component city in the province of Samar, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 186,960 people.
It lies ...
, Oquendo Oquendo or de Oquendo is a surname of Basque originhttps://www.ancestry.com/name-origin?surname=oquendo and is a Hispanicization, Castilianized variant of "Okendo". Notable people with the surname include:
*Angel Oquendo, Puerto Rican actor
*Anto ...
, Tinambac)
* Davao City: 11 (Agdao, Baguio, Buhangin, Bunawan, Calinan, Marilog, Paquibato, Poblacion, Talomo, Toril, Tugbok)
* Iloilo City: 7 ( Arevalo, City Proper, Jaro, La Paz
La Paz (), officially known as Nuestra Señora de La Paz (Spanish pronunciation: ), is the seat of government of the Bolivia, Plurinational State of Bolivia. With an estimated 816,044 residents as of 2020, La Paz is the List of Bolivian cities ...
, Lapuz, Mandurriao
Mandurriao () is one of the seven districts of Iloilo City, in the province of Iloilo, on the island of Panay, in the Western Visayas region, in the Philippines. It is the second-largest district by land area as well as the third-most populous di ...
, Molo)
* Manila: 16 (Binondo
Binondo () is a district in Manila and is referred to as the city's Chinatown. Its influence extends beyond to the places of Quiapo, Santa Cruz, San Nicolas and Tondo. It is the oldest Chinatown in the world, established in 1594 by the ...
, Ermita, Intramuros, Malate, Paco, Pandacan, Port Area, Quiapo, Sampaloc, San Andres, San Miguel, San Nicolas, Santa Ana, Santa Cruz, Santa Mesa, Tondo)
* Samal: 3 (Babak, Kaputian, Peñaplata)
* Sorsogon City
Sorsogon City, officially the City of Sorsogon (Southern Sorsogon language, Waray Sorsogon: ''Syudad san Sorsogon''; bcl, Siyudad nin Sorsogon; fil, Lungsod ng Sorsogon), is a 3rd class Cities of the Philippines#Legal classification, component ...
: 2 (Bacon
Bacon is a type of salt-cured pork made from various cuts, typically the belly or less fatty parts of the back. It is eaten as a side dish (particularly in breakfasts), used as a central ingredient (e.g., the bacon, lettuce, and tomato sand ...
, Sorsogon)
* Zamboanga City: 13 (Ayala, Baliwasan, Curuan, Islands, Labuan, Manicahan, Mercedes, Putik, Santa Barbara, Santa Maria, Tetuan, Vitali, Zamboanga Central)
Three cities also officially organize their barangays into numbered zones: Caloocan (Zones 1–16), Manila (Zones 1–100), and Pasay (Zones 1–20). The 100 zones in Manila serve as an administrative layer immediately below the geographic district level.
Many barangay names contain the words "district" (170 barangays) or "zone" (264 barangays), but they are fully functioning barangays and are not just mere administrative categories.
Sitios and puroks
Many barangays are divided into ''sitio
A ''sitio'' (Spanish for "site") in the Philippines is a territorial enclave that forms part of a barangay. Typically rural, a ''sitios location is usually far from the center of the barangay itself and could be its own barangay if its popul ...
s'' and ''purok
A ''purok'' ( en, district or zone) is a division within a barangay in the Philippines. While not officially considered a local government unit (LGU), a purok often serves as a unit for delivering services and administration within a barangay ...
s''. Sitios are usually hamlets within rural barangays where human settlement is polycentric
Polycentric is an English adjective, meaning "having more than one center," derived from the Greek words ''polús'' ("many") and ''kentrikós'' ("center"). Polycentricism (or polycentricity) is the abstract noun formed from polycentric. They may r ...
, i.e., multiple communities spread across a wide area, separated by farmland, mountains, or water. Puroks are often neighborhoods or zones in densely populated areas of barangays of more urban character. Purok and sitio boundaries are rarely defined precisely and may use natural landmarks such as roads, rivers or other natural features to unofficially delineate divisions. A single sitio or purok, or groups of these, form the basis of creating a new barangay.
Sitios and puroks are not local government units and therefore do not officially have an organized government subordinate to the barangay. However, there are sometimes unofficial arrangements that result in direct representation of purok or sitio interests in the barangay government. For example, a barangay council
The Sangguniang Barangay, also known as the Barangay Council, and formerly as the Rural Council and then the Barrio Council, is the legislative body of a barangay, the lowest form of government in the Philippines. The term is coined from the Tag ...
member may be officially designated as a purok leader, while sitio leaders may be appointed and drawn from the hamlet's residents.
Judicial regions
Ferdinand Marcos
Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos Sr. ( , , ; September 11, 1917 – September 28, 1989) was a Filipino politician, lawyer, dictator, and kleptocrat who was the 10th president of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. He ruled under martial ...
during his rule, except for the transfer of Aurora to the third judicial region from the fourth. These judicial regions are used for the appointment of judges of the different Regional Trial Courts.
Legislative districts
To elect legislators at national, regional, and local levels, the Philippines is divided into ''legislative districts''.National
Regional
The electoral constituencies for the election of members of theBangsamoro Parliament
, legislature = 2nd BTA (Interim) Parliament
, linking_name =
, coa_pic = Bangsamoro_Parliament_Seal.png
, coa_res =
, session_room = File:BARMM lawmakers refile local governance code.jpg
, sessi ...
will be called ''parliamentary districts'', the Bangsamoro Transition Authority will decide the parliamentary districts for the first parliamentary elections, with the succeeding elections' districts being decided by the parliament.
The Bangsamoro Autonomous Region
ar, منطقة بانجسامورو ذاتية الحكم فى مسلمى مينداناو
, native_name =
, settlement_type = Autonomous region
, anthem = Bangsamoro Hymn
, image_skyline ...
's predecessor, the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (1990–2019), had a Regional Legislative Assembly (RLA) which elected three members from each of its eight ''assembly districts''. These assembly districts were coterminous with the existing congressional districts of the time, except that the assembly districts excluded territories that are not under the jurisdiction of the ARMM (i.e., Isabela City excluded from the assembly district of Basilan; Cotabato City excluded from the first assembly district of Maguindanao
Maguindanao (, Maguindanao language, Maguindanaon: ''Prubinsya nu Magindanaw''; Iranun language, Iranun'': Perobinsia a Magindanao''; tl, Lalawigan ng Maguindanao) was a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines located in the ...
). Before voting for inclusion into the ARMM in 2001, Marawi City
Marawi, officially the Islamic City of Marawi (Maranao: ''Inged a Marawi''; fil, Islamikong Lungsod ng Marawi), is a 4th class component city and capital of the province of Lanao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a po ...
was also excluded from the first assembly district of Lanao del Sur.
Local
The electoral constituencies for the election of territory-based members of theSangguniang Panlalawigan
Sangguniang Panlalawigan (abbreviated as SP; ), commonly known as the Provincial Board, are the legislatures in Philippine provinces. They are the legislative branches of the provinces, and their powers and responsibilities are defined by the Loca ...
of all 81 provinces, the Sangguniang Panlungsod
The Sangguniang Panlungsod (SP) is the local legislative body of a city governments in the Philippines. The name of the legislative body comes from the Tagalog words "''sanggunian''" ("council") – ultimately from the rootword "''sangguni''" ...
of 26 cities and the Sangguniang Bayan of Pateros
Pateros, officially the Municipality of Pateros ( tgl, Bayan ng Pateros), is the lone municipality of Metro Manila, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,643 people.
This municipality is famous for its duck-rai ...
, are more precisely ''sanggunian districts''.
* Sangguniang Panlalawigan districts: COMELEC divides provinces that comprise a lone congressional district into two SP districts. In provinces that are already divided into more than one congressional district, SP districts mostly follow the same boundaries, with the main exceptions being the exclusion of independent cities
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity (such as a province).
Historical precursors
In the Holy Roman Empire, and to a degree in its successor states ...
. SP districts in Bulacan and Laguna
Laguna (Italian and Spanish for lagoon) may refer to:
People
* Abe Laguna (born 1992), American DJ known as Ookay
* Andrés Laguna (1499–1559), Spanish physician, pharmacologist, and botanist
* Ana Laguna (born 1955), Spanish-Swedish ballet d ...
also include the cities of San Jose del Monte (Bulacan), and Biñan
Biñan (), officially the City of Biñan ( fil, Lungsod ng Biñan), is a 1st class Cities of the Philippines#Legal classification, component city in the Provinces of the Philippines, province of Laguna (province), Laguna, Philippines. According ...
, Calamba and Santa Rosa
Santa Rosa is the Italian, Portuguese and Spanish name for Saint Rose.
Santa Rosa may also refer to:
Places Argentina
*Santa Rosa, Mendoza, a city
* Santa Rosa, Tinogasta, Catamarca
* Santa Rosa, Valle Viejo, Catamarca
*Santa Rosa, La Pampa
* Sa ...
(Laguna) in their former congressional districts. Sangguniang Panlalawigan districts are sometimes called ''provincial board districts''.
* Sangguniang Panlungsod districts: The election of regular SP members in 26 cities is through territory-based districts that encompass only portions of each city. The SP district boundaries in 10 cities are coterminous with congressional district boundaries; the SP districts in Taguig also mostly follow the congressional district boundaries, except that Pateros
Pateros, officially the Municipality of Pateros ( tgl, Bayan ng Pateros), is the lone municipality of Metro Manila, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,643 people.
This municipality is famous for its duck-rai ...
is factored out. Two cities ( Manila and Quezon City) are divided into six SP districts; four ( Caloocan, Davao City, Samal and Sorsogon City
Sorsogon City, officially the City of Sorsogon (Southern Sorsogon language, Waray Sorsogon: ''Syudad san Sorsogon''; bcl, Siyudad nin Sorsogon; fil, Lungsod ng Sorsogon), is a 3rd class Cities of the Philippines#Legal classification, component ...
) into three SP districts; and the remaining 20 into two SP districts. Sangguniang Panlungsod districts are sometimes called ''councilor districts''.
* Sangguniang Bayan districts: Only the Metro Manila municipality of Pateros
Pateros, officially the Municipality of Pateros ( tgl, Bayan ng Pateros), is the lone municipality of Metro Manila, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,643 people.
This municipality is famous for its duck-rai ...
is divided into two SB districts for electing regular members to the Sangguniang Bayan. The Sangguniang Bayan districts of Pateros are sometimes called ''councilor districts''.
Special-purpose districts
The various executive departments has also divided the country into their respective districts. The Department of Public Works and Highways, Department of Education, and theBureau of Internal Revenue
The Bureau of Internal Revenue'' ''( fil, Kawanihan ng Rentas Internas, or BIR) is a revenue service for the Philippine government, which is responsible for collecting more than half of the total revenues of the government. It is an agency o ...
, for example, divide the country into "engineering," "school," and "revenue" districts, respectively.
Summary
The following table summarizes the number and structure of regions, provinces, cities, municipalities, and barangays in the Philippines as of March 31, 2020.See also
* Local government in the Philippines * Federalism in the PhilippinesReferences
External links
The Local Government Code of the Philippines
{{Asia topic, Administrative divisions of Philippines pt:Divisões administrativas das Filipinas