Australasia temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Australasia is a region that comprises
Australasia is a region that comprises
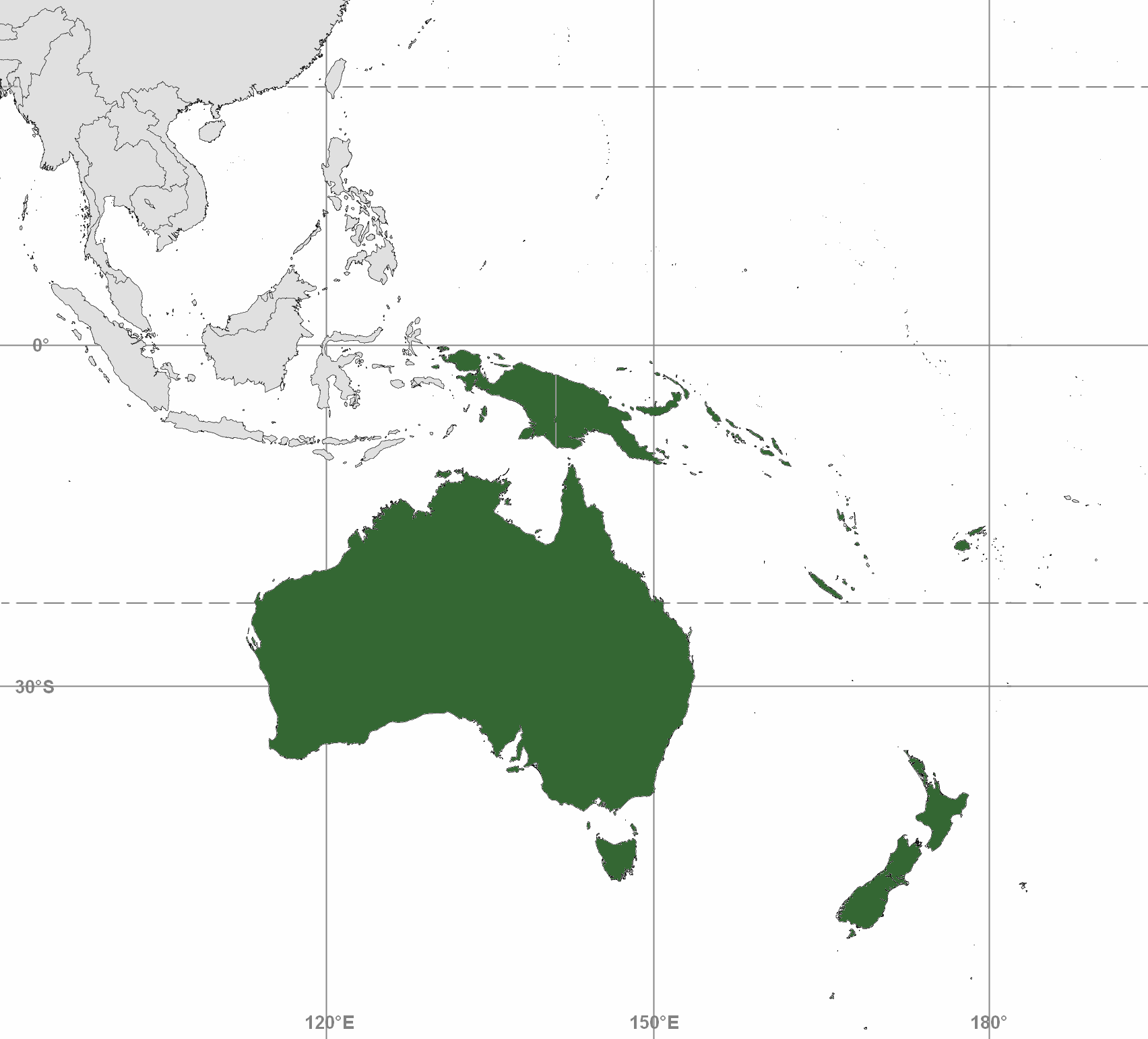 Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific (
Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific (
 Australasia is a region that comprises
Australasia is a region that comprises Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically
Geopolitics (from Greek γῆ ''gê'' "earth, land" and πολιτική ''politikḗ'' "politics") is the study of the effects of Earth's geography (human and physical) on politics and international relations. While geopolitics usually refers to ...
, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different, but related regions.
Derivation and definitions
 Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific (
Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific (Magellanica
(Latin: '"Southern Land'") was a hypothetical continent first posited in antiquity and which appeared on maps between the 15th and 18th centuries. Its existence was not based on any survey or direct observation, but rather on the idea that ...
).
In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colonies) and New Zealand. Australasia found continued geopolitical attention in the early 20th century. Historian Hansong Li finds that against the backdrop of British colonialism, German geopoliticians considered "Australasia" as a counterweight to the former German South Sea Edge (Südseerand), both of which form the "Indo-Pacific" region.
The ''New Zealand Oxford Dictionary'' gives two meanings of "Australasia". One, especially in Australian use, is "Australia, New Zealand, New Guinea, and the neighbouring islands of the Pacific". The other, especially in New Zealand use, is just Australia and New Zealand.
Two Merriam-Webster dictionaries online (''Collegiate'' and ''Unabridged'') define Australasia as "Australia, New Zealand, and Melanesia". The ''American Heritage Dictionary'' online recognizes two senses
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system rec ...
in use: one more precise, being similar to the aforementioned senses, and the other broader, loosely covering all of Oceania.
See also
*Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific (APAC) is the part of the world near the western Pacific Ocean. The Asia-Pacific region varies in area depending on context, but it generally includes East Asia, Russian Far East, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia and Pacific Isla ...
* Australasia at the Olympics
* Austral-Asia Cup
* Down Under
* Sundaland
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It ...
* Trans-Tasman
* Zealandia
Notes
References
*External links
{{Authority control