|
Physiogeographical
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere. This focus is in contrast with the branch of human geography, which focuses on the built environment, and technical geography, which focuses on using, studying, and creating tools to obtain,analyze, interpret, and understand spatial information. The three branches have significant overlap, however. Sub-branches Physical geography can be divided into several branches or related fields, as follows: * Geomorphology is concerned with understanding the surface of the Earth and the processes by which it is shaped, both at the present as well as in the past. Geomorphology as a field has several sub-fields that deal with the specific landforms of various environments e.g. desert geomorphology and fluvial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform and terrain history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphologists work within disciplines such as physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology, climatology, and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field. Overview Earth's surface is modified by a combination of surface processes that shape landscapes, and geologic processes that cause tectonic uplift and subsidence, and shape the coastal geography. Surface processes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluvial
In geography and geology, fluvial processes are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by them. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluvioglacial is used. Fluvial processes Fluvial processes include the motion of sediment and erosion or deposition on the river bed. The movement of water across the stream bed exerts a shear stress directly onto the bed. If the cohesive strength of the substrate is lower than the shear exerted, or the bed is composed of loose sediment which can be mobilized by such stresses, then the bed will be lowered purely by clearwater flow. In addition, if the river carries significant quantities of sediment, this material can act as tools to enhance wear of the bed ( abrasion). At the same time the fragments themselves are ground down, becoming smaller and more rounded (attrition). Sediment in rivers is transported as either bedload (the coarser fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
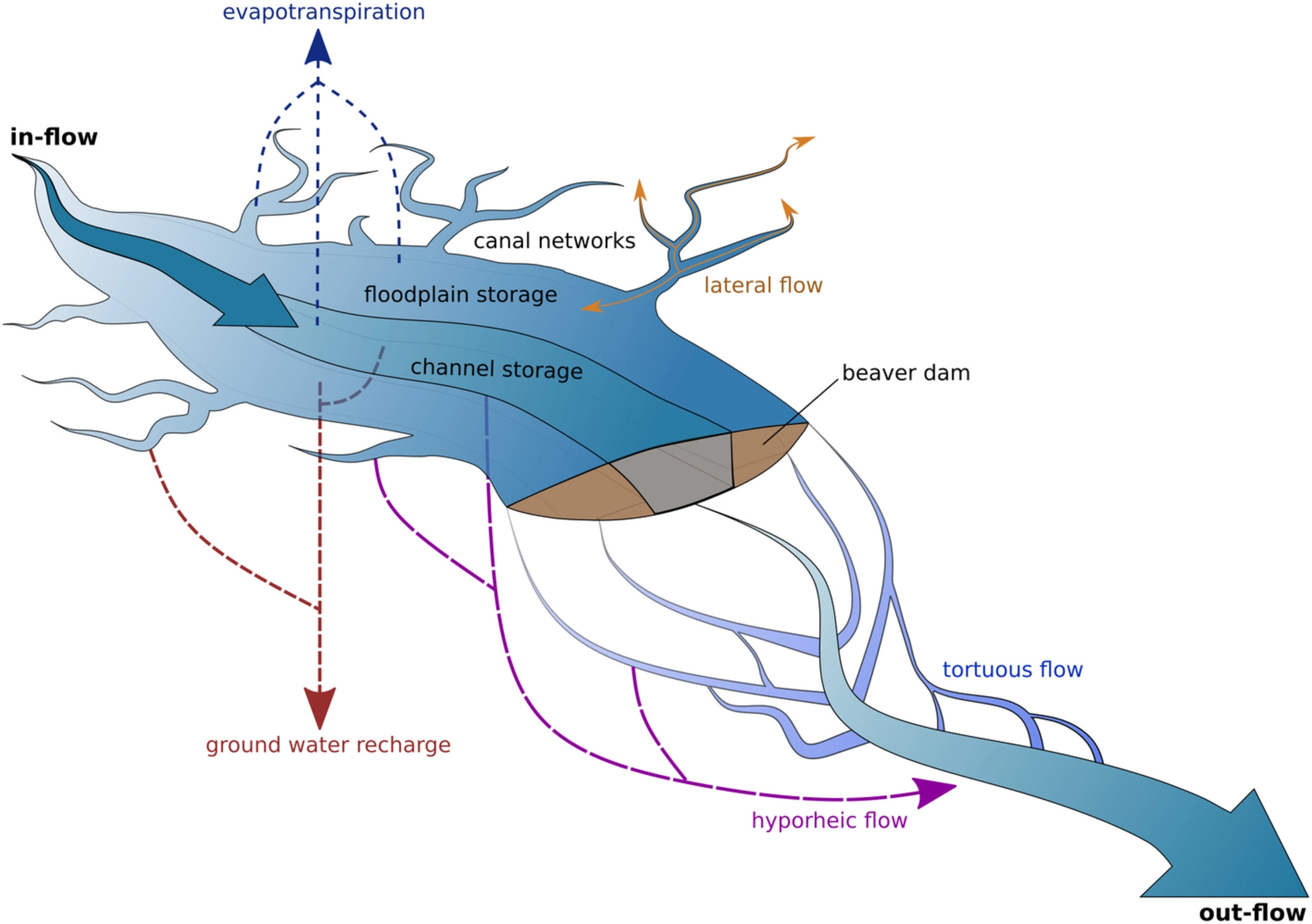
Ecohydrology
Ecohydrology (from Greek , ''oikos'', "house(hold)"; , ''hydōr'', "water"; and , '' -logia'') is an interdisciplinary scientific field studying the interactions between water and ecological systems. It is considered a sub discipline of hydrology, with an ecological focus. These interactions may take place within water bodies, such as rivers and lakes, or on land, in forests, deserts, and other terrestrial ecosystems. Areas of research in ecohydrology include transpiration and plant water use, adaption of organisms to their water environment, influence of vegetation and benthic plants on stream flow and function, and feedbacks between ecological processes, the soil carbon sponge and the hydrological cycle. Key concepts The hydrologic cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface on the earth. This flow is altered by ecosystems at numerous points. Transpiration from plants provides the majority of flow of water to the atmosphere. Water is infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limnology
Limnology ( ; from Greek λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake" and λόγος, ''logos'', "knowledge") is the study of inland aquatic ecosystems. The study of limnology includes aspects of the biological, chemical, physical, and geological characteristics of fresh and saline, natural and man-made bodies of water. This includes the study of lakes, reservoirs, ponds, rivers, springs, streams, wetlands, and groundwater.Wetzel, R.G. 2001. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed. Academic Press () Water systems are often categorized as either running (lotic) or standing (lentic). Limnology includes the study of the drainage basin, movement of water through the basin and biogeochemical changes that occur en route. A more recent sub-discipline of limnology, termed landscape limnology, studies, manages, and seeks to conserve these ecosystems using a landscape perspective, by explicitly examining connections between an aquatic ecosystem and its drainage basin. Recently, the need to underst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres, namely biosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and geosphere. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science, but with a much older history. Earth science encompasses four main branches of study, the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere, each of which is further broken down into more specialized fields. There are both reductionist and holistic approaches to Earth sciences. It is also the study of Earth and its neighbors in space. Some Earth scientists use their knowledge of the planet to locate and develop energy and mineral resources. Others study the impact of human activity on Earth's environment, and design methods to protect the planet. Some use their knowledge about Earth processes suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more specialized List of engineering branches, fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on particular areas of applied mathematics, applied science, and types of application. See glossary of engineering. The term ''engineering'' is derived from the Latin ''ingenium'', meaning "cleverness" and ''ingeniare'', meaning "to contrive, devise". Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (ECPD, the predecessor of Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, ABET) has defined "engineering" as: The creative application of scientific principles to design or develop structures, machines, apparatus, or manufacturing processes, or works utilizing them singly or in combination; or to construct o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology. Related terms include aquitard, which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, and aquiclude (or ''aquifuge''), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer, the pressure of which could create a confined aquifer. The classification of aquifers is as follows: Saturated versus unsaturated; aquifers versus aquitards; confined versus unconfined; isotropic versus anisotropic; porous, karst, or fractured; transboundary aquifer. Challenges for using groundwater include: overdrafting (extracting groundwater beyond the Dynamic equilibrium, equilibrium yield of the aquifer), groundwater-related subsidence of land, gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as Stream#Creek, creek, Stream#Brook, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to Geographical feature, geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "Burn (landform), burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation through a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrological Cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time but the partitioning of the water into the major reservoirs of ice, fresh water, saline water (salt water) and atmospheric water is variable depending on a wide range of climatic variables. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes of evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, surface runoff, and subsurface flow. In doing so, the water goes through different forms: liquid, solid (ice) and vapor. The ocean plays a key role in the water cycle as it is the source of 86% of global evaporation. The water cycle involves the exchange of energy, which leads to temperature changes. When water evaporates, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydrologist. Hydrologists are scientists studying earth or environmental science, civil or environmental engineering, and physical geography. Using various analytical methods and scientific techniques, they collect and analyze data to help solve water related problems such as environmental preservation, natural disasters, and water management. Hydrology subdivides into surface water hydrology, groundwater hydrology (hydrogeology), and marine hydrology. Domains of hydrology include hydrometeorology, surface hydrology, hydrogeology, drainage-basin management, and water quality, where water plays the central role. Oceanography and meteorology are not included because water is only one of many important aspects within those fields. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |