Target pricing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Target costing is an approach to determine a product's
 The first step is to set a product-level target cost. Since the allowable cost is simply obtained from external conditions without considering the design capabilities of the company as well as the realistic cost for manufacturing, it may not be always achievable in practice. Thus, it is necessary to adjust the unachievable allowable cost to an achievable target cost that the cost increase should be reduced with great effort. The second step is to discipline this target cost process, including monitoring the relationship between the target cost and the estimated product cost at any point during the design process, applying the cardinal rule so that the total target costs at the component-level does not exceed the target cost of the product, and allowing exceptions for products violating the cardinal rule. For a product exception to the cardinal rule, two analyses are often performed after the launch of the product. One involves reviewing the design process to find out why the target cost was unachieved. The other is an immediate effort to reduce the excessive cost to ensure that the period of violation is as short as possible. Once the target cost-reduction objective is identified, the product-level target costing comes to the final step, finding ways to achieve it. Engineering methods such as
The first step is to set a product-level target cost. Since the allowable cost is simply obtained from external conditions without considering the design capabilities of the company as well as the realistic cost for manufacturing, it may not be always achievable in practice. Thus, it is necessary to adjust the unachievable allowable cost to an achievable target cost that the cost increase should be reduced with great effort. The second step is to discipline this target cost process, including monitoring the relationship between the target cost and the estimated product cost at any point during the design process, applying the cardinal rule so that the total target costs at the component-level does not exceed the target cost of the product, and allowing exceptions for products violating the cardinal rule. For a product exception to the cardinal rule, two analyses are often performed after the launch of the product. One involves reviewing the design process to find out why the target cost was unachieved. The other is an immediate effort to reduce the excessive cost to ensure that the period of violation is as short as possible. Once the target cost-reduction objective is identified, the product-level target costing comes to the final step, finding ways to achieve it. Engineering methods such as
Management Accounting Quarterly 12 Winter 2003Japanese Target CostingImplementing Target Costing
Management accounting Lean manufacturing Design for X
life-cycle cost
Whole-life cost is the total cost of ownership over the life of an asset. The concept is also known as life-cycle cost (LCC) or lifetime cost, and is commonly referred to as "cradle to grave" or "womb to tomb" costs. Costs considered include the f ...
which should be sufficient to develop specified functionality and quality, while ensuring its desired profit
Profit may refer to:
Business and law
* Profit (accounting), the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market
* Profit (economics), normal profit and economic profit
* Profit (real property), a nonpossessory intere ...
. It involves setting a target cost by subtracting a desired profit margin
Profit margin is a measure of profitability. It is calculated by finding the profit as a percentage of the revenue.
\text = =
There are 3 types of profit margins: gross profit margin, operating profit margin and net profit margin.
* Gross Prof ...
from a competitive market price. A target cost is the maximum amount of cost that can be incurred on a product, however, the firm can still earn the required profit margin from that product at a particular selling price. Target costing decomposes the target cost from product level to component level. Through this decomposition, target costing spreads the competitive pressure faced by the company to product's designers and suppliers. Target costing consists of cost planning in the design phase of production as well as cost control throughout the resulting product life cycle
In industry, Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM ...
. The cardinal rule of target costing is to never exceed the target cost. However, the focus of target costing is not to minimize costs, but to achieve a desired level of cost reduction
Cost reduction is the process used by companies to reduce their costs and increase their profits. Depending on a company’s services or products, the strategies can vary. Every decision in the product development process affects cost: design i ...
determined by the target costing process.
Definition
Target costing is defined as "a disciplined process for determining and achieving a full-stream cost at which a proposed product with specified functionality, performance, and quality must be produced in order to generate the desired profitability at the product’s anticipated selling price over a specified period of time in the future." This definition encompasses the principal concepts: products should be based on an accurate assessment of the wants and needs of customers in different market segments, and cost targets should be what result after a sustainable profit margin is subtracted from what customers are willing to pay at the time of product introduction and afterwards. The fundamental objective of target costing is to manage the business to be profitable in a highly competitive marketplace. In effect, target costing is a proactive cost planning,cost management
Cost accounting is defined as "a systematic set of procedures for recording and reporting measurements of the cost of manufacturing goods and performing services in the aggregate and in detail. It includes methods for recognizing, classifying, al ...
, and cost reduction
Cost reduction is the process used by companies to reduce their costs and increase their profits. Depending on a company’s services or products, the strategies can vary. Every decision in the product development process affects cost: design i ...
practice whereby costs are planned and managed out of a product and business early in the design and development cycle, rather than during the later stages of product development and production.
History
Target costing was developed independently in both USA and Japan in different time periods. Target costing was adopted earlier by American companies to reduce cost and improve productivity, such asFord Motor
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobile ...
from 1900s, American Motors from 1950s-1960s. Although the ideas of target costing were also applied by a number of other American companies including Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product ...
, Caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Sym ...
, Northern Telecom
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ra ...
, few of them apply target costing as comprehensively and intensively as top Japanese companies such as Nissan
, trade name, trading as Nissan Motor Corporation and often shortened to Nissan, is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automobile manufacturer headquartered in Nishi-ku, Yokohama, Japan. The company sells ...
, Toyota
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 ...
, Nippondenso. Target costing emerged from Japan from 1960s to early 1970s with the particular effort of Japanese automobile industry, including Toyota and Nissan. It did not receive global attention until late 1980s to 1990s when some authors such as Monden (1992), Sakurai (1989), Tanaka (1993), and Cooper (1992) described the way that Japanese companies applied target costing to thrive in their business (IMA 1994). With superior implementation systems, Japanese manufacturers are more successful than the American companies in developing target costing. Traditional cost-plus pricing
Cost-plus pricing is a pricing strategy by which the selling price of a product is determined by adding a specific fixed percentage (a " markup") to the product's unit cost. Essentially, the markup percentage is a method of generating a particular ...
strategy has been impeding the productivity and profitability for a long time. As a new strategy, target costing is replacing traditional cost-plus pricing strategy by maximizing customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction (often abbreviated as CSAT) is a term frequently used in marketing. It is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation. Customer satisfaction is defined as "the number of c ...
by accepted level of quality and functionality while minimizing costs.
Process of target costing
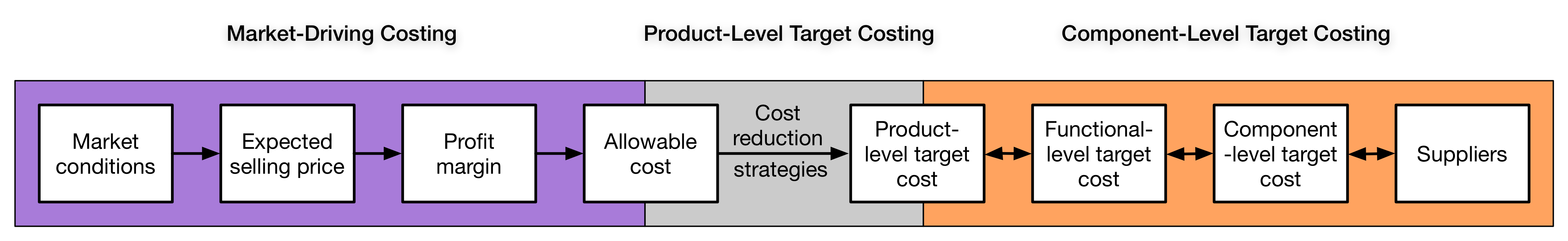
The process of target costing can be divided into three sections: the first section involves in market-driven target costing, which focuses on studying market conditions to identify a product's allowable cost in order to meet the company's long-term profit at expected selling price; the second section involves performing cost reduction strategies with the product designer's effort and creativity to identify the product-level target cost; the third section is component-level target cost which decomposes the production cost to functional and component levels to transmit cost responsibility to suppliers.
Market-driven target costing
Market driven target costing is the first section in the target costing process which focuses on studying market conditions and determining the company'sprofit margin
Profit margin is a measure of profitability. It is calculated by finding the profit as a percentage of the revenue.
\text = =
There are 3 types of profit margins: gross profit margin, operating profit margin and net profit margin.
* Gross Prof ...
in order to identify the allowable cost of a product. Market driven costing can go through 5 steps including: establish company's long-term sales and profit objective; develop the mix of products; identify target selling price for each product; identify profit margin for each product; and calculate allowable cost of each product.
Company's long-term sales and profit objectives are developed from an extensive analysis of relevant information relating to customers, market and products. Only realistic plans are accepted to proceed to the next step. Product mix is designed carefully to ensure that it satisfies many customers, but also does not contain too many products to confuse customers. Company may use simulation to explore the impact of overall profit objective to different product mixes and determine the most feasible product mix. Target selling price, target profit margin and allowable cost are identified for each product. Target selling price need to consider to the expected market condition at the time launching the product. Internal factors such as product's functionality and profit objective, and external factors such as company's image or expected price of competitive products will influence target selling price. Company's long-term profit plan and life-cycle cost are considered when determining target profit margin. Firms might set up target profit margin based on either actual profit margin of previous products or target profit margin of product line. Simulation for overall group profitability can help to make sure achieving group target. Subtracting target profit margin from target selling price results in allowable cost for each product. Allowable cost is the amount that can spent on a product to ensure its profit target is met if it is sold at its target price. It is the signal about the magnitude of cost saving that team need to achieve.
Product-level target costing
Following the completion of market-driven costing, the next task of the target costing process is product-level target costing. Product-level target costing concentrates on designing products that satisfy the company's customers at the allowable cost. To achieve this goal, product-level target costing is typically divided into three steps as shown below. The first step is to set a product-level target cost. Since the allowable cost is simply obtained from external conditions without considering the design capabilities of the company as well as the realistic cost for manufacturing, it may not be always achievable in practice. Thus, it is necessary to adjust the unachievable allowable cost to an achievable target cost that the cost increase should be reduced with great effort. The second step is to discipline this target cost process, including monitoring the relationship between the target cost and the estimated product cost at any point during the design process, applying the cardinal rule so that the total target costs at the component-level does not exceed the target cost of the product, and allowing exceptions for products violating the cardinal rule. For a product exception to the cardinal rule, two analyses are often performed after the launch of the product. One involves reviewing the design process to find out why the target cost was unachieved. The other is an immediate effort to reduce the excessive cost to ensure that the period of violation is as short as possible. Once the target cost-reduction objective is identified, the product-level target costing comes to the final step, finding ways to achieve it. Engineering methods such as
The first step is to set a product-level target cost. Since the allowable cost is simply obtained from external conditions without considering the design capabilities of the company as well as the realistic cost for manufacturing, it may not be always achievable in practice. Thus, it is necessary to adjust the unachievable allowable cost to an achievable target cost that the cost increase should be reduced with great effort. The second step is to discipline this target cost process, including monitoring the relationship between the target cost and the estimated product cost at any point during the design process, applying the cardinal rule so that the total target costs at the component-level does not exceed the target cost of the product, and allowing exceptions for products violating the cardinal rule. For a product exception to the cardinal rule, two analyses are often performed after the launch of the product. One involves reviewing the design process to find out why the target cost was unachieved. The other is an immediate effort to reduce the excessive cost to ensure that the period of violation is as short as possible. Once the target cost-reduction objective is identified, the product-level target costing comes to the final step, finding ways to achieve it. Engineering methods such as value engineering
Value engineering (VE) is a systematic analysis of the functions of various components and materials to lower the cost of goods, products and services with a tolerable loss of performance or functionality. Value, as defined, ...
(VE), design for manufacture and assembly (DFMA), and quality function deployment
Quality function deployment (QFD) a method developed in Japan beginning in 1966 to help transform the voice of the customer into engineering characteristics for a product.Larson et al. (2009). p. 117. Yoji Akao, the original developer, described QF ...
(QFD) are commonly adopted in this step.
Target costing and value engineering
Value engineering
Value engineering (VE) is a systematic analysis of the functions of various components and materials to lower the cost of goods, products and services with a tolerable loss of performance or functionality. Value, as defined, ...
(VE), also known as value analysis (VA), plays a crucial role in the target costing process, particularly at the product level and the component level. Among the three aforementioned methods in achieving the target cost, VE is the most critical one because not only does it attempt to reduce costs, but also aims to improve the functionality and quality of products. There are a variety of practical VE strategies, including zero-look, first-look and second-look VE approaches, as well as teardown approaches.
Regarding the complexity of problems in the real world, implementing the target costing process often relies on the computer simulation
Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be dete ...
to reproduce stochastic elements. For example, many firms use simulation to study the complex relationship between selling prices and profit margins, the impact of individual product decisions on overall group profitability, the right mix of products to enhance overall profit, or other economic modeling to overcome organizational inertia by getting the most productive reasoning. In addition, simulation helps estimate results rapidly for dynamic process changes.
Factors affecting target costing
The factors influencing the target costing process is broadly categorized based on how a company's strategy for a product's quality, functionality and price change over time. However, some factors play a specific role based on what drives a company's approach to target costing.Factors influencing market-driven costing
Intensity of competition and nature of the customer affect market-driven costing. Competitors introducing similar products has been shown to drive rival companies to expend energy on implementing target costing systems such as in the case of Toyota and Nissan orApple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
and Google
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...
. The costing process is also affected by the level of customer sophistication, changing requirements and the degree to which their future requirements are known. The automotive and camera
A camera is an Optics, optical instrument that can capture an image. Most cameras can capture 2D images, with some more advanced models being able to capture 3D images. At a basic level, most cameras consist of sealed boxes (the camera body), ...
industry are prime examples for how customers affect target costing based on their exact requirements.
Factors influencing product-level costing
Product strategy
Product strategy defines the high-level plan for developing and marketing a product, how the product supports the business strategy and goals, and is brought to life through product roadmaps. A product strategy describes a vision of the future wit ...
and product characteristics affect product-level target costing. Characteristics of product strategy such as number of products in line, rate of redesign operations and level of innovation are shown to have an effect. Higher number of products has a direct correlation with the benefits of target costing. Frequent redesigns lead to the introduction of new products that have created better benefits to target costing. It has to be noted that the value of historical information reduces with greater innovation, thereby, reducing the benefits of product level target costing.
The degree of complexity of the product, level of investments required and the duration of product development process make up the factors that affect the target costing process based on product characteristics. Product viability is determined by the aforementioned factors. In turn, the target costing process is also modified to suit the different degrees of complexity required.
Factors influencing component-level costing
Supplier-Base strategy is the main factor that determines component-level target costing because it is known to play a key role in the details a firm has about its supplier capabilities. There are three characteristics that make up the supplier-base strategy, including the degree ofhorizontal integration
Horizontal integration is the process of a company increasing production of goods or services at the same part of the supply chain. A company may do this via internal expansion, acquisition or merger.
The process can lead to monopoly if a co ...
, power over suppliers and nature of supplier relations. Horizontal integration captures the fraction of product costs sourced externally. Cost pressures on suppliers can drive target costing if the buying power
Bargaining power is the relative ability of parties in an argumentative situation (such as bargaining, contract writing, or making an agreement) to exert influence over each other. If both parties are on an equal footing in a debate, then they wi ...
of firms is high enough. In turn, this may lead to better benefits. More cooperative supplier relations have been shown to increase mutual benefits in terms of target costs particularly at a component level.
Applications
Aside from the application of target costing in the field of manufacturing, target costing are also widely used in the following areas.Energy
An Energy Retrofit Loan Analysis Model has been developed using a Monte Carlo (MC) method for target costing in Energy Efficient buildings and construction. MC method has been shown to be effective in determining the impact of financial uncertainties in project performance. Target Value Design Decision Making Process (TVD-DMP) groups a set of energy efficiency methods at different optimization levels to evaluate costs and uncertainties involved in the energy efficiency process. Some major design parameters are specified using this methods including Facility Operation Schedule, Orientation,Plug load Plug load is the energy used by products that are powered by means of an ordinary AC plug (e.g., 100, 115, or 230 V). This term generally excludes building energy that is attributed to major end uses (HVAC, lighting, water heating, etc.)
Definitio ...
, HVAC
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HV ...
and lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylig ...
systems.
The entire process consists of three phases: initiation, definition and alignment. Initiation stage involves developing a business case for energy efficiency using target value design (TVD) training, organization and compensation. The definition process involves defining and validating the case by tools such as values analysis and bench marking processes to determine the allowable costs. By setting targets and designing the design process to align with those targets, TVD-DMP has been shown to achieve a high level of collaboration needed for energy efficiency investments. This is done by using risk analysis tools, pull planning and rapid estimating processes.
Healthcare
Target costing and target value design have applications in building healthcare facilities including critical components such asNeonatal Intensive Care Unit
A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of life. Neonatal care, as kn ...
s (NICUs). The process is influenced by unit locations, degree of comfort, number of patients per room, type of supply location and access to nature. According to National Vital Statistics Reports, 12.18% of 2009 births were premature and the cost per infant was $51,600. This led to opportunities for NICUs to implement target value design for deciding whether to build a single-family room or more open-bay NICUs. This was achieved using set-based design analysis which challenges the designer to generate multiple alternatives for the same functionality. Designs are evaluated keeping in mind the requirements of the various stakeholders in the NICU including nurses, doctors, family members and administrators. Unlike linear point-based design, set-based design narrows options to the optimal one by eliminating alternatives simultaneously defined by user constraints.
Construction
About 15% construction project in Japan adopted target costing for their cost planning and management as recognized by Jacomit (2008). In the U.S., target costing research has been carried out within the framework of lean construction as target value design (TVD) method and have been disseminated widely over construction industry in recent years. Research has proven that if being applied systematically, TVD can deliver a significant improvement in project performance with average reduction of 15% in comparison with market cost. TVD in construction project considers the final cost of project as a design parameter, similar to the capacity and aesthetics requirements for the project. TVD requires the project team to develop a target cost from the beginning. The project team is expected not to design exceeding the target cost without the owner's approval, and must use different skills to maintain this target cost. In some cases, the cost can increase but the project team must commit to decrease and must try their best to decrease without impacting on other functions of the project.See also
*Design-to-cost
Design-to-Cost (DTC), as part of cost management techniques, describes a systematic approach to controlling the costs of product development and manufacturing. The basic idea is that costs are designed "into the product", even from the earliest co ...
References
{{reflistExternal links
Management Accounting Quarterly 12 Winter 2003
Management accounting Lean manufacturing Design for X