Steroid biosynthesis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A steroid is a biologically active

File:Testosteron.svg, alt=Chemical diagram,
In addition to the ring scissions (cleavages), expansions and contractions (cleavage and reclosing to a larger or smaller rings)—all variations in the carbon-carbon bond framework—steroids can also vary:
* in the
 The hundreds of steroids found in animals, fungi, and
The hundreds of steroids found in animals, fungi, and
 The mevalonate pathway (also called HMG-CoA reductase pathway) begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) and isopentenyl pyrophosphate, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP).
DMAPP and IPP donate isoprene units, which are assembled and modified to form terpenes and terpenoid, isoprenoids (a large class of lipids, which include the carotenoids and form the largest class of plant
The mevalonate pathway (also called HMG-CoA reductase pathway) begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) and isopentenyl pyrophosphate, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP).
DMAPP and IPP donate isoprene units, which are assembled and modified to form terpenes and terpenoid, isoprenoids (a large class of lipids, which include the carotenoids and form the largest class of plant
 Steroidogenesis is the biological process by which steroids are generated from cholesterol and changed into other steroids. The metabolic pathway, pathways of steroidogenesis differ among species. The major classes of steroid hormones, as noted above (with their prominent members and functions), are the
Steroidogenesis is the biological process by which steroids are generated from cholesterol and changed into other steroids. The metabolic pathway, pathways of steroidogenesis differ among species. The major classes of steroid hormones, as noted above (with their prominent members and functions), are the
organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ...
with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration The molecular configuration of a molecule is the ''permanent'' geometry that results from the spatial arrangement of its bonds. The ability of the same set of atoms to form two or more molecules with different configurations is stereoisomerism. ...
. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
s that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular ...
. Hundreds of steroids are found in plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
s, animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
s and fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols
Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom in position 3 by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the gon ...
lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under en ...
(opisthokonts
The opisthokonts () are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and ...
) or cycloartenol
Cycloartenol is an important triterpenoid of the sterol class which is found in plants. It is the starting point for the synthesis of almost all plant steroids, making them chemically distinct from the steroids of fungi and animals, which are, ...
(plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where ...
of the triterpene
Triterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of three terpene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of six isoprene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squa ...
squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpenoid with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as ''Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). A ...
.
The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohe ...
rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane
Cyclopentane (also called C pentane) is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C5H10 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It occ ...
ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest ...
attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
of the rings. Sterol
Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom in position 3 by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the go ...
s are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane
Cholestane is a saturated tetracyclic triterpene. This 27-carbon biomarker is produced by diagenesis of cholesterol and is one of the most abundant biomarkers in the rock record. Presence of cholestane, its derivatives and related chemical compo ...
. ''Also available with the same authors at'' ; ''Also available online at'' Steroids can also be more radically modified, such as by changes to the ring structure, for example, cutting
Cutting is the separation or opening of a physical object, into two or more portions, through the application of an acutely directed force.
Implements commonly used for wikt:cut, cutting are the knife and saw, or in medicine and science the scal ...
one of the rings. Cutting Ring B produces secosteroid
A secosteroid () is a type of steroid with a "broken" ring. The word ''secosteroid ''derives from the Latin verb ''secare'' meaning "to cut", and 'steroid'. Secosteroids are alternatively described as a subclass of steroids; ; or derived from st ...
s one of which is vitamin D3.
Examples include anabolic steroids
Anabolic steroids, also known more properly as anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS), are steroidal androgens that include natural androgens like testosterone as well as synthetic androgens that are structurally related and have similar effects t ...
, the lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell memb ...
, the sex hormones estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development o ...
and testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
, and the anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as o ...
drug dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena ...
.
Nomenclature


Gonane
Gonane is a chemical compound with formula , whose molecule can be described as three molecules or entities of cyclohexane and one of cyclopentane, fused in a particular way. More specifically, the molecule can be described as that of cycloh ...
, also known as steran or cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene, the simplest steroid and the nucleus of all steroids and sterols, is composed of seventeen carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
atoms in carbon-carbon bonds forming four fused rings in a three-dimensional shape. The three cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohe ...
rings (A, B, and C in the first illustration) form the skeleton of a perhydro derivative of phenanthrene
Phenanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a colorless, crystal-like solid, but can also appear yellow. Phenanthrene is used to make dyes, plastics and pesticides, ...
. The D ring has a cyclopentane
Cyclopentane (also called C pentane) is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C5H10 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It occ ...
structure. When the two methyl groups and eight carbon side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a molecule that is attached to a ...
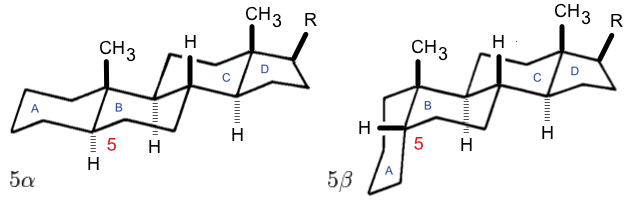
s (at C-17, as shown for cholesterol) are present, the steroid is said to have a cholestane framework. The two common 5α and 5β stereoisomeric forms of steroids exist because of differences in the side of the largely planar ring system where the hydrogen (H) atom at carbon-5 is attached, which results in a change in steroid A-ring conformation. Isomerisation at the C-21 side chain produces a parallel series of compounds, referred to as isosteroids.
Examples of steroid structures are:
Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
, the principal male sex hormone
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effect ...
and an anabolic steroid
Anabolic steroids, also known more properly as anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS), are steroidal androgens that include natural androgens like testosterone as well as synthetic androgens that are structurally related and have similar effects ...
File:Cholsäure.svg, alt=Chemical diagram, Cholic acid
Cholic acid, also known as 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid is a primary bile acid that is insoluble in water (soluble in alcohol and acetic acid), it is a white crystalline substance. Salts of cholic acid are called cholates. Chol ...
, a bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.
Primar ...
, showing the carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxyli ...
and additional hydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
s often present
File:Dexamethasone structure.svg, alt=Chemical diagram, Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena ...
, a synthetic corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
drug
File:Lanosterin.svg, alt=Chemical diagram, Lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under en ...
, the biosynthetic
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed process where substrate (chemistry), substrates are converted into more complex Product (chemistry), products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple Chemical compound, compounds are mo ...
precursor to animal steroids. The number of carbons (30) indicates its triterpenoid
Triterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of three terpene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of six isoprene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squal ...
classification.
File:Progesteron.svg, alt=Chemical diagram, Progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the majo ...
, a steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis
File:Medrogestone.png, alt=Chemical diagram, Medrogestone, a synthetic drug with effects similar to progesterone
File:Sitosterol structure.svg, alt=Chemical diagram, β-Sitosterol
β-sitosterol (beta-sitosterol) is one of several phytosterols (plant sterols) with chemical structures similar to that of cholesterol. It is a white, waxy powder with a characteristic odor, and is one of the components of the food additive E499 ...
, a plant or phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phyt ...
, with a fully branched hydrocarbon side chain at C-17 and an hydroxyl group at C-3
bond order
In chemistry, bond order, as introduced by Linus Pauling, is defined as the difference between the number of bonds and anti-bonds.
The bond order itself is the number of electron pairs ( covalent bonds) between two atoms. For example, in diat ...
s within the rings,
* in the number of methyl groups attached to the ring (and, when present, on the prominent side chain at C17),
* in the functional groups attached to the rings and side chain, and
* in the configuration
Configuration or configurations may refer to:
Computing
* Computer configuration or system configuration
* Configuration file, a software file used to configure the initial settings for a computer program
* Configurator, also known as choice bo ...
of groups attached to the rings and chain.
For instance, sterol
Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom in position 3 by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the go ...
s such as cholesterol and lanosterol have a hydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
attached at position C-3, while testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
and progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the majo ...
have a carbonyl (oxo substituent) at C-3; of these, lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under en ...
alone has two methyl groups at C-4 and cholesterol (with a C-5 to C-6 double bond) differs from testosterone and progesterone (which have a C-4 to C-5 double bond).
Species distribution and function
Ineukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s, steroids are found in fungi, animals, and plants.
Fungal steroids
Fungal steroids include theergosterol
Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a sterol found in cell membranes of fungi and protozoa, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Because many fungi and protozoa cannot survive without ergosterol, t ...
s, which are involved in maintaining the integrity of the fungal cellular membrane. Various antifungal drugs, such as amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis ...
and azole antifungals
Azoles are a class of five-membered heterocyclic compounds containing a nitrogen atom and at least one other non-carbon atom (i.e. nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen) as part of the ring.
Their names originate from the Hantzsch–Widman nomenclatur ...
, utilize this information to kill pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...
fungi. Fungi can alter their ergosterol content (e.g. through loss of function mutations in the enzymes ERG3 or ERG6, inducing depletion of ergosterol, or mutations that decrease the ergosterol content) to develop resistance to drugs that target ergosterol.
Ergosterol is analogous to the cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell memb ...
found in the cellular membranes of animals (including humans), or the phytosterols found in the cellular membranes of plants. All mushrooms contain large quantities of ergosterol, in the range of tens to hundreds of milligrams per 100 grams of dry weight. Oxygen is necessary for the synthesis of ergosterol
Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a sterol found in cell membranes of fungi and protozoa, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Because many fungi and protozoa cannot survive without ergosterol, t ...
in fungi.
Ergosterol is responsible for the vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
content found in mushrooms; ergosterol is chemically converted into provitamin D2 by exposure to ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiatio ...
. Provitamin D2 spontaneously forms vitamin D2. However, not all fungi utilize ergosterol in their cellular membranes; for example, the pathogenic fungal species ''Pneumocystis jirovecii
''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' (previously ''P. carinii'') is a yeast-like fungus of the genus ''Pneumocystis''. The causative organism of ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia, it is an important human pathogen, particularly among immunocompromised hosts. P ...
'' does not, which has important clinical implications (given the mechanism of action of many antifungal drugs). Using the fungus ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have b ...
'' as an example, other major steroids include ergosta‐5,7,22,24(28)‐tetraen‐3β‐ol, zymosterol
Zymosterol is an intermediate in cholesterol biosynthesis. Disregarding some intermediate compounds (e.g. 4-4-dimethylzymosterol) lanosterol can be considered a precursor of zymosterol in the cholesterol synthesis pathway. The conversion of zymo ...
, and lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under en ...
. ''S. cerevisiae'' utilizes 5,6‐dihydroergosterol in place of ergosterol in its cell membrane.
Animal steroids
Animal steroids include compounds ofvertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
and insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pa ...
origin, the latter including ecdysteroid
Ecdysteroids are arthropod steroid hormones that are mainly responsible for molting, development and, to a lesser extent, reproduction; examples of ecdysteroids include ecdysone, ecdysterone, turkesterone and 2-deoxyecdysone. These compounds are ...
s such as ecdysterone
20-Hydroxyecdysone (ecdysterone or 20E) is a naturally occurring ecdysteroid hormone which controls the ecdysis (moulting) and metamorphosis of arthropods. It is therefore one of the most common moulting hormones in insects, crabs, etc. It is als ...
(controlling molting in some species). Vertebrate examples include the steroid hormones
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Withi ...
and cholesterol; the latter is a structural component of cell membranes
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
that helps determine the fluidity of cell membranes
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
and is a principal constituent of plaque
Plaque may refer to:
Commemorations or awards
* Commemorative plaque, a plate or tablet fixed to a wall to mark an event, person, etc.
* Memorial Plaque (medallion), issued to next-of-kin of dead British military personnel after World War I
* Pl ...
(implicated in atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no s ...
). Steroid hormones include:
* Sex hormone
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effect ...
s, which influence sex differences
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most anim ...
and support reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual or ...
. These include androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
s, estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
s, and progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the bod ...
s.
* Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s, including most synthetic steroid drugs, with natural product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical sy ...
classes the glucocorticoids (which regulate many aspects of metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
and immune function
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splin ...
) and the mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances ( electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
s (which help maintain blood volume and control renal
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; bloo ...
excretion of electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon ...
s)
* Anabolic steroid
Anabolic steroids, also known more properly as anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS), are steroidal androgens that include natural androgens like testosterone as well as synthetic androgens that are structurally related and have similar effects ...
s, natural
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans ar ...
and synthetic, which interact with androgen receptors to increase muscle and bone synthesis. In popular use, the term "steroids" often refers to anabolic steroids.
Plant steroids
Plant steroids include steroidalalkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of simila ...
s found in Solanaceae
The Solanaceae , or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and or ...
and Melanthiaceae
Melanthiaceae, also called the bunchflower family, is a family of flowering herbaceous perennial plants native to the Northern Hemisphere. Along with many other lilioid monocots, early authors considered members of this family to belong to t ...
(specially the genus Veratrum), cardiac glycoside
Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump. Their beneficial medical uses are as treatments for c ...
s, the phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phyt ...
s and the brassinosteroid
Brassinosteroids (BRs or less commonly BS) are a class of polyhydroxysteroids that have been recognized as a sixth class of
plant hormones and may have utility as an anticancer drug for endocrine-responsive cancers to induce apoptosis and inhibit ...
s (which include several plant hormones).
Prokaryotes
Inprokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Con ...
, biosynthetic pathways exist for the tetracyclic steroid framework (e.g. in mycobacteria
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis ('' M. tuberculosis'') and ...
) – where its origin from eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s is conjectured – and the more-common pentacyclic triterpinoid hopanoid framework.
Types
By function
The major classes ofsteroid hormones
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Withi ...
, with prominent members and examples of related functions, are:
* Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s:
** Glucocorticoids:
*** Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the '' zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal g ...
, a glucocorticoid whose functions include immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
** Mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances ( electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
s:
*** Aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays a c ...
, a mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances ( electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
that helps regulate blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure ...
through water and electrolyte balance
* Sex steroid
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effect ...
s:
** Progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the bod ...
s:
*** Progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the majo ...
, which regulates cyclical changes in the endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer ...
of the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
and maintains a pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
** Androgens
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
:
*** Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
, which contributes to the development and maintenance of male secondary sex characteristic
Secondary sex characteristics are features that appear during puberty in humans, and at sexual maturity in other animals. These characteristics are particularly evident in the sexually dimorphic phenotypic traits that distinguish the sexes of a s ...
s
** Estrogens
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal acti ...
:
*** Estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development o ...
, which contributes to the development and maintenance of female secondary sex characteristics
Additional classes of steroids include:
* Neurosteroid
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term ''neurosteroid'' was co ...
s such as and allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone is a naturally occurring neurosteroid which is made in the body from the hormone progesterone. As a medication, allopregnanolone is referred to as brexanolone, sold under the brand name Zulresso, and used to treat postpartum ...
* Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.
Primar ...
s such as taurocholic acid
* Aminosteroid
Aminosteroids are a group of steroids with a similar structure based on an amino-substituted steroid nucleus. They are neuromuscular blocking agents, acting as competitive antagonists of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), and block th ...
neuromuscular blocking agent
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs block neuromuscular transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors.
In clin ...
s (mainly synthetic) such as pancuronium bromide
Pancuronium (trademarked as Pavulon) is an aminosteroid muscle relaxant with various medical uses. It is used in euthanasia and is used in some states as the second of three drugs administered during lethal injections in the United States.
Mecha ...
* Steroidal antiandrogens (mainly synthetic) such as cyproterone acetate
Cyproterone acetate (CPA), sold alone under the brand name Androcur or with ethinylestradiol under the brand names Diane or Diane-35 among others, is an antiandrogen and progestin medication used in the treatment of androgen-dependent condition ...
* Steroidogenesis inhibitor
A steroidogenesis inhibitor, also known as a steroid biosynthesis inhibitor, is a type of drug which inhibits one or more of the enzymes that are involved in the process of steroidogenesis, the biosynthesis of endogenous steroids and steroid hor ...
s (mainly exogenous) such as alfatradiol
* Membrane sterols such as cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell memb ...
, ergosterol
Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a sterol found in cell membranes of fungi and protozoa, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Because many fungi and protozoa cannot survive without ergosterol, t ...
, and various phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phyt ...
s
* Toxins such as steroidal saponin
Saponins (Latin "sapon", soap + "-in", one of), also selectively referred to as triterpene glycosides, are bitter-tasting usually toxic plant-derived organic chemicals that have a foamy quality when agitated in water. They are widely distributed ...
s and cardenolides/cardiac glycoside
Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump. Their beneficial medical uses are as treatments for c ...
s
As well as the following class of secosteroid
A secosteroid () is a type of steroid with a "broken" ring. The word ''secosteroid ''derives from the Latin verb ''secare'' meaning "to cut", and 'steroid'. Secosteroids are alternatively described as a subclass of steroids; ; or derived from st ...
s (open-ring steroids):
* Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
forms such as ergocalciferol
Ergocalciferol, also known as vitamin D2 and nonspecifically calciferol, is a type of vitamin D found in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to prevent and treat vitamin D deficiency. This includes vitamin D defici ...
, cholecalciferol
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 and colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D that is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.
Cholecalciferol is made in the skin fo ...
, and calcitriol
Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D, normally made in the kidney. It is also known as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. It is a hormone which binds to and activates the vitamin D receptor in the nucleus of the cell, which then increases the ...
By structure
Intact ring system
Steroids can be classified based on their chemical composition. One example of howMeSH
A mesh is a barrier made of connected strands of metal, fiber, or other flexible or ductile materials. A mesh is similar to a web or a net in that it has many attached or woven strands.
Types
* A plastic mesh may be extruded, oriented, exp ...
performs this classification is available at the Wikipedia MeSH catalog. Examples of this classification include:
In biology, it is common to name the above steroid classes by the number of carbon atoms present when referring to hormones: C18-steroids for the estranes (mostly estrogens), C19-steroids for the androstanes (mostly androgens), and C21-steroids for the pregnanes (mostly corticosteroids). The classification " 17-ketosteroid" is also important in medicine.
The gonane (steroid nucleus) is the parent 17-carbon tetracyclic hydrocarbon molecule with no alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloa ...
sidechains.
Cleaved, contracted, and expanded rings
Secosteroids (Latin ''seco'', "to cut") are a subclass of steroidal compounds resulting, biosynthetically or conceptually, from scission (cleavage) of parent steroid rings (generally one of the four). Major secosteroid subclasses are defined by the steroid carbon atoms where this scission has taken place. For instance, the prototypical secosteroidcholecalciferol
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 and colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D that is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.
Cholecalciferol is made in the skin fo ...
, vitamin D3 (shown), is in the 9,10-secosteroid subclass and derives from the cleavage of carbon atoms C-9 and C-10 of the steroid B-ring; 5,6-secosteroids and 13,14-steroids are similar.
Norsteroids (nor- In chemical nomenclature, nor- is a prefix to name a structural analog that can be derived from a parent compound by the removal of one carbon atom along with the accompanying hydrogen atoms. The nor-compound can be derived by removal of a , , or C ...
, L. ''norma''; "normal" in chemistry, indicating carbon removal) and homosteroids (homo-, Greek ''homos''; "same", indicating carbon addition) are structural subclasses of steroids formed from biosynthetic steps. The former involves enzymic ring expansion-contraction reactions, and the latter is accomplished ( biomimetically) or (more frequently) through ring closure
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where a ...
s of acyclic precursors with more (or fewer) ring atoms than the parent steroid framework.
Combinations of these ring alterations are known in nature. For instance, Sheep, ewes who graze on Veratrum, corn lily ingest cyclopamine (shown) and veratramine, two of a sub-family of steroids where the C- and D-rings are contracted and expanded respectively via a biosynthesis, biosynthetic migration of the original C-13 atom. Ingestion of these C-nor-D-homosteroids results in birth defects in lambs: cyclopia from cyclopamine and leg deformity from veratramine. A further C-nor-D-homosteroid (nakiterpiosin) is excreted by Okinawan cyanobacteria, cyanobacteriosponges. e.g., ''Terpios hoshinota'', leading to coral mortality from black coral disease. Nakiterpiosin-type steroids are active against the signaling pathway involving the smoothened and hedgehog (cell signaling), hedgehog proteins, a pathway which is hyperactive in a number of cancers.
Biological significance
Steroids and their metabolites often function as signal transduction, signalling molecules (the most notable examples are steroid hormones), and steroids and phospholipids are components ofcell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
s. Steroids such as cholesterol decrease membrane fluidity.
Similar to lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
s, steroids are highly concentrated energy stores. However, they are not typically sources of energy; in mammals, they are normally metabolized and excreted.
Steroids play critical roles in a number of disorders, including malignancies like prostate cancer, where steroid production inside and outside the tumour promotes cancer cell aggressiveness.
Biosynthesis and metabolism
plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
s are made from lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under en ...
(in animals and fungi; see examples above) or cycloartenol
Cycloartenol is an important triterpenoid of the sterol class which is found in plants. It is the starting point for the synthesis of almost all plant steroids, making them chemically distinct from the steroids of fungi and animals, which are, ...
(in other eukaryotes). Both lanosterol and cycloartenol derive from cyclization
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where ...
of the triterpene, triterpenoid squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpenoid with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as ''Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). A ...
. Lanosterol and cycloartenol are sometimes called protosterols because they serve as the starting compounds for all other steroids.
Steroid biosynthesis is an anabolism, anabolic pathway which produces steroids from simple precursors. A unique biosynthetic pathway is followed in animals (compared to many other organisms), making the pathway a common target for antibiotics and other anti-infection drugs. Steroid metabolism in humans is also the target of cholesterol-lowering drugs, such as statins. In humans and other animals the biosynthesis of steroids follows the mevalonate pathway, which uses acetyl-CoA as building blocks for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) and isopentenyl pyrophosphate, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP).
In subsequent steps DMAPP and IPP conjugate to form Farnesyl pyrophosphate, farnesyl diphosphate (FPP), which further conjugates with each other to form the linear triterpenoid squalene. Squalene biosynthesis is catalyzed by Farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase, squalene synthase, which belongs to the squalene/phytoene synthase family. Subsequent Epoxide, epoxidation and cyclization of squalene generate lanosterol, which is the starting point for additional modifications into other steroids (steroidogenesis). In other eukaryotes, the cyclization product of epoxidized squalene (oxidosqualene) is cycloartenol.
Mevalonate pathway
natural product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical sy ...
s. Here, the isoprene units are joined to make squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpenoid with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as ''Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). A ...
and folded into a set of rings to make lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under en ...
. Lanosterol can then be converted into other steroids, such as cholesterol and ergosterol
Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a sterol found in cell membranes of fungi and protozoa, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Because many fungi and protozoa cannot survive without ergosterol, t ...
.
Two classes of medication, drugs target the mevalonate pathway: statins (like rosuvastatin), which are used to reduce hypercholesterolemia, elevated cholesterol levels, and bisphosphonates (like zoledronate), which are used to treat a number of bone-degenerative diseases.
Steroidogenesis
progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the bod ...
s, corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s (corticoids), androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
s, and estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
s. Human steroidogenesis of these classes occurs in a number of locations:
*Progestogens are the precursors of all other human steroids, and all human tissues which produce steroids must first convert cholesterol to pregnenolone. This conversion is the rate-limiting step of steroid synthesis, which occurs inside the mitochondrion of the respective tissue.
*Cortisol, corticosterone, aldosterone, and testosterone are produced in the adrenal cortex.
*Estradiol, estrone and progesterone are made primarily in the ovary, estriol in placenta during pregnancy, and testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
primarily in the testes (some testosterone is also produced in the adrenal cortex).
*Estradiol is converted from testosterone directly (in males), or via the primary pathway DHEA - androstenedione - estrone and secondarily via testosterone (in females).
*Stromal cells have been shown to produce steroids in response to signaling produced by androgen-starved prostate cancer cells.
*Some neurons and glia in the central nervous system (CNS) express the enzymes required for the local synthesis of pregnenolone, progesterone, DHEA and DHEAS, de novo synthesis, ''de novo'' or from peripheral sources.
Alternative pathways
In plants and bacteria, the non-mevalonate pathway (MEP pathway) uses Pyruvic acid, pyruvate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate as substrates to produce IPP and DMAPP. During diseases pathways otherwise not significant in healthy humans can become utilized. For example, in one form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia a congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency, deficiency in the 21-hydroxylase enzymatic pathway leads to an excess of 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) – this pathological excess of 17-OHP in turn may be converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT, a potent androgen) through among others CYP17A1, 17,20 Lyase (a member of the cytochrome P450 family of enzymes), 5α-Reductase and 3α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.Catabolism and excretion
Steroids are primarily oxidized by cytochrome P450, cytochrome P450 oxidase enzymes, such as CYP3A4. These reactions introduce oxygen into the steroid ring, allowing the cholesterol to be broken up by other enzymes into bile acids. These acids can then be eliminated by secretion from the liver in bile. The expression of the oxidase gene can be Downregulation and upregulation, upregulated by the steroid sensor PXR when there is a high blood concentration of steroids. Steroid hormones, lacking the side chain of cholesterol and bile acids, are typically Hydroxylation, hydroxylated at various ring positions or 17-ketosteroid, oxidized at the 17 position, Conjugated system, conjugated with sulfate or glucuronic acid and excreted in the urine.Isolation, structure determination, and methods of analysis
Steroid ''isolation'', depending on context, is the isolation of chemical matter required for chemical structure elucidation, derivitzation or degradation chemistry, biological testing, and other research needs (generally milligrams to grams, but often more or the isolation of "analytical quantities" of the substance of interest (where the focus is on identifying and quantifying the substance (for example, in biological tissue or fluid). The amount isolated depends on the analytical method, but is generally less than one microgram. The methods of isolation to achieve the two scales of product are distinct, but include extraction (chemistry), extraction, precipitation, adsorption, chromatography, and crystallization. In both cases, the isolated substance is purified to chemical homogeneity; combined separation and analytical methods, such as Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, LC-MS, are chosen to be "orthogonal"—achieving their separations based on distinct modes of interaction between substance and isolating matrix—to detect a single species in the pure sample. ''Structure determination'' refers to the methods to determine the chemical structure of an isolated pure steroid, using an evolving array of chemical and physical methods which have included NMR and small-molecule crystallography. ''Methods of analysis'' overlap both of the above areas, emphasizing analytical methods to determining if a steroid is present in a mixture and determining its quantity.Chemical synthesis
Microbial catabolism ofphytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phyt ...
side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a molecule that is attached to a ...
s yields C-19 steroids, C-22 steroids, and 17-ketosteroids (i.e. Precursor (chemistry), precursors to adrenocortical hormones and contraceptives). The addition and modification of functional groups is key when producing the wide variety of medications available within this chemical classification. These modifications are performed using conventional organic synthesis and/or biotransformation techniques.
Precursors
Semisynthesis
The semisynthesis of steroids often begins from precursors such ascholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell memb ...
, phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phyt ...
s, or sapogenins. The efforts of Syntex, a company involved in the Mexican barbasco trade, used ''Dioscorea mexicana'' to produce the sapogenin diosgenin in the early days of the synthetic steroid Fine chemical#Pharmaceuticals, pharmaceutical industry.
Total synthesis
Some steroidal hormones are economically obtained only by total synthesis from petrochemicals (e.g. 13-alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloa ...
steroids). For example, the pharmaceutical Norgestrel begins from methoxy-1-tetralone, a petrochemical derived from phenol.
Research awards
A number of Nobel Prizes have been awarded for steroid research, including: * 1927 (Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Chemistry) Heinrich Otto Wieland — Constitution of bile acids and sterols and their connection to vitamins * 1928 (Chemistry) Adolf Otto Reinhold Windaus — Constitution of sterols and their connection to vitamins * 1939 (Chemistry) Adolf Butenandt and Leopold Ruzicka, Leopold Ružička — Isolation and structural studies of steroid sex hormones, and related studies on higher terpenes * 1950 (Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Physiology or Medicine) Edward Calvin Kendall, Tadeus Reichstein, and Philip Hench — Structure and biological effects of adrenocortical hormone, adrenal hormones * 1965 (Chemistry) Robert Burns Woodward — In part, for the synthesis of cholesterol, cortisone, andlanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under en ...
* 1969 (Chemistry) Derek Barton and Odd Hassel — Development of the concept of conformation in chemistry, emphasizing the steroid nucleus
* 1975 (Chemistry) Vladimir Prelog — In part, for developing methods to determine the stereochemical course of cholesterol biosynthesis from mevalonic acid via squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpenoid with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as ''Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). A ...
See also
* Adrenal gland * Batrachotoxin * List of steroid abbreviations * List of steroids * Membrane steroid receptor * Pheromone * Reverse cholesterol transport *Steroidogenesis inhibitor
A steroidogenesis inhibitor, also known as a steroid biosynthesis inhibitor, is a type of drug which inhibits one or more of the enzymes that are involved in the process of steroidogenesis, the biosynthesis of endogenous steroids and steroid hor ...
* Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
* Steroidogenic enzyme
References
Bibliography
* * * A concise history of the study of steroids. * A review of the history of steroid synthesis, especially biomimetic. * Adrenal steroidogenesis pathway. * * {{Authority control Steroids, Metabolic pathways Wikipedia articles with sections published in WikiJournal of Medicine