Spring and Autumn Period on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Spring and Autumn period () was a period in
The Spring and Autumn period () was a period in
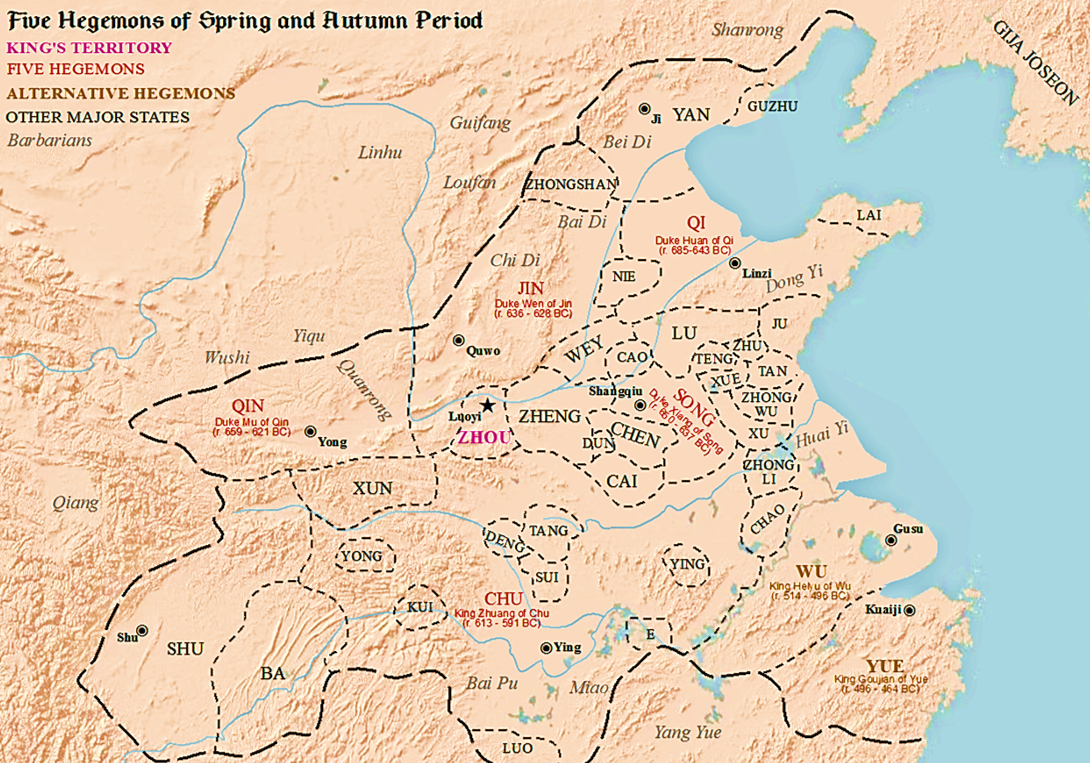
 Some version of the
Some version of the
 The Five Hegemons (春秋五霸):
With the royal house of Zhou lacking the military strength to defend itself, and with the various states experiencing tension and conflict, certain very powerful lords took the position of hegemon, ostensibly to uphold the house of Zhou and maintain the peace to the degree possible. They paid tribute to the royal court, and were owed tribute by the other rulers. Traditional history lists five hegemons during the Spring and Autumn period:
* Duke Huan of Qi (r. 685–643 BCE)
* Duke Xiang of Song (r. 650–637 BCE)
* Duke Wen of Jin (r. 636–628 BCE)
*
The Five Hegemons (春秋五霸):
With the royal house of Zhou lacking the military strength to defend itself, and with the various states experiencing tension and conflict, certain very powerful lords took the position of hegemon, ostensibly to uphold the house of Zhou and maintain the peace to the degree possible. They paid tribute to the royal court, and were owed tribute by the other rulers. Traditional history lists five hegemons during the Spring and Autumn period:
* Duke Huan of Qi (r. 685–643 BCE)
* Duke Xiang of Song (r. 650–637 BCE)
* Duke Wen of Jin (r. 636–628 BCE)
*
Chinese history
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
corresponding roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou
The Eastern Zhou (256 BCE) is a period in Chinese history comprising the latter two-thirds of the Zhou dynasty. The period follows the Western Zhou era and is named due to the Zhou royal court relocating the capital eastward from Fenghao ...
(256 BCE), characterized by the gradual erosion of royal power as local lords nominally subject to the Zhou exercised increasing political autonomy. The period's name derives from the '' Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 481 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the phil ...
(551–479 BCE).
During this period, local polities negotiated their own alliances, waged wars against one another, up to defying the king's court in Luoyi
Luoyang ( zh, s=洛阳, t=洛陽, p=Luòyáng) is a city located in the confluence area of the Luo River and the Yellow River in the west of Henan province, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengz ...
. The gradual Partition of Jin
The Partition of Jin (), refers to the division of the State of Jin between rival families into the three states of Han, Zhao and Wei, a watershed event marking the division between the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods. Proceedi ...
, one of the most powerful states, is generally considered to mark the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
. The periodization dates to the late Western Han
The Han dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring int ...
().
Background
In 771 BCE, aQuanrong
The Quanrong () or Dog Rong were an ethnic group, classified by the ancient Chinese as " Qiang", active in the northwestern part of China during and after the Zhou dynasty (1046–221 BCE). Their language or languages are considered to have been ...
invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng
Zeng (, ) is a Chinese family name. In Cantonese, it is Tsang; In Wade–Giles, such as those in Taiwan, Tseng or Tzeng; in Malaysia and Singapore, Tsen, Chen or Cheng; in the Philippines, Chan; in Indonesia, Tjan; in Vietnam, Tăng. The surname ...
and Shen—the latter polity being the fief of the grandfather of the disinherited crown prince Yijiu—destroyed the Western Zhou
The Western Zhou ( zh, c=西周, p=Xīzhōu; 771 BC) was a period of Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Zhou dynasty. It began when King Wu of Zhou overthrew the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye and ended in 77 ...
capital at Haojing, killing King You and establishing Yijiu as king at the eastern capital Luoyi
Luoyang ( zh, s=洛阳, t=洛陽, p=Luòyáng) is a city located in the confluence area of the Luo River and the Yellow River in the west of Henan province, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengz ...
. The event ushered in the Eastern Zhou dynasty, which is divided into the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States
The Warring States period in Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and struggles for gre ...
periods. During the Spring and Autumn period, China's feudal '' fengjian'' system became largely irrelevant. The Zhou court, having lost its homeland in the Guanzhong
Guanzhong (, formerly romanization of Chinese, romanised as Kwanchung) region, also known as the Guanzhong Basin, Wei River Basin, or uncommonly as the Shaanzhong region, is a historical region of China corresponding to the crescentic graben str ...
region, held nominal power, but had real control over only a small royal demesne
A demesne ( ) or domain was all the land retained and managed by a lord of the manor under the feudal system for his own use, occupation, or support. This distinguished it from land subinfeudation, sub-enfeoffed by him to others as sub-tenants. ...
centered on Luoyi. During the early part of the Zhou dynasty period, royal relatives and generals had been given control over fiefdoms in an effort to maintain Zhou authority over vast territory. As the power of the Zhou kings waned, these fiefdoms became increasingly independent states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
.
The most important states (known later as the twelve vassals) came together in regular conferences where they decided important matters, such as military expeditions against foreign groups or against offending nobles. During these conferences one vassal ruler was sometimes declared hegemon
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one state over other states, either regional or global.
In Ancient Greece (ca. 8th BC – AD 6th c.), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' ...
.
As the era continued, larger and more powerful states annexed or claimed suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">st ...
over smaller ones. By the 6th century BCE, most small states had disappeared and just a few large and powerful principalities dominated China. Some southern states, such as Chu and Wu, claimed independence from the Zhou, who undertook wars against some of them (Wu and Yue).
Amid the interstate power struggles, internal conflict was also rife: six elite landholding families waged war on each other inside Jin, political enemies set about eliminating the Chen family in Qi, and the legitimacy of the rulers was often challenged in civil wars by various royal family members in Qin and Chu. Once all these powerful rulers had firmly established themselves within their respective dominions, the bloodshed focused more fully on interstate conflict in the Warring States period, which began in 403 BCE when the three remaining elite families in Jin—Zhao, Wei, and Han—partitioned the state.
Early Spring and Autumn (771–685 BCE)
Court moves east (771)
After the Zhou capital was sacked by the Marquess of Shen and theQuanrong
The Quanrong () or Dog Rong were an ethnic group, classified by the ancient Chinese as " Qiang", active in the northwestern part of China during and after the Zhou dynasty (1046–221 BCE). Their language or languages are considered to have been ...
barbarians, the Zhou moved the capital east from the now desolated Zongzhou in Haojing near modern Xi'an
Xi'an is the list of capitals in China, capital of the Chinese province of Shaanxi. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong plain, the city is the third-most populous city in Western China after Chongqing and Chengdu, as well as the most populou ...
to Wangcheng in the Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan H ...
Valley. The Zhou royalty was then closer to its main supporters, particularly Jin, and Zheng; the Zhou royal family had much weaker authority and relied on lords from these vassal states for protection, especially during their flight to the eastern capital. In Chengzhou, Prince Yijiu was crowned by his supporters as King Ping. However, with the Zhou domain greatly reduced to Chengzhou and nearby areas, the court could no longer support the six army groups it had in the past; Zhou kings had to request help from powerful vassal states for protection from raids and for resolution of internal power struggles. The Zhou court would never regain its original authority; instead, it was relegated to being merely a figurehead of the regional states and ritual leader of the Ji clan ancestral temple. Though the king retained the Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven ( zh, t=天命, p=Tiānmìng, w=, l=Heaven's command) is a Chinese ideology#Political ideologies, political ideology that was used in History of China#Ancient China, Ancient China and Chinese Empire, Imperial China to legit ...
, the title held little actual power.
With the decline of Zhou power, the Yellow River drainage basin was divided into hundreds of small, autonomous states, most of them consisting of a single city, though a handful of multi-city states, particularly those on the periphery, had power and opportunity to expand outward. A total of 148 states are mentioned in the chronicles for this period, 128 of which were absorbed by the four largest states by the end of the period.
Shortly after the royal court's move to Chengzhou, a hierarchical alliance system arose where the Zhou king would give the title of hegemon () to the leader of the state with the most powerful military; the hegemon was obligated to protect both the weaker Zhou states and the Zhou royalty from the intruding non-Zhou peoples: the Northern Di, the Southern Man, the Eastern Yi, and the Western Rong. This political framework retained the ''fēngjiàn
''Fēngjiàn'' ( zh, c=封建, l=demarcation and establishment) was a governance system and political thought in History of China#Ancient China, Ancient China and History of China#Imperial China, Imperial China, whose social structure formed a d ...
'' power structure, though interstate and intrastate conflict often led to declining regard for clan customs, respect for the Ji family, and solidarity with other Zhou peoples. The king's prestige legitimized the military leaders of the states, and helped mobilize collective defense of Zhou territory against " barbarians".
Over the next two centuries, the four most powerful states— Qin, Jin, Qi and Chu—struggled for power. These multi-city states often used the pretext of aid and protection to intervene and gain suzerainty over the smaller states. During this rapid expansion, interstate relations alternated between low-level warfare and complex diplomacy.
Zheng falls out with the court (722–685)
Duke Yin of Lu
Duke Yin of Lu (, died 30 November 712 BC), personal name Ji Xigu, was a duke of the Lu state, reigning from 722 to 712 BC. He is notable in Chinese history as being the first ruler of Lu whose reign was recorded by the '' Spring and Autumn Annal ...
ascended the throne in 722. From this year on, the state of Lu kept an official chronicle, the Spring and Autumn Annals, which along with its commentaries is the standard source for the Spring and Autumn period. Corresponding chronicles are known to have existed in other states as well, but all but the Lu chronicle have been lost.
In 717, Duke Zhuang of Zheng went to the capital for an audience with King Huan. During the encounter the duke felt he was not treated with the respect and etiquette which would have been appropriate, given that Zheng was now the chief protector of the capital. In 715, Zheng also became involved in a border dispute with Lu regarding the Fields of Xu. The fields had been put in the care of Lu by the king for the exclusive purpose of producing royal sacrifices for the sacred Mount Tai
Mount Tai () is a mountain of historical and cultural significance located north of the city of Tai'an. It is the highest point in Shandong province, China. The tallest peak is the ''Jade Emperor Peak'' (), which is commonly reported as being t ...
. For Zheng to regard the fields as just any other piece of land was an insult to the court.
By 707, relations had soured enough that the king launched a punitive expedition against Zheng. The duke counterattacked and raided Zhou territory, defeating the royal forces in the Battle of Xuge and injuring the king himself. Zheng was the first vassal to openly defy the king, kicking off the centuries of warfare without respect for the old traditions which would characterize the period.
The display of Zheng's martial strength was effective until succession problems after Zhuang's death in 701 weakened the state.
In 692, there was a failed assassination attempt against King Zhuang, orchestrated by elements at court.
The Five Hegemons (685–591 BCE)

Hegemony of Qi (685–643)
The first hegemon was Duke Huan of Qi (r. 685–643). With the help of his prime minister, Guan Zhong, Duke Huan reformed Qi to centralize its power structure. The state consisted of 15 " townships" () with the duke and two senior ministers each in charge of five; military functions were also united with civil ones. These and related reforms provided the state, already powerful from control of trade crossroads, with a greater ability to mobilize resources than the more loosely organized states. By 667, Qi had clearly shown its economic and military predominance, and Duke Huan assembled the leaders of Lu,Song
A song is a musical composition performed by the human voice. The voice often carries the melody (a series of distinct and fixed pitches) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs have a structure, such as the common ABA form, and are usu ...
, Chen, and Zheng, who elected him as their leader. Soon after, King Hui of Zhou
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by f ...
conferred the title of ''bà'' (hegemon), giving Duke Huan royal authority in military ventures. An important basis for justifying Qi's dominance over the other states was presented in the slogan 'Revere the King, Expel the Barbarians' (). The role of subsequent hegemons would also be framed in this way: as the primary defender and supporter of nominal Zhou authority and the existing order. Using this authority, during the first eleven years of his hegemony, Duke Huan intervened in a power struggle in Lu; protected Yan from encroaching Western Rong nomads; drove off Northern Di nomads after their invasions of Wey and Xing
Xing may refer to:
* an abbreviation for crossing such as Pedestrian crossing, Pedestrian Xing or Wildlife crossing, Wildlife Xing, primarily used in North America
* Chinese surname (姓, ''xing'')
* Xing (surname) (邢), a Chinese surname
* Xing ...
, providing the people with provisions and protective garrison units; and led an alliance of eight states to conquer Cai and thereby block the northward expansion of Chu.
At his death in 643, five of Duke Huan's sons contended for the throne, badly weakening the state so that it was no longer regarded as the hegemon. For nearly ten years, no ruler held the title.
Hegemony of Song (643–637)
Duke Xiang of Song attempted to claim the hegemony in the wake of Qi's decline, perhaps driven by a desire to restore theShang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou d ...
from which Song had descended. He hosted peace conferences in the same style as Qi had done, and conducted aggressive military campaigns against his rivals. Duke Xiang's ambitions met their end when, against the advice of his staff, he attacked the much larger state of Chu. The Song forces were defeated at the battle of Hong ( 泓) in 638, and the duke himself died in the following year from an injury sustained in the battle. After Xiang's death his successors adopted a more modest foreign policy, better suited to the country's small size.
As Duke Xiang was never officially recognized as hegemon by the King of Zhou, not all sources list him as one of the Five Hegemons.
Hegemony of Jin (636–628)
When Duke Wen of Jin came to power in 636 after extensive peregrinations in exile, he capitalized on the reforms of his father, Duke Xian (r. 676–651), who had centralized the state, killed off relatives who might threaten his authority, conquered sixteen smaller states, and even absorbed some Rong and Di peoples to make Jin much more powerful than it had been previously. When he assisted King Xiang in a succession struggle in 635, the king awarded Jin with strategically valuable territory near Chengzhou. Duke Wen then used his growing power to coordinate a military response with Qi, Qin, and Song against Chu, which had begun encroaching northward after the death of Duke Huán of Qi. With a decisive Chu loss at the Battle of Chengpu in 632, Duke Wen's loyalty to the Zhou king was rewarded at an interstate conference when King Xīang awarded him the title of ''bà''. After the death of Duke Wen in 628, a growing tension manifested in interstate violence that turned smaller states, particularly those at the border between Jin and Chu, into sites of constant warfare; Qi and Qin also engaged in numerous interstate skirmishes with Jin or its allies to boost their own power.Hegemony of Qin (628–621)
Duke Mu of Qin
Duke Mu of Qin (died 621BC), born Ying Renhao, was a duke of the state of Qin. Sometimes considered one of the Five Hegemons of the Spring and Autumn period, Duke Mu greatly expanded the territory of Qin during the reign of King Xiang of Zhou. ...
ascended the throne in 659 and forged an alliance with Jin by marrying his daughter to Duke Wen. In 624, he established hegemony over the western Rong barbarians and became the most powerful lord of the time. However he did not chair any alliance with other states nor was he officially recognized as hegemon by the king. Therefore, not all sources accept him as one of the Five Hegemons.
Hegemony of Chu (613–591)
King Zhuang of Chu expanded the borders of Chu well north of theYangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
River, threatening the Central States in modern Henan
Henan; alternatively Honan is a province in Central China. Henan is home to many heritage sites, including Yinxu, the ruins of the final capital of the Shang dynasty () and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the historical capitals of China, Lu ...
. At one point the Chu forces advanced to just outside the royal capital of Chengzhou, upon which King Zhuang sent a messenger to inquire into the heft and bulk of the Nine Cauldrons – the symbols of royal ritual authority – implying he might soon arrange to have them moved to his own capital. In the end the Zhou capital was spared, and Chu shifted focus to harassing the nearby state of Zheng. The once-hegemon state of Jin intervened to rescue Zheng from the Chu invaders but were resolutely defeated, which marks the ascension of Chu as the dominant state of the time.
Despite his ''de facto'' hegemony, King Zhuang's self-proclaimed title of "king" was never recognized by the Zhou states. In the '' Spring and Autumn Annals'' he is defiantly referred to as ''Zi'' (, ruler; unratified lord), even at a time when he dominated most of south China. Later historians however always include him as one of the Five Hegemons.
Late Spring and Autumn (591–453 BCE)
The Six Ministers (588)
In addition to interstate conflict, internal conflicts between state leaders and local aristocrats also occurred. Eventually the dukes of Lu, Jin, Zheng, Wey and Qi would all become figureheads to powerful aristocratic families. In the case of Jin, the shift happened in 588 when the army was split into six independent divisions, each dominated by a separate noble family: Zhi (智), Zhao (趙), Han (韓), Wei (魏), Fan (范), and Zhonghang (中行). The heads of the six families were conferred the titles of viscounts and made ministers, each heading one of the six departments of Zhou dynasty government. From this point on, historians refer to "The Six Ministers" as the true power brokers of Jin. The same happened to Lu in 562, when the Three Huan divided the army into three parts and established their own separate spheres of influence. The heads of the three families were always among the department heads of Lu.Rise of Wu (584)
Wu was a state in modernJiangsu
Jiangsu is a coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province in East China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administra ...
outside the Zhou cultural sphere, considered "barbarian", where the inhabitants sported short hair and tattoos and spoke an unintelligible language. Although its ruling house claimed to be a senior lineage in the Ji ancestral temple, Wu did not participate in the politics and wars of China until the last third of the Spring and Autumn period.
Their first documented interaction with the Spring and Autumn states was in 584, when a Wu force attacked the small border state of Tan ( 郯) causing some alarm in the various Chinese courts. Jin was quick to dispatch an ambassador to the court of the Wu king, Shoumeng. Jin promised to supply Wu with modern military technology and training in exchange for an alliance against Chu, a neighbour of Wu and Jin's nemesis in the struggle for hegemony. King Shoumeng accepted the offer, and Wu would continue to harass Chu for years to come.
Attempts at peace (579)
After a period of increasingly exhausting warfare, Qi, Qin, Jin and Chu met at a disarmament conference in 579 and agreed to declare a truce to limit their military strength. This peace did not last very long and it soon became apparent that the ''bà'' role had become outdated; the four major states had each acquired their own spheres of control and the notion of protecting Zhou territory had become less cogent as the control over (and the resulting cultural assimilation of) non-Zhou peoples, as well as Chu's control of some Zhou areas, further blurred an already vague distinction between Zhou and non-Zhou. In addition, new aristocratic houses were founded with loyalties to powerful states, rather than directly to the Zhou kings, though this process slowed down by the end of the seventh century, possibly because territory available for expansion had been largely exhausted. The Zhou kings had also lost much of their prestige so that, when Duke Dao of Jin (r. 572–558) was recognized as ''bà'', it carried much less meaning than it had before.Hegemony of Wu (506–496)
In 506, King Helü ascended the throne of Wu. With the help ofWu Zixu
:''Note: names are in simplified characters followed by traditional and Pinyin transliteration.''
Wu Yun (died 484 BC), better known by his courtesy name Zixu, was a Chinese military general and politician of the Wu (state), Wu kingdom in the Spr ...
and Sun Tzu
Sun Tzu (; zh, t=孫子, s=孙子, first= t, p=Sūnzǐ) may have been a Chinese General, military general, strategist, philosopher, and writer who lived during the Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC). Sun Tzu is traditionally credited as the au ...
, the author of ''The Art of War'', he launched major offensives against the state of Chu. They prevailed in five battles, one of which was the Battle of Boju, and conquered the capital Ying. However, Chu managed to ask the state of Qin for help, and after being defeated by Qin, the vanguard general of Wu troops, Fugai, a younger brother of Helü, led a rebellion. After beating Fugai, Helü was forced to leave Chu. Fugai later retired to Chu and settled there. King Helü died during an invasion of Yue in 496. Some sources such as the Confucian text '' Bai Hu Tong'' list him as one of the Five Hegemons.
He was succeeded by his son King Fuchai of Wu, who nearly destroyed the Yue state, imprisoning King Goujian of Yue. Subsequently, Fuchai defeated Qi and extended Wu influence into central China.
In 499, the philosopher Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the phil ...
was made acting prime minister of Lu. He is traditionally (if improbably) considered the author or editor of the ''Spring and Autumn annals'', from which much of the information for this period is drawn. After only two years he was forced to resign and spent many years wandering between different states before returning to Lu. After returning to Lu he did not resume a political career, preferring to teach. Tradition holds that it was in this time he edited or wrote the Five Classics
The Four Books and Five Classics are authoritative and important books associated with Confucianism, written before 300 BC. They are traditionally believed to have been either written, edited or commented by Confucius or one of his disciples. S ...
, including the ''Spring and Autumn Annals''.
Hegemony of Yue (496–465)
In 482, King Fuchai of Wu held an interstate conference to solidify his power base, but Yue captured the Wu capital. Fuchai rushed back but was besieged and died when the city fell in 473. Yue then concentrated on weaker neighbouring states, rather than the great powers to the north. With help from Wu's enemy Chu, Yue was able to be victorious after several decades of conflict. King Goujian destroyed and annexed Wu in 473, after which he was recognized as hegemon. The '' Zuozhuan'', '' Guoyu'', and ''Shiji
The ''Shiji'', also known as ''Records of the Grand Historian'' or ''The Grand Scribe's Records'', is a Chinese historical text that is the first of the Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written during the late 2nd and early 1st cen ...
'' provide almost no information about Goujian's subsequent reign or policies. What little is said is told from the perspective of other states, such as Duke Ai of Lu trying to enlist Yue's help in a coup against the Three Huan. Sima Qian notes that Goujian reigned on until his death, and that afterwards his descendants—for whom no biographical information is given—continued to rule for six generations before the state was finally absorbed into Chu during the Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
.
Partition of Jin
After the great age of Jin power, the Jin rulers began to lose authority over their ministerial lineages. A full-scale civil war between 497 and 453 ended with the elimination of most noble lines; the remaining aristocratic families divided Jin into three successor states: Han, Wei, and Zhao. This is the last event recorded in the '' Zuozhuan''. With the absorption of most of the smaller states in the era, this partitioning left seven major states in the Zhou world: the three fragments of Jin, the three remaining great powers of Qin, Chu and Qi, and the weaker state of Yan () near modern Beijing. The partition of Jin, along with the Usurpation of Qi by Tian, marks the beginning of theWarring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
.
Interstate relations
Ancient sources such as the ''Zuo Zhuan
The ''Zuo Zhuan'' ( zh, t=左傳, w=Tso Chuan; ), often translated as ''The Zuo Tradition'' or as ''The Commentary of Zuo'', is an ancient Chinese narrative history traditionally regarded as a commentary on the ancient Chinese chronicle the '' ...
'' and the eponymous '' Chunqiu'' record the various diplomatic activities, such as court visits paid by one ruler to another (), meetings of officials or nobles of different states (), missions of friendly inquiries sent by the ruler of one state to another (), emissaries sent from one state to another (), and hunting parties attended by representatives of different states ().
Because of Chu's non-Zhou origin, the state was considered semi-barbarian and its rulers—beginning with King Wu in 704 BCE—proclaimed themselves kings in their own right. Chu intrusion into Zhou territory was checked several times by the other states, particularly in the major battles of Chengpu (632 BCE), Bi (595 BCE) and Yanling (575 BCE), which restored the states of Chen and Cai.
Literature
 Some version of the
Some version of the Five Classics
The Four Books and Five Classics are authoritative and important books associated with Confucianism, written before 300 BC. They are traditionally believed to have been either written, edited or commented by Confucius or one of his disciples. S ...
existed in Spring and Autumn period, as characters in the '' Zuozhuan'' and ''Analects
The ''Analects'', also known as the ''Sayings of Confucius'', is an ancient Chinese philosophical text composed of sayings and ideas attributed to Confucius and his contemporaries, traditionally believed to have been compiled by his followers. ...
'' frequently quote the '' Book of Poetry'' and ''Book of Documents
The ''Book of Documents'' ( zh, p=Shūjīng, c=書經, w=Shu King) or the ''Classic of History'', is one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. It is a collection of rhetorical prose attributed to figures of ancient China, a ...
''. On the other hand, the ''Zuozhuan'' depicts some characters actually ''composing'' poems that would later be included in the received text of the '' Book of Poetry''. In the ''Analects'' there are frequent references to "The Rites", but as Classical Chinese does not employ punctuation or any markup to distinguish book titles from regular nouns it is not possible to know if what is meant is the '' Etiquette and Ceremonial'' (known then as the ''Book of Rites'') or just the concept of ritual in general. On the other hand, the existence of the '' Book of Changes'' is well-attested in the ''Zuozhuan'', as multiple characters use it for divination and accurately quote the received text.
Sima Qian
Sima Qian () was a Chinese historian during the early Han dynasty. He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for the ''Shiji'' (sometimes translated into English as ''Records of the Grand Historian''), a general history of China cov ...
claims that it was Confucius who, towards the close of the Spring and Autumn period, edited the received versions of the '' Book of Poetry'', ''Book of Documents
The ''Book of Documents'' ( zh, p=Shūjīng, c=書經, w=Shu King) or the ''Classic of History'', is one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. It is a collection of rhetorical prose attributed to figures of ancient China, a ...
'', and ''Book of Rites
The ''Book of Rites'', also known as the ''Liji'', is a collection of texts describing the social forms, administration, and ceremonial rites of the Zhou dynasty as they were understood in the Warring States and the early Han periods. The '' ...
''; wrote the "Ten Wings" commentary on the '' Book of Changes''; and wrote the entirety of the '' Spring and Autumn Annals''. This was long the predominant opinion in China, but modern scholarship considers it unlikely that all five classics could be the product of one man. The transmitted versions of these works all derive from the versions edited by Liu Xin in the century following Sima Qian.
While many philosophers such as Lao Tzu
Laozi (), also romanized as Lao Tzu #Name, among other ways, was a semi-legendary Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosopher and author of the ''Tao Te Ching'' (''Laozi''), one of the foundational texts of Taoism alongside the ''Zhuangzi (book) ...
and Sun Tzu
Sun Tzu (; zh, t=孫子, s=孙子, first= t, p=Sūnzǐ) may have been a Chinese General, military general, strategist, philosopher, and writer who lived during the Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC). Sun Tzu is traditionally credited as the au ...
were active in the Spring and Autumn period, their ideas were probably not put into writing until the following Warring States period.
Aristocracy
While the aristocracy of theWestern Zhou
The Western Zhou ( zh, c=西周, p=Xīzhōu; 771 BC) was a period of Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Zhou dynasty. It began when King Wu of Zhou overthrew the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye and ended in 77 ...
frequently interacted via the medium of the royal court, the collapse of central power at the end of the first half of the dynasty left in its wake hundreds of autonomous polities varying drastically in size and resources, nominally connected by bonds of cultural and ritual affiliation increasingly attenuated by the passage of time. Whole lineage groups moved around under socioeconomic stress, border groups not associated with the Zhou culture gained in power and sophistication, and the geopolitical situation demanded increased contact and communication.
Under this new regime, an emergent systematization of noble ranks took root. Where the Western Zhou had concerned itself with politics, the ancestral temples, and legitimacy, in the Eastern Zhou politics came to the fore. Titles which had previously reflected lineage seniority took on purely political meanings. At the top of the bunch were ''Gong
A gongFrom Indonesian language, Indonesian and ; ; zh, c=鑼, p=luó; ; ; ; ; is a percussion instrument originating from Southeast Asia, and used widely in Southeast Asian and East Asian musical traditions. Gongs are made of metal and ...
'' () and ''Hou'' (), favoured lineages of old with generally larger territories and greater resources and prestige at their disposal. The majority of rulers were of the middling but tiered grades ''Bo'' () and ''Zi'' (). The rulers of two polities maintained the title ''Nan'' (). A 2012 survey found no difference in grade between ''Gong'' and ''Hou'', or between ''Zi'' and ''Nan''. Meanwhile, a new class of lower-tier aristocrats formed: the ''Shi'' (), gentlemen too distantly related to the great houses to be born into a life of wielding power, but still part of the elite culture, aiming at upward social mobility, typically through the vector of officialdom.
One individual well attested in the process of fixing the ranks of rulers into a coherent scheme was Zichan of Zheng, who both submitted a memorial to the king of Chu informing him of the proposed new system in 538 BCE, and argued at a 529 BCE interstate conference that tributes should be graded based on rank, given the disparity in available resources.
Alongside this development, there was precedent of Zhou kings "upgrading" noble ranks as a reward for service to the throne, giving the recipients a bit more diplomatic prestige without costing the royal house any land. During the decline of the royal house, although real power was wrested from their grasp, their divine legitimacy was not brought into question, and even with the king reduced to something of a figurehead, his prestige remained supreme as Heaven's eldest son.
Archaeologically excavated primary sources and received literature agree to a high degree of systematization and stability in noble titles during the Eastern Zhou, indicating an actual historical process. A 2007 survey of bronze inscriptions from 31 states found only eight polities whose rulers used varying titles of nobility to describe themselves.
Important figures
 The Five Hegemons (春秋五霸):
With the royal house of Zhou lacking the military strength to defend itself, and with the various states experiencing tension and conflict, certain very powerful lords took the position of hegemon, ostensibly to uphold the house of Zhou and maintain the peace to the degree possible. They paid tribute to the royal court, and were owed tribute by the other rulers. Traditional history lists five hegemons during the Spring and Autumn period:
* Duke Huan of Qi (r. 685–643 BCE)
* Duke Xiang of Song (r. 650–637 BCE)
* Duke Wen of Jin (r. 636–628 BCE)
*
The Five Hegemons (春秋五霸):
With the royal house of Zhou lacking the military strength to defend itself, and with the various states experiencing tension and conflict, certain very powerful lords took the position of hegemon, ostensibly to uphold the house of Zhou and maintain the peace to the degree possible. They paid tribute to the royal court, and were owed tribute by the other rulers. Traditional history lists five hegemons during the Spring and Autumn period:
* Duke Huan of Qi (r. 685–643 BCE)
* Duke Xiang of Song (r. 650–637 BCE)
* Duke Wen of Jin (r. 636–628 BCE)
* Duke Mu of Qin
Duke Mu of Qin (died 621BC), born Ying Renhao, was a duke of the state of Qin. Sometimes considered one of the Five Hegemons of the Spring and Autumn period, Duke Mu greatly expanded the territory of Qin during the reign of King Xiang of Zhou. ...
(r. 659–621 BCE)
* King Zhuang of Chu (r. 613–591 BCE)
Alternatively:
* Duke Huan of Qi (r. 685–643 BCE)
* Duke Wen of Jin (r. 636–628 BCE)
* King Zhuang of Chu (r. 613–591 BCE)
* King Fuchai of Wu (r. 495–473 BCE)
* King Goujian of Yue (r. 496–465 BCE)
Bureaucrats or Officers
* Guan Zhong, advisor of Duke Huan of Qi
* Baili Xi, prime minister of Qin
* Wu Zixu
:''Note: names are in simplified characters followed by traditional and Pinyin transliteration.''
Wu Yun (died 484 BC), better known by his courtesy name Zixu, was a Chinese military general and politician of the Wu (state), Wu kingdom in the Spr ...
, Duke of Shen, important adviser of King Helü, early culture hero, sometimes considered "the single best recorded individual in the history of the Spring and Autumn period"
* Bo Pi, bureaucrat under King Helü who played an important diplomatic role in Wu–Yue relations
* Wen Zhong, advisor of King Goujian of Yue in his war against Wu
* Fan Li, another advisor to Goujian, also renowned for his incredible business acumen
* Zichan, leader of self-strengthening movements in Zheng
* Yan Ying or ''Yanzi'', central figure of the '' Yanzi Chunqiu''
Influential scholars
* Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the phil ...
or ''Kongzi'', leading figure in Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, Religious Confucianism, religion, theory of government, or way of li ...
* Lao-tse or ''Laozi'', teacher of Taoism
Taoism or Daoism (, ) is a diverse philosophical and religious tradition indigenous to China, emphasizing harmony with the Tao ( zh, p=dào, w=tao4). With a range of meaning in Chinese philosophy, translations of Tao include 'way', 'road', ' ...
* Mo Di, ''Mozi'', or ''Mo-tse'', founder of Mohism
Mohism or Moism (, ) was an ancient Chinese philosophy of ethics and logic, rational thought, and scientific technology developed by the scholars who studied under the ancient Chinese philosopher Mozi (), embodied in an eponymous book: the '' ...
* Sun Tzu
Sun Tzu (; zh, t=孫子, s=孙子, first= t, p=Sūnzǐ) may have been a Chinese General, military general, strategist, philosopher, and writer who lived during the Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC). Sun Tzu is traditionally credited as the au ...
or ''Sunzi'', author of ''The Art of War
''The Art of War'' is an ancient Chinese military treatise dating from the late Spring and Autumn period (roughly 5th century BC). The work, which is attributed to the ancient Chinese military strategist Sun Tzu ("Master Sun"), is compos ...
''
Other people
* Lu Ban, master builder
* Yao Li, sent by King Helü to kill Qing Ji
* Zhuan Zhu
Zhuan Zhu (專諸; died 515 BC) was an assassin in the Spring and Autumn period. Zhuan Zhu used to be a butcher, he was very filial to his mother. As Prince Guang (later King Helü of Wu) wanted to kill King Liao of Wu and take the throne himself, ...
, sent by Helü to kill his cousin King Liao
* Bo Ya, outstanding musician
* Ou Yezi, swordsmaker
List of states
The '' Liji'' claims that the Eastern Zhou was divided into 1773states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
, of which 148 are known by name as mentioned in the Zuo Zhuan
The ''Zuo Zhuan'' ( zh, t=左傳, w=Tso Chuan; ), often translated as ''The Zuo Tradition'' or as ''The Commentary of Zuo'', is an ancient Chinese narrative history traditionally regarded as a commentary on the ancient Chinese chronicle the '' ...
.
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * ** ** ** ** * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
* – linked to their occurrences in classical Chinese texts. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Spring and Autumn period 1st millennium BC in China 8th-century BC establishments